Why in the news?
The Prime Minister of India attended the Quad Leaders' Summit in Wilmington (US).
More about the news
- Over the past four years, Quad Leaders have met six times, including twice virtually.
- The year 2024 marks 20 years since the formation of the grouping.
- The Quad Leaders' Summit adopted the Wilmington Declaration.
- India will host the 2025 Quad Leaders Summit.
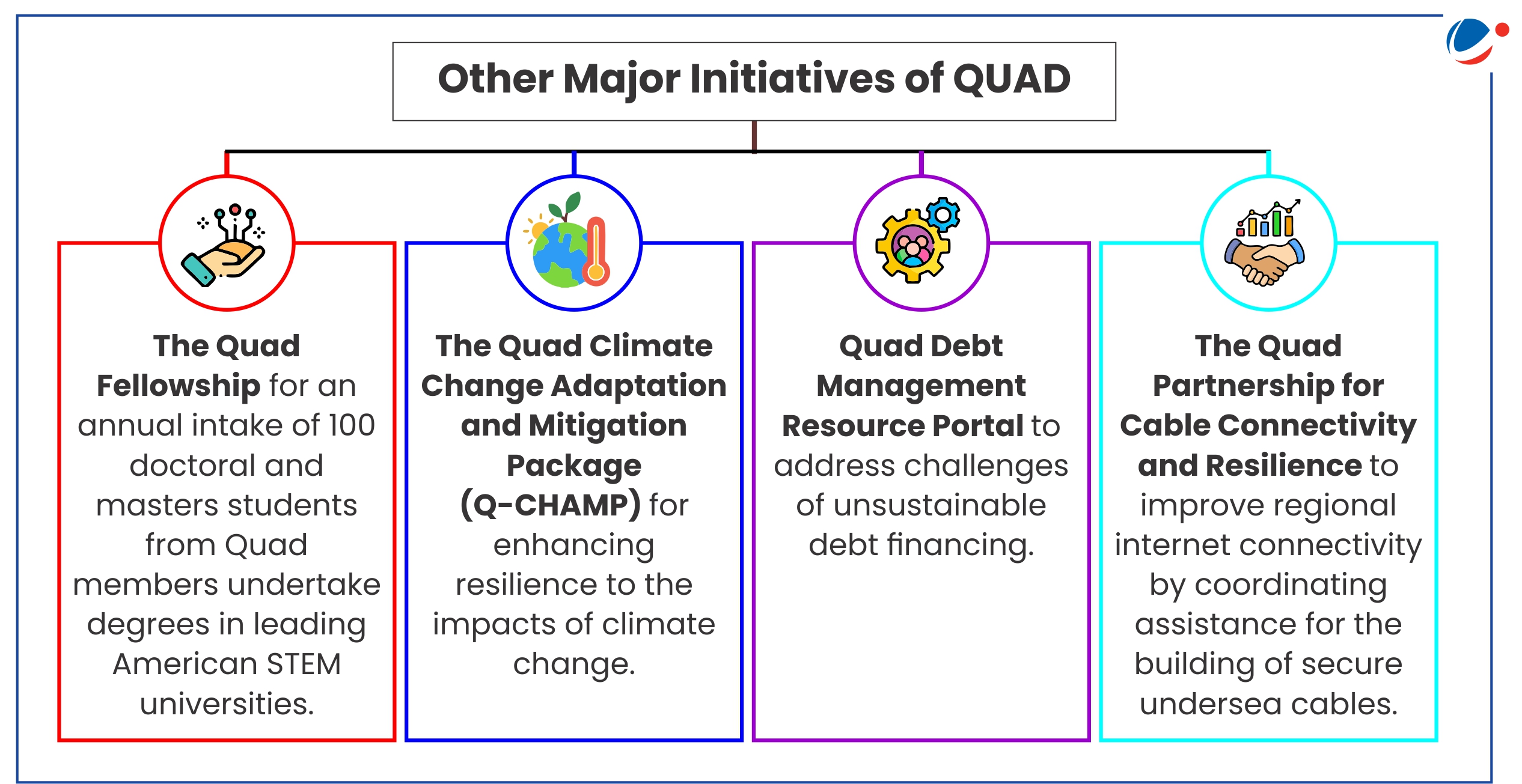
Key announcements in the Wilmington Declaration
- Health Security: 'Quad Cancer Moonshot', a partnership to save lives in the Indo-Pacific region by combating cervical cancer.
- Quality Infrastructure: 'Quad Ports of the Future Partnership' which will harness the Quad's collective expertise to support sustainable port infrastructure development.
- Critical and Emerging Technologies: A 'Semiconductor Supply Chains Contingency Network Memorandum of Cooperation' to enhance the resilience of Quad's semiconductor supply chains.
- Quad Investors Network (QUIN): Mobilizing several investments to promote supply chain resilience, advance joint research
- Climate and Clean Energy: Collective Quad effort to boost energy efficiency, including deployment and manufacturing of high-efficiency affordable cooling systems in the region.
- Space: India's establishment of a space-based web portal for Mauritius, to support the concept of open science for space-based monitoring of extreme weather events and climate impact.
- Maritime Security:
- 'Maritime Initiative for Training in the Indo-Pacific (MAITRI)' to maximize tools provided through Indo-Pacific Partnership for Maritime Domain Awareness (announced in 2022) and other Quad initiatives.
- 'Quad-at-Sea Ship Observer Mission' in 2025 to improve interoperability and advance maritime safety.
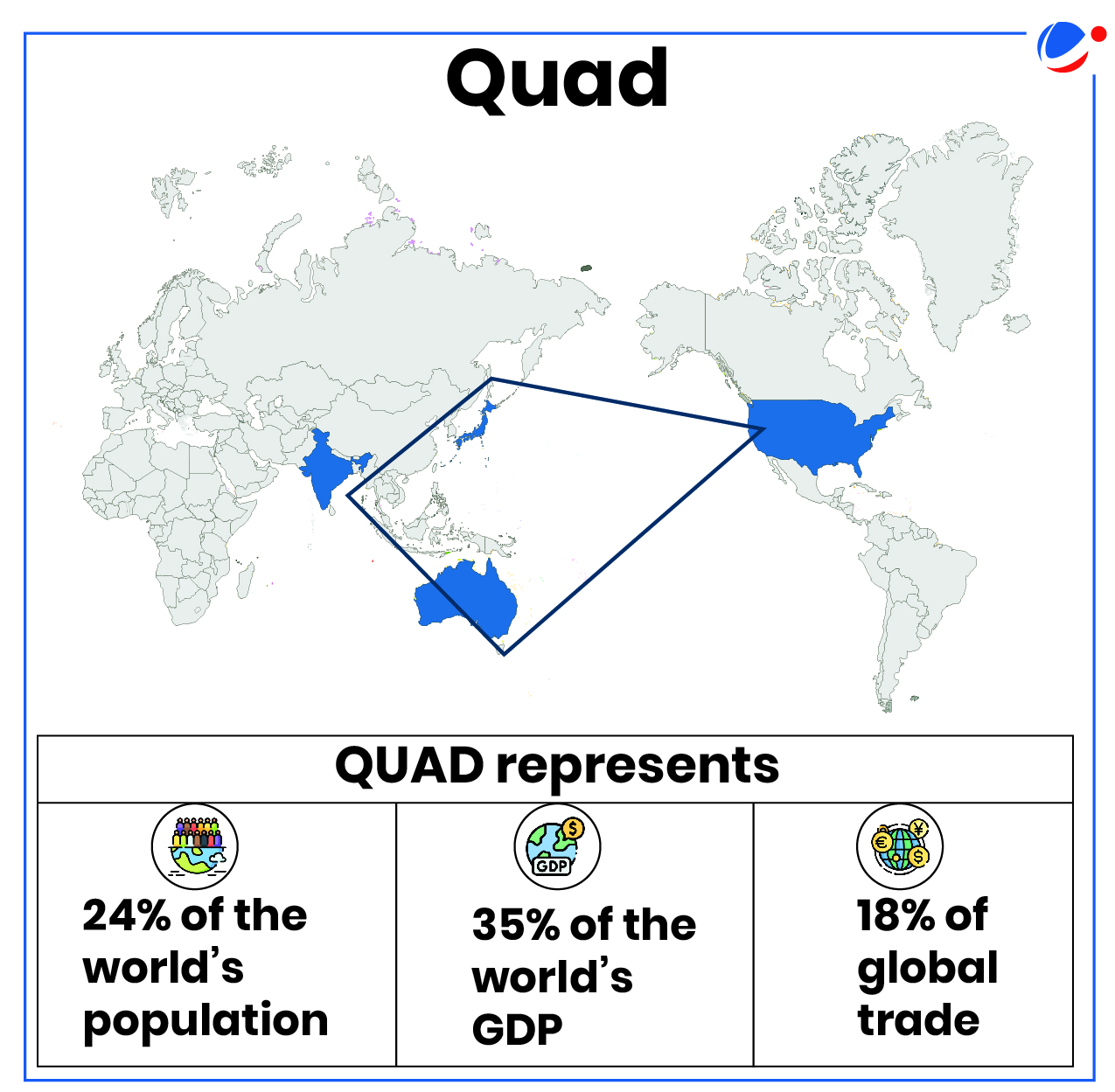
About Quadrilateral Security Dialogue (Quad)
- Quad is a Plurilateral framework of maritime democracies and a Global Force for Good that delivers real, positive, and enduring impact for the Indo-Pacific.
- Members: The Quad is a diplomatic partnership (neither a military alliance nor a mutual defence agreement) between Australia, India, Japan, and the US.
- Purpose: It is committed to supporting an open, stable and prosperous Indo-Pacific that is inclusive and resilient.
- Key Summit: Quad Leaders' Summits and Foreign Ministers' Meetings are held on an annual basis.
- The mandate of the Quad has gradually expanded with six working groups covering health, climate, critical and emerging technology, space, infrastructure and cyber.
Global Significance of QUAD | Significance of Quad for India |
|
|
Challenges to QUAD
- Less institutionalisation: In its current form, Quad remains relatively institutionalized. The forum is maintained by meetings, semi-regular summits, information exchanges.
- Perceived as a Cold War mentality: China has criticized the Quad diplomacy as reflective of a "Cold War mentality" and an attempt to establish an "Asian NATO".
- Divergent National Interests: For instance, India focuses mainly on regional security, especially regarding China, while the U.S. has broader global strategic interests.
- Australia's economic reliance on China and Japan's security dependence on the U.S. further complicates alignment.
- Maintain its unique character: Defining the Quad's purpose as distinct from other regional groupings like ASEAN, Pacific Islands Forum, and IORA has proven to be difficult.
- US is distracted from Indo-Pacific: In international policy, wars in Europe and the Middle East mean that US attention to Asia will be more limited.
India's concerns regarding QUAD
|
Way Forward
- Institutionalizing the Quad: Establishing a formal structure or secretariat could enhance its effectiveness, making it a more permanent feature in regional security and diplomatic engagements.
- Augment existing organisations in region: Quad, rather than replacing, should seek to augment other multi-laterals or regional organizations and provide an inclusive vision for cooperation.
- Engage other players: Quad needs to proactively engage with regional partners in initiatives that resonate with their respective interests and priorities.
- Balancing clarity and ambiguity: By not explicitly highlighting traditional security concerns, such as potential Chinese military actions, the Quad can focus on areas of shared interests while minimizing the risk of direct confrontation with China.
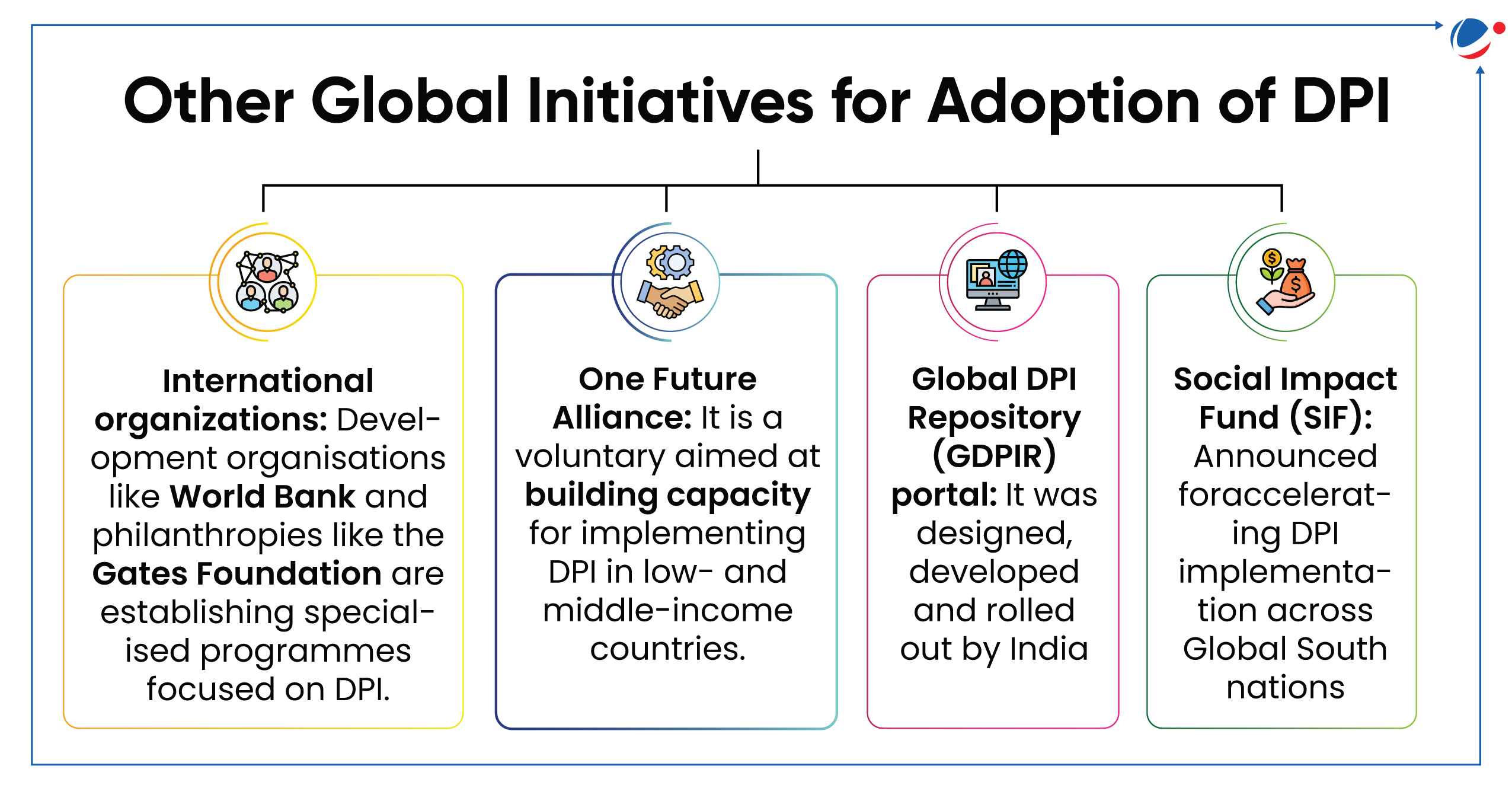
Related NewsQuad 'Principles for Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI)' The principle for DPI was released acknowledging the importance of digitalisation to transform societies and to achieve the UN 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development. About DPI
Quad's Key Principles for DPI
 |








