Why in the News?
International Monetary Fund's (IMF's) Executive Board completed the first review of Pakistan's economic reform program supported by the Extended Fund Facility (EFF) Arrangement.
More on the News
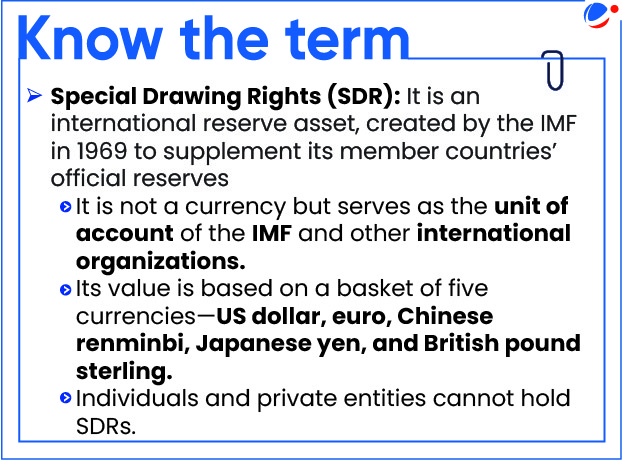
- IMF allowed the disbursement of around $1 billion (Special Drawing Rights (SDR) 760 million) under EFF.
- EFF: It assists countries experiencing serious payment imbalances because of structural impediments or slow growth and an inherently weak balance-of-payments position.
- It also approved lending of US$1.4 billion (SDR 1 billion) under the Resilience and Sustainability Facility (RSF) lending program.
- India criticized the approval of the lending and abstained from the voting process.

Key Lending Instruments of IMF Funds | ||
General Resources Account (GRA) | Poverty Reduction and Growth Trust (PRGT) | Resilience and Sustainability Trust (RST) |
|
|
|
Concerns raised by India over IMF's Lending
- Misuse of Funds: Funds could be used for military and state-sponsored cross border terrorist activities.
- Role of military: Pakistan military's strong involvement in economic matters increases the risk of policy failures and reversal of reforms.
- Undermining Global Values: Lending could be seen as a reward to countries that sponsored cross-border terrorism (linked to proxy warfare), exposing funding agencies and donors to reputational risks.
- Prolonged Use of IMF Resources: Due to repeated bailouts, Pakistan now has a heavy debt burden, making it too big to fail debtor for the IMF.
- Undermines effectiveness of the IMF program: Since 1989, Pakistan has received IMF funds in 28 out of 35 years, raising doubts about the effectiveness of the IMF's programs, their monitoring, or Pakistan's implementation.
Other Key Challenges/Concerns associated with IMF
- Ineffective voting process: There is no provision to vote against a loan or proposal.
- E.g., India had to abstain from the IMF vote as the system does not allow a formal "no" vote.
- Undemocratic Governance Structure: Distribution of voting power (based on quota) remains severely imbalanced in favour of the US, European countries and Japan, in particular.
- E.g. In 2010, IMF changed its rule to lend Greece.
- Ineffective Evaluation Process: IMF established the Independent Evaluation Office (IEO) in 2001 to evaluate various aspects of IMF performance.
- However, although IEO is being positioned as 'independent' but it is governed and financed directly by IMF.
- Varied success: IMF conditionalities have sometimes led to short-term macroeconomic stability but at the cost of increased poverty and reduced social spending due to Fiscal consolidation measures (or austerity).
- Implementation issues: Member countries that borrow from the IMF have primary responsibility for selecting, designing, and implementing policies to make their economic program successful.
Conclusion
While the IMF plays a crucial role in stabilizing the global financial system, it faces serious challenges related to governance imbalance, rigid conditionalities, etc. To remain credible and effective, it must accelerate quota and voting power reforms to reflect the rise of emerging economies and enhance transparency and accountability in its lending and evaluation processes.




