Introduction
With the advent of the social media and new-age technologies like AI, along with the exponential rise in the reach of the smartphones, a large section of the societies are facing a looming threat of disinformation pandemic. Persuasion as a social tool offers a proactive approach to countering disinformation by influencing beliefs, attitudes, and behaviors.
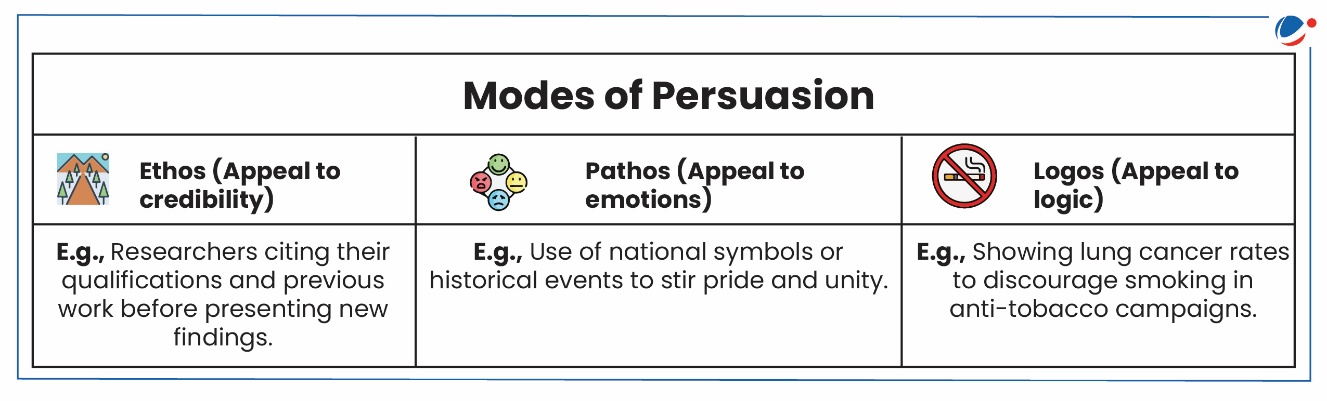 Persuasion as a Concept
Persuasion as a Concept
- Persuasion is the deliberate effort to shape beliefs or actions of others through argument, emotion, or trust, distinct from coercion or manipulation.
- Features: Mostly intentional, explicit and verbal, based on ideas of perceived friendship through similarities in language and interests.
Factors affecting Persuasion
- Source: Credibility, charisma, expertise, authority, etc., of the source.
- e.g., Dr. Randeep Guleria, former Director AIIMS (Delhi), communicating about COVID-19 measures.
- Message content: Relevance of the message to the audience, clarity and unambiguity of the message, etc.
- e.g., Swachh Bharat Abhiyan using clear and relevant messages about sanitation and its impact on health and dignity.
- Audience characteristics: Existing beliefs and information of the audience, cultural background, etc.
- e.g., Tailoring financial literacy programs to different demographics - simplified messages for rural areas, more sophisticated content for urban professionals.
- Reciprocity: Offering something of value before making a request.
- e.g., 'Give It Up' campaign for LPG Subsidy followed by PM Ujjwala Yojana.
- Social proof: Demonstrating that others have already adopted the belief or behaviour.
- e.g., 'Aadarsh Gram Yojana' is developing some villages as model village to inspire and motivate neighboring villages to adopt similar development practices.
- Timing and context: Environment in which message is delivered, current issues, etc.
- e.g., Launch of "Vocal for Local" campaign during the pandemic when concerns about economic self-reliance were high.
How Persuasion Can Work Against Disinformation?
- Building trust and reduce resistance: Persuasive communication focuses on establishing common ground, using credible messengers (like community leaders or peers), and showing empathy. This softens resistance and increases openness to correction.
- e.g., In vaccine hesitancy, using local doctors or religious leaders to communicate the importance of vaccines can be more persuasive.
- Use of narratives to counter-narratives: Rather than relying only on statistics, persuasive responses use stories, visuals, and emotional appeals to engage the audience on the same level.
- e.g., Sharing stories of people harmed by misinformation (like someone refusing COVID treatment and later regretting it) can be more impactful than citing scientific studies alone.
- Promotes Critical Thinking without Confrontation: Persuasion involves Socratic questioning, offering alternative explanations, and encouraging people to evaluate sources themselves, which promotes reflection over defensiveness.
- e.g., Deradicalization programs use dialogue-based interventions, asking open-ended questions about inconsistencies in ideology — leading the individual to rethink their beliefs themselves.
- Sustained engagement over time: Repeated exposure to persuasive, respectful messaging can erode false beliefs gradually by building relationships and trust.
- This is particularly important because one-off fact-checks are rarely enough; disinformation is often sticky and emotionally charged.

Check your Ethical AptitudeYou are a District Magistrate in a rural district of India where a false WhatsApp rumor has recently surfaced, claiming that a particular community is poisoning the local water supply to harm others. This disinformation has led to rising tensions, with some villagers refusing to drink water and others threatening violence against the accused community. The situation is escalating rapidly, and there is a risk of communal violence. Based on the above case study, answer the following questions:
|



