Why in the News?
Recently, Jal Sanchay Jan Bhagidari initiative was launched from Surat, Gujarat.
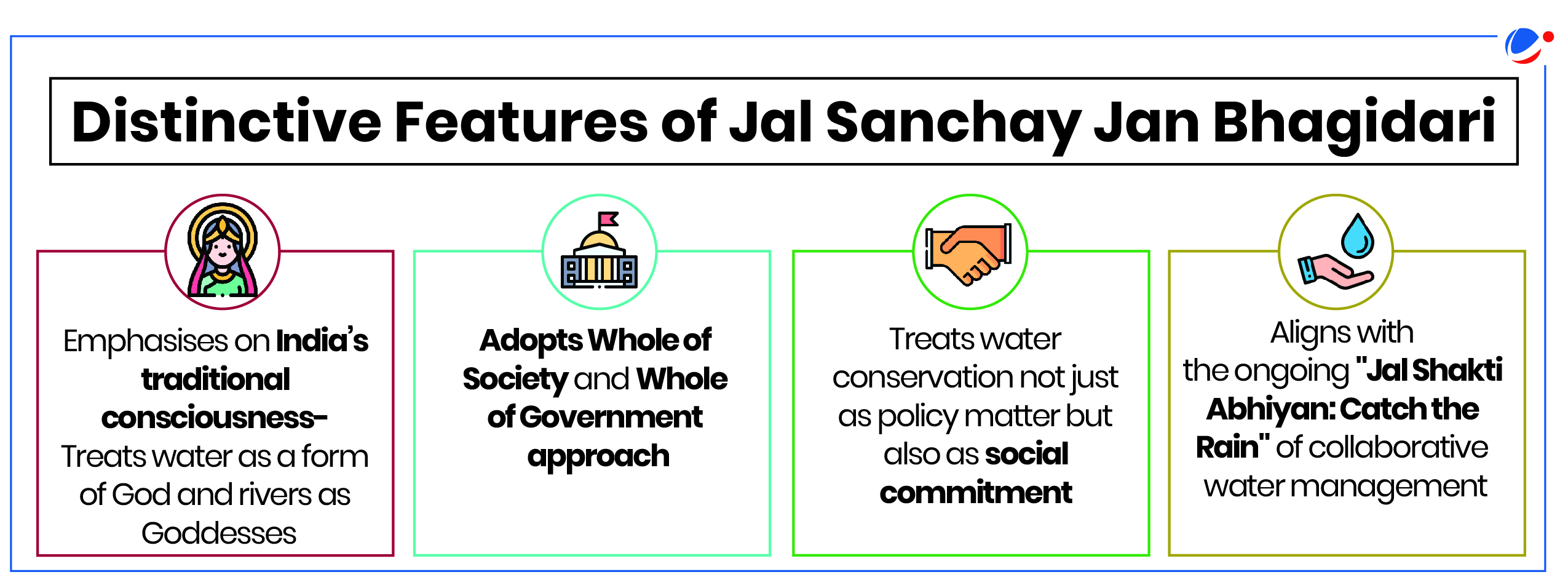
About Jal Sanchay Jan Bhagidari initiative
- This initiative seeks to conserve water with a strong emphasis on community partnership and ownership,
- It aims to construct around 24,800 rainwater harvesting structures through community participation, ensuring long-term water sustainability across state.
- It is based on the success of the Jal Sanchay initiative of Gujarat Government that dealt with the mobilization of citizens, local bodies, industries and other stakeholders.
- Ministry: Ministry of Jal Shakti
Significance of Community Participation in Water Conservation
- Foster Behavioural response: Propelling actual action in contrast to latent policy-driven reaction.
- Ex. Jal Sahelis in the Pani-Panchayats of Bundelkhand have sparked a cultural shift towards Conservation.
- Utilization of Local Knowledge and Insights: Understanding of area-specific water needs and challenges lies with them.
- Ex. Bari Farming System (Assam) involves co-existence of fruit trees, vegetable cultivations, and the pond.
- Instilling a sense of ownership: Shared stewardship for adopting water-efficient practices and preserving resources for future generations.
- Ex. Pani Panchayat, Odisha involves the voluntary farmers' participation in harvesting and distribution of surface and ground water.
- Promotes Inclusivity and Equity: Addressing concerns of vulnerable communities and bridging social disparities.
- Bringing innovative experiences: Based on the life experiences of the involved communities leading to development of locally relevant water conservation initiatives.
Some Examples of Community Participation in Water Conservation
Traditional water storage systems in India
|
Challenges with the community participation in Water Conservation
- Limited Information and Capacity: Due to lack of accessibility and complexity of the water resources data, limited technical knowledge required for water conservation.
- Policy processes perpetuate Inequality: Dominance of specialists having technical and scientific knowledge.
- Mere Ceremonial Involvement: At times legal requirements call for the participation of the communities, but their proposals are seldom considered.
- Limited association with Outsiders: Prevents the communities from participating networking that help in reaching a consensus and promotes future consultations.
Way forward on promoting Participative Water Conservation
- Creating an accessible baseline data: Governments should facilitate wide and comprehensive communication process on water policy related matters.
- Tapping Corporate Social Responsibility: Approximately 10, 000 bore well recharge structures in various districts of Gujarat have been completed through it.
- Promoting Sustainable practices: Through initiatives like LiFe (Lifestyle for Environment), promoting Reduce, Reuse, Recharge, and Recycle of water.
- Innovative approaches and Modern Technologies: Including Solar- Powered Water Filtration; Desalination systems, use of Nanotechnology, etc.
- Policy Support: To lesser water intensive crops like Maize, oilseeds, pulses, millets, etc. by incentivising farmers, fostering capacity building, etc.
Other Government Initiatives fostering Community Participation in Water Conservation
|
To know more about the Ground Water situation in India, Refer to Article 5.8 Ground Water In India in December 2023 Monthly Current Affairs






