Why in the News?
Recently, Wolf attacks were reported from few villages in Uttar Pradesh bringing the issue of Human-Wildlife Conflict (HWC) to light.
About Human-Wildlife Conflict

- It refers to the struggles that emerge when the presence or behaviour of wildlife poses a threat to human interests leading to negative impacts on people and/or wildlife.
- It usually occurs in areas where wildlife and human populations overlap.
- Management of HWC is the primary responsibility of the respective State/ UT Government.
- Recently, Kerala has also declared HWC as a state-specific disaster, shifting the responsibility to the State Disaster Management Authority.
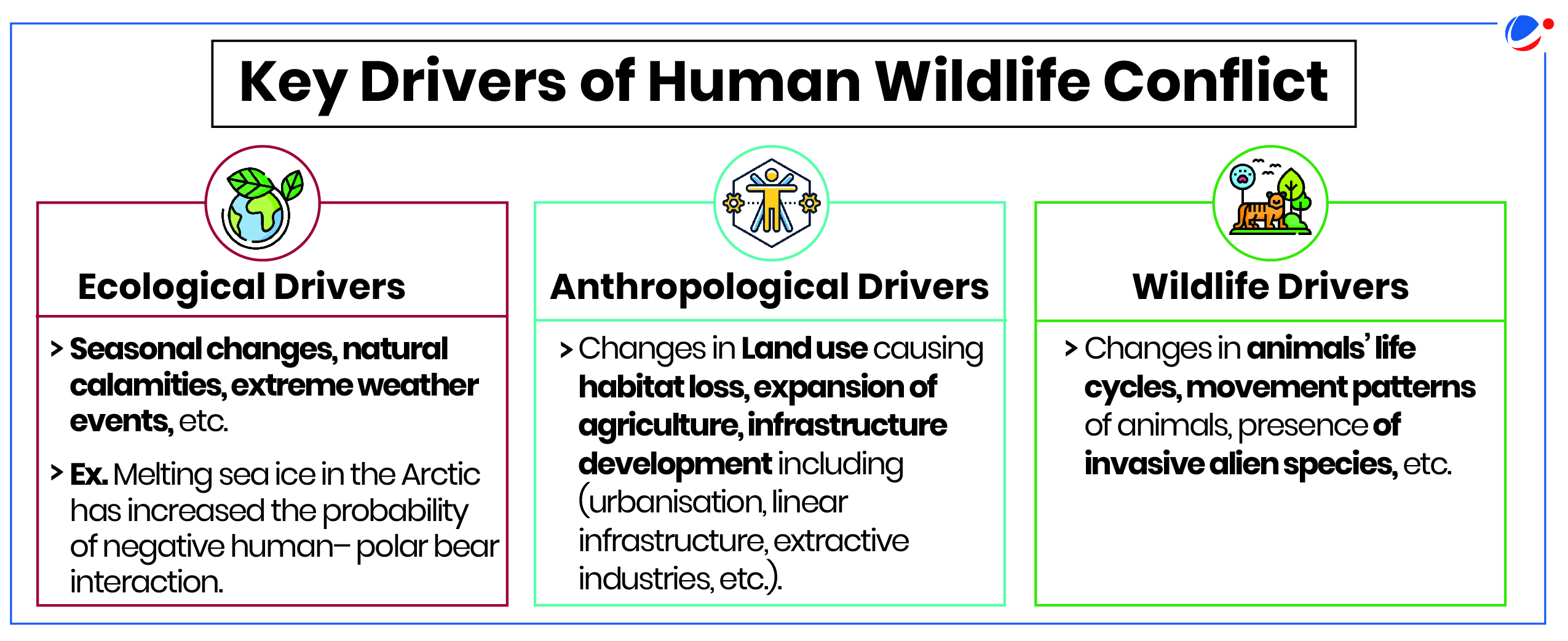
Impact of the Human Wildlife Conflict
- Impact on Wildlife: It threatens the survival of various terrestrial and marine species as retaliation or pre-emptive killings may drive the species to extinction.
- Impact on Ecosystems: It may cause damage to crops and livestock population, further disturbing the predator-prey balance.
- Impact on Social Dynamics: Discord among stakeholders as farmers blame government for species' protection and conservationists blame farmers and industries for clearing habitats.
- Impact on Local Communities: Resulting loss of lives, livestock, crops, property, is more pronounced on vulnerable, poor and marginalised communities.
- Impact on Commodity Production: Negatively affect businesses dealing with agricultural produce cause decrease in their productivity and profitability.
- Other Impacts: Livelihood insecurity; food insecurity; translocation of animals; etc.
Initiatives taken for mitigation of HWC
|
Way Forward on preventing Human Wildlife Conflict
- Shifting focus from Conflict to Coexistence: It incorporates holistic and integrated approach of managing HWC.
- Ex. The Wild Life (Protection) Act of India, 1972, empowers the Chief Wildlife Wardens of the States to take measures for peaceful coexistence of humans and wildlife inside and outside national parks and sanctuaries
- Understanding the conflict: Adequate Research to understand the context of conflict, mapping hotspot, spatial and temporal characteristics, etc.
- Building Barriers: Including activities like construction/erection of physical barriers such as barbed wire fence, solar powered electric fence, bio-fencing, etc.
- Enabling Policy Frameworks: By incorporating suitable principles, protocols and provisions for effective HWC management plans in international, national laws and conventions.
- Ex. WWF suggested for inclusion of HWC management plan within the Sustainable Development Goals or UN Convention for Biological Diversity.
- Role of Community: Community-based volunteers or rapid response teams like the existing 'friends of wild animals' should be encouraged.
About Wolf (Canis lupus)
| |
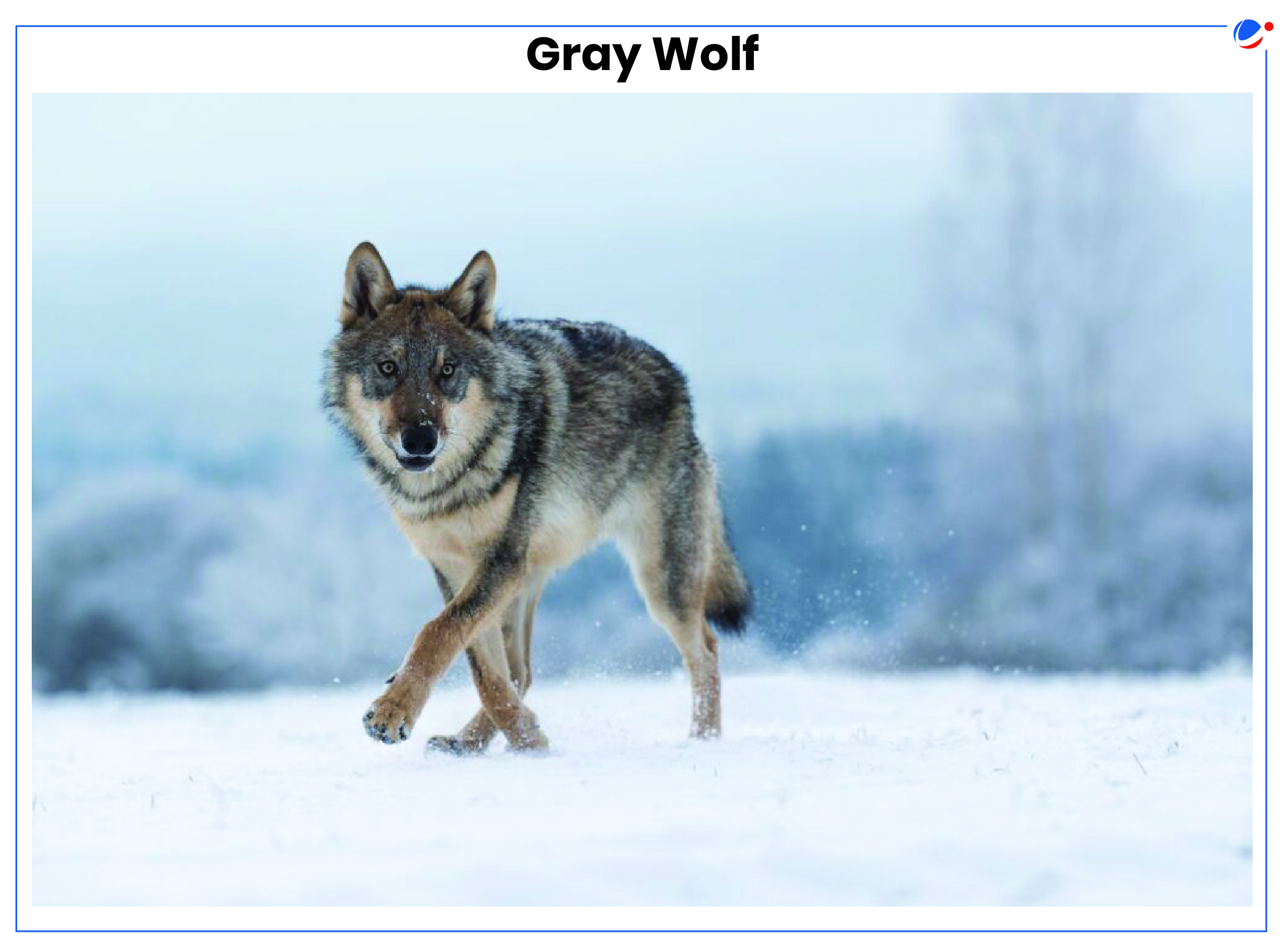
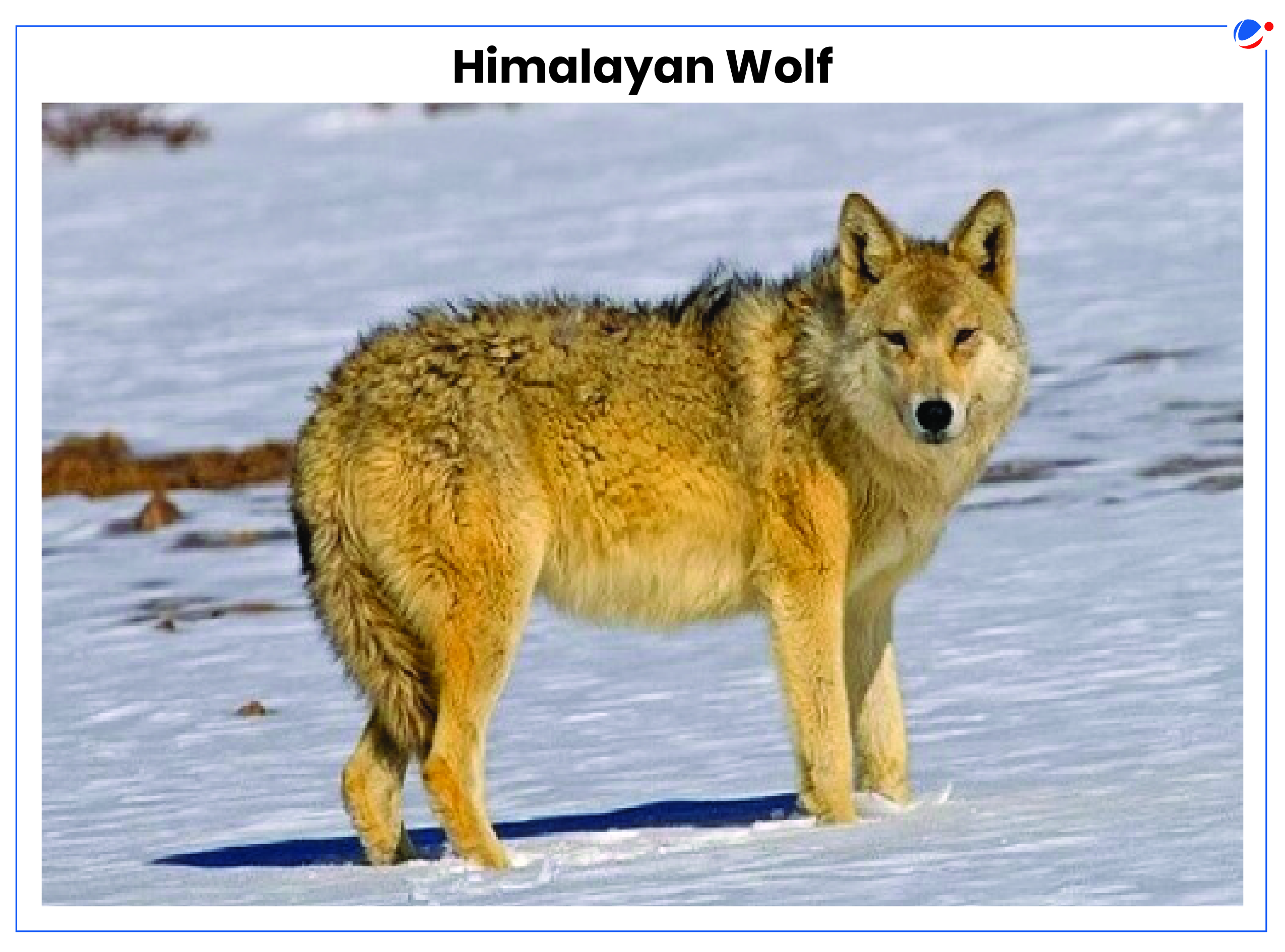
There are two species of Wolf found in India: Gray Wolf and Himalayan Wolf. | |
Gray or Indian Wolf (Canis lupus pallipes)
 | Himalayan or Tibetan wolf (Canis lupus chanco)

|





