Recently, India signed and exchanged first-of-its-kind agreements focused on Clean Economy, Fair Economy, and IPEF Overarching arrangement under Indo-Pacific Economic Framework (IPEF) for Prosperity.
- IPEF is structured around 4-pillars (refer infographics).

IPEF Clean Economy Agreement (Pillar-III)
- Development and deployment of clean energy technologies: To accelerate energy security, climate resilience, and emissions mitigation among IPEF partners.
- Investments and capacity building: For industries, especially MSMEs and integrate Indian companies into global value chains through collaborative programs such as IPEF Catalytic Capital Fund, IPEF Accelerator, etc.
IPEF Fair Economy Agreement (Pillar-IV)
- Transparent and predictable trade and investment environment: By combating corruption and supporting initiatives to improve tax transparency, domestic resource mobilization, and tax administration.
- Enhancing information sharing, facilitating asset recovery, and strengthening cross-border investigations and prosecutions.
Overarching IPEF Agreement
- Aim: Establish a high-level political oversight framework at Ministerial level over various individual IPEF agreements.
- Significance: Provide identity to the group and longevity to IPEF partnership by creating a formal mechanism, potential to enhance India's productive capacity, integration into supply chains, etc.
Article Sources
1 sourcePacific Islands forum (PIF) endorsed the Australia-funded Pacific Policing Initiative (PPI).
- PPI is designed to elevate the law enforcement capabilities of Pacific nations, ensuring they are better equipped to handle law and order challenges and internal security threats.

- PPI aligns with the Pacific Islands Forum's 2050 Strategy for the Blue Pacific Continent
- Analysts see it as a move to limit China's influence over Pacific security.
About PIF
- It is the region’s premier political and economic policy organization and works towards a Pacific Vision of peace, harmony, and prosperity.
- Founded in 1971, PIF has 18 members across Pacific Ocean. (Refer Infographic)
Issues Faced by Pacific Countries
- Climate Change: PIF members are the worst affected, due to sea level rise, ocean warming, acidification, etc.
- Geopolitical Power struggle: Between China and the US for influence over the region.
- International Drug Trafficking: Pacific Islands are used as a stop on transnational narcotics smuggling routes from Asia and the Americas.
India’s engagement with Pacific Region
- Significance: Pacific Islands are vital for India’s energy security and maritime interests, in line with a broader strategy of ensuring a free, open, and inclusive Indo-Pacific region.
- Initiatives: Indo-Pacific Oceans Initiative (2019), Forum for India-Pacific Islands Cooperation (2014), etc.
Pact along with its annexes Global Digital Compact and a Declaration on Future Generations is designed to address 21st century challenges (E.g. climate change, conflict, human rights etc.) through militarism
- Pact has been adopted by member countries by consensus with a small group of seven countries led by Russia holding out.
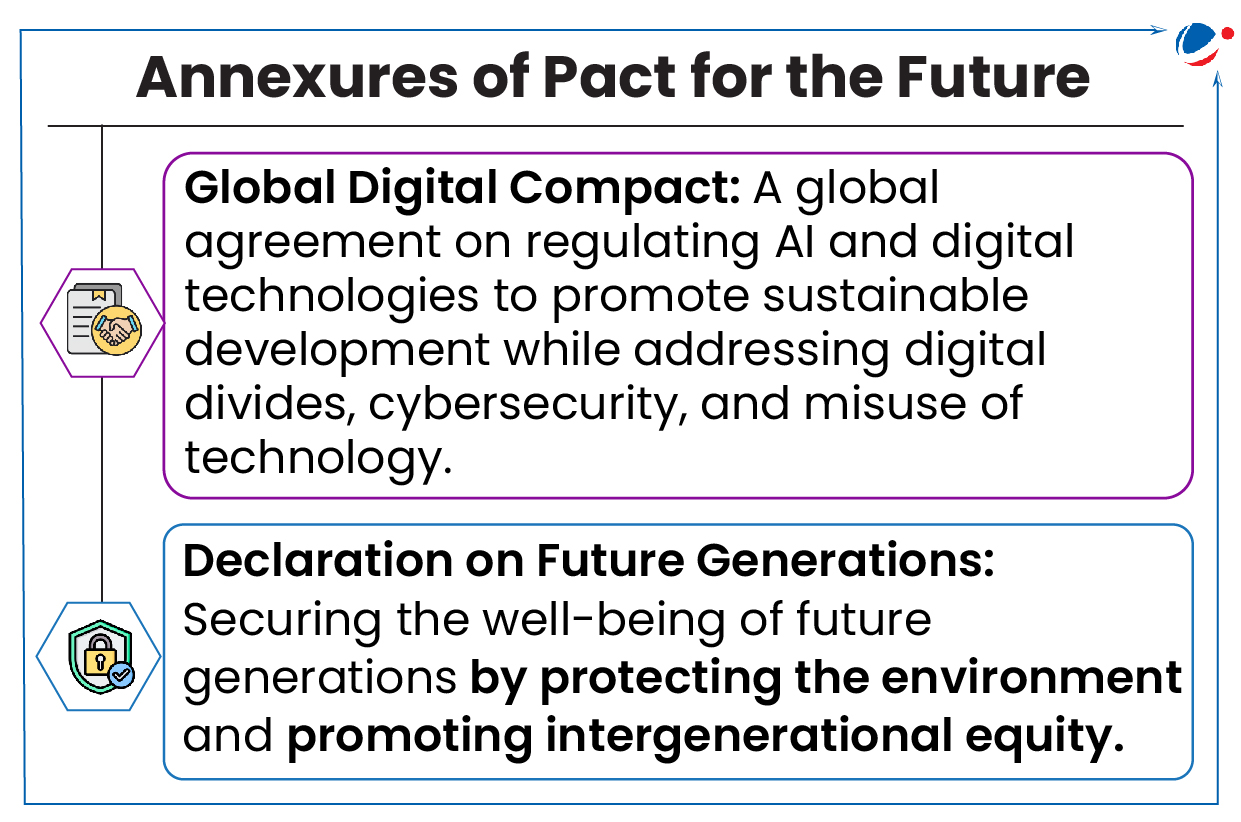
Key deliverables in Pact include:
- Sustainable development and financing for development
- Giving developing countries a greater say at international financial institutions;
- Strengthening the global financial safety net to protect the poorest.
- International Peace and Security
- Recommitment to nuclear disarmament with goal of totally eliminating nuclear weapons.
- Avoid weaponization and misuse of new technologies, such as lethal autonomous weapons.
- Science, Technology, and innovation, and digital cooperation
- Scientific research in responsible and ethical manner protecting human rights.
- Protect indigenous and traditional knowledge, empower women and remove gender-risks emanating from emerging technologies.
- Youth and Future Generation: Take account of future generations in our decision-making
- Transforming Global Governance
- Strengthen international frameworks that govern outer space (Also preventing arms race in outer space).
- Reform effectiveness and representativeness of UNSC prioritizing under-representation of Africa.
Article Sources
1 sourceJoint Action Plan 2024-2028 was adopted at the recently held 1st ever India–Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) Joint Ministerial Meeting for Strategic Dialogue.
Key Outcomes of the Ministerial Meeting
- Joint Action Plan 2024-2028: for undertaking various joint activities in diverse areas including health, trade, security, agriculture and food security, transportation, energy, culture, amongst others.
- More areas of cooperation can be included in the Joint Action Plan, based on mutual consensus, later on.
- 3P Framework: India affirmed framework of 3Ps—people, Prosperity and Progress to enhance partnership between India & GCC.
- Humanitarian crisis in Gaza: External Affairs Minister states that India’s position has been principled and consistent and any response must take into account the principles of humanitarian law.
India-GCC Relations
- Political: 1st India-GCC Political Dialogue was held in 2003. Currently, India has strategic partnerships with Saudi Arabia, UAE, &Oman.
- Trade & Investment: Bilateral trade stood at USD 161.59 billion in FY 2023-24.
- UAE is the 7th largest source of FDI in India.
- Diaspora: Approximately 8.9 million Indian expats (66% of NRIs) reside in GCC countries.
- Share of inward remittances from the GCC region are about 30% (2020-21).
- Energy: GCC countries contribute to 35% of India’s oil imports and 70% of gas imports (2021-22).

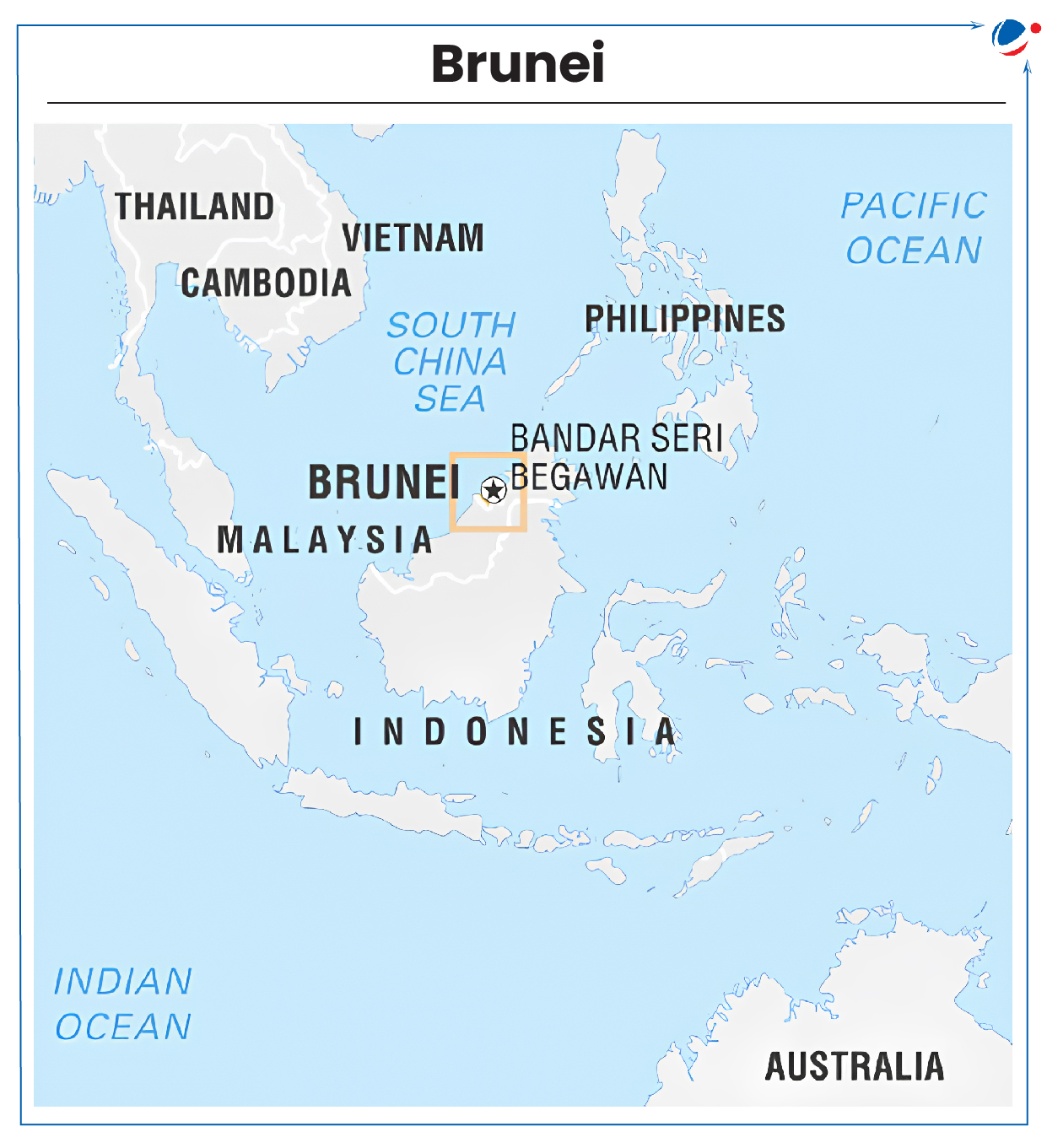
‘Enhanced Partnership’ symbolizes a new phase in India-Brunei relations, with a focus on mutual cooperation and shared strategic interests.
- It was the first bilateral visit by an Indian Prime Minister to Brunei.
- Both countries established diplomatic relations in 1984.
Key Highlights of the visit
- Acknowledged to expand defence cooperation through joint exercises, training programs etc.
- Agreed on the importance of pursuing a policy of development rather than expansionism in Southeast Asia.
- Experts observe it as a counter to Chinese influence.
- Agreed to work together for enhanced multilateralism reflective of contemporary realities.
- Cooperation in the operation of Telemetry, Tracking, and Telecommand Station for Satellite and Launch Vehicles.
- Leveraging respective strengths including in technology, finance, manufacturing and processing.
Significance of Brunei Darussalam for India
- Strategic Importance: Important partner in India’s Act East Policy and Indo-Pacific Vision.
- Brunei is also an ASEAN member.
- Indian Diaspora: Approximately 14,000 Indians are residing in Brunei.
Article Sources
1 sourceRecently, MoUs were signed under Green Strategic Partnership to strengthen the India-Denmark’s maritime relations.
About Green Strategic Partnership(GSP):
- Signed in 2020, It expands economic relations and green growth, creates jobs and strengthens cooperation on addressing global challenges.
- Focus of GSP: Implementation of the Paris Agreement and the UN Sustainable Development Goals.
- Joint Action Plan on Green Strategic Partnership (2021-2026): was also drawn up for furthering GSP.
- Under GSP, collaboration has expanded across key areas such as Quality shipping, Cooperation on Port State Control, Maritime training and education etc.
Article Sources
1 sourceThe Minister of External Affairs meets foreign ministers of G4 nations in New York.
- The group reaffirmed its commitment to urgent reform of the United Nations Security Council through text-based negotiations.
About G4 Nations
- It includes Brazil, Germany, India, and Japan.
- The G4 nations support each other's bids for permanent seats on the United Nations Security Council.
- Group has proposed that Council's membership shall be increased from 15 to 25-26, by adding six permanent and four or five non-permanent members.
In recent months, India's military diplomacy has intensified with consecutive exercises involving countries from around the world for all three Services.
What is Military Diplomacy?
- Also known as Defense Diplomacy, it refers to pursuing foreign policy objectives through the peaceful employment of defense resources and capabilities.
- India’s military diplomacy involves contributing to UN peacekeeping, providing humanitarian assistance, conducting joint exercises, etc.
What are the significances of Military Diplomacy?
- Building trust and confidence: Regular dialogue and military exchanges can help reduce mistrust and likelihood of conflicts.
- Strengthening alliances and partnerships: Defense cooperation agreements, technology transfers, and joint military drills, etc., can result in greater collaboration in regional security architectures. e.g., QUAD Security Dialogue.
- Defense modernization and capabilities: Through transfer of technology, knowledge sharing, and training. e.g., Joint development of BrahMos missiles by India and Russia.
- Others: Strategic balancing in geopolitically sensitive regions; enhanced soft power through humanitarian aids, etc.
Challenges in India’s Military Diplomacy: Balancing strategic partnerships with major global powers like the US and Russia, ‘Big Brother’ perception among South Asian nations, capacity gaps in terms of domestic manufacturing capabilities, etc.
India’s proactive engagements—through military exercises, capacity building, and peacekeeping operations—demonstrate its commitment to fostering security cooperation and shaping future security architecture of Indo-Pacific and beyond.
- Exercise Varuna: Indian Navy's P8I Poseidon Aircraft is on 1st-ever deployment in Europe to participate in 2024 edition of 'Exercise Varuna’.
- Exercise Varuna is bilateral naval exercise between India and France. 2024 edition was conducted in Mediterranean Sea.
- Exercise Eastern Bridge VII: The 7th edition of the Exercise Eastern Bridge between Indian Air Force (IAF) and the Royal Air Force of Oman (RAFO) concluded. It was held at Masirah (Oman).
- EXERCISE AL NAJAH V: Indian Army Contingent participated in 5th edition of INDIA- OMAN Joint Military Exercise AL NAJAH V at Rabkoot Training Area in Salalah, Oman.
- Yudh Abhyas: India-US Bilateral Army Exercise.
- Tarang Shakti: Multilateral Air Exercise involving countries like Australia, Greece, Sri Lanka, etc.
- Malabar Naval Exercise: Involving India, Australia, Japan and the US.
- Indra: Bilateral exercise between India and Russia.
Article Sources
1 sourceIndia launched Operation Sadbhav to provide humanitarian assistance and disaster relief (HADR) to Laos, Myanmar and Vietnam.
- The operation was launched in the wake of disasters caused by Typhoon Yagi.
- Operation Sadbhav is part of India’s broader effort to contribute to HADR within the ASEAN region, in line with its longstanding ‘Act East Policy’.
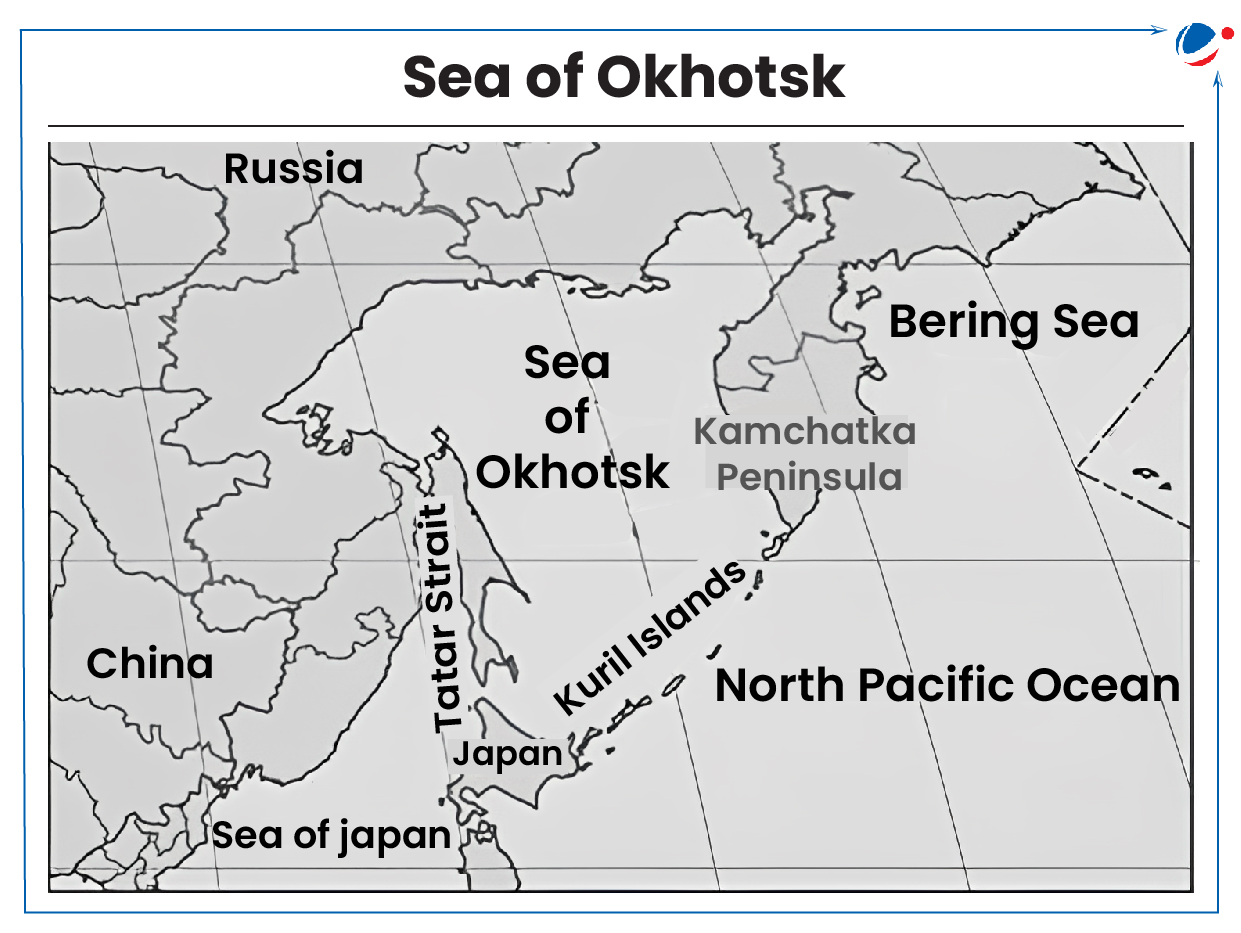
Recently, China and Russia announced joint naval and air drills ‘Northern United-2024’ in the Sea of Japan and the Sea of Okhotsk.
About Northern United 2024
- It aims to improve strategic cooperation between the China and Russia and “strengthen their ability to jointly deal with security threats.”
About Sea of Japan and Okhotsk
- Sea of Japan is marginal sea of the western Pacific Ocean. It is bounded by Japan and Sakhalin Island to the east and by Russia and Korea to the west.
- Sea of Okhotsk is bounded on by Kamchatka Peninsula and the Kuril Islands (East and Southeast), by northern coast of Japanese island of Hokkaido (South), and by Sakhalin Island (Southwest).
About Axis of Resistance
- It is a network of autonomous militant Islamist groups led by Iran and its roots goes back to the Iranian Revolution of 1979.
- It includes
- Hezbollah (Lebanese Shia militant organization)
- Hamas (Palestinian Sunni militant group)
- Palestinian Islamic Jihad
- Houthis (Yemen militant group)
- Hezbollah (meaning ‘Party of God’) which was founded in the early 1980s in Lebanon is the biggest and most capable member of the “axis of resistance”.
Article Sources
1 sourceMore than 18,000 individuals registered on the first list of FTI-TTP.
- In June 2024 the FTI-TTP was inaugurated at Indira Gandhi International Airport, New Delhi.
About FTI-TTP
- Nodal Ministry: Ministry of Home Affairs
- Objective: To speed up the Immigration clearance process for eligible persons at select major airports through electronic gates.
- Two phases: In the first phase, Indian citizens and OCI cardholders are covered and in the second phase, foreign travellers will be covered.
- Airports covered: 21 major airports in the country will be covered.
- Nodal agency: Bureau of Immigration





