Why in the news?
Recently, Ministry of Personnel, Public Grievances & Pensions (MoPPG&P) issued comprehensive Guidelines for Handling Public Grievances for making grievance redressal time-bound, accessible and meaningful.
Key highlights of Comprehensive Guidelines for Handling Public Grievances
- An integrated user-friendly grievance filing platform with CPGRAMS to provide citizen a single window experience.
- This will help de-duplication and save time/efforts of officials from resolving same grievances on multiple portals.
- Appointment of Nodal Officers for Public Grievances in all Ministries/ Departments who will address grievances promptly, fairly and efficiently.
- Dedicated Grievance Cells shall be set-up in every Ministry/ Department with sufficient resources having knowledge of schemes and activities.
- Timelines for effective grievance redressal have been reduced to 21 days from existing 30 days.
- Grievance redressal assessment index for ranking Ministries/ Departments shall be issued on monthly basis.
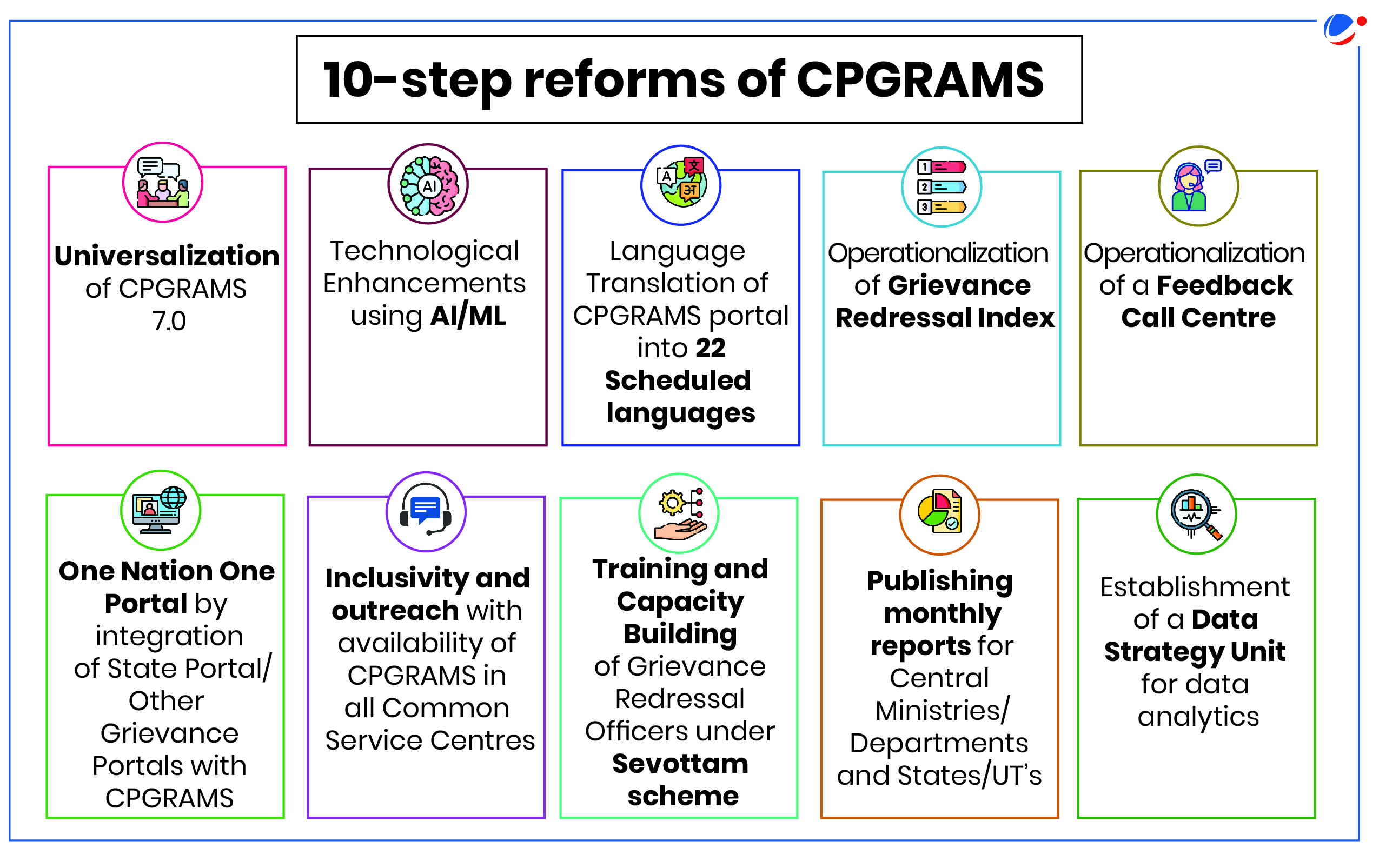
- 2024 Policy Guidelines manifest technology improvements undertaken with 10-step reform process adopted.
- Government implemented 10-step reforms of CPGRAMS (Centralised Public Grievance Redress and Monitoring System) in 2022.
About Grievance Redressal Mechanism (GRM)
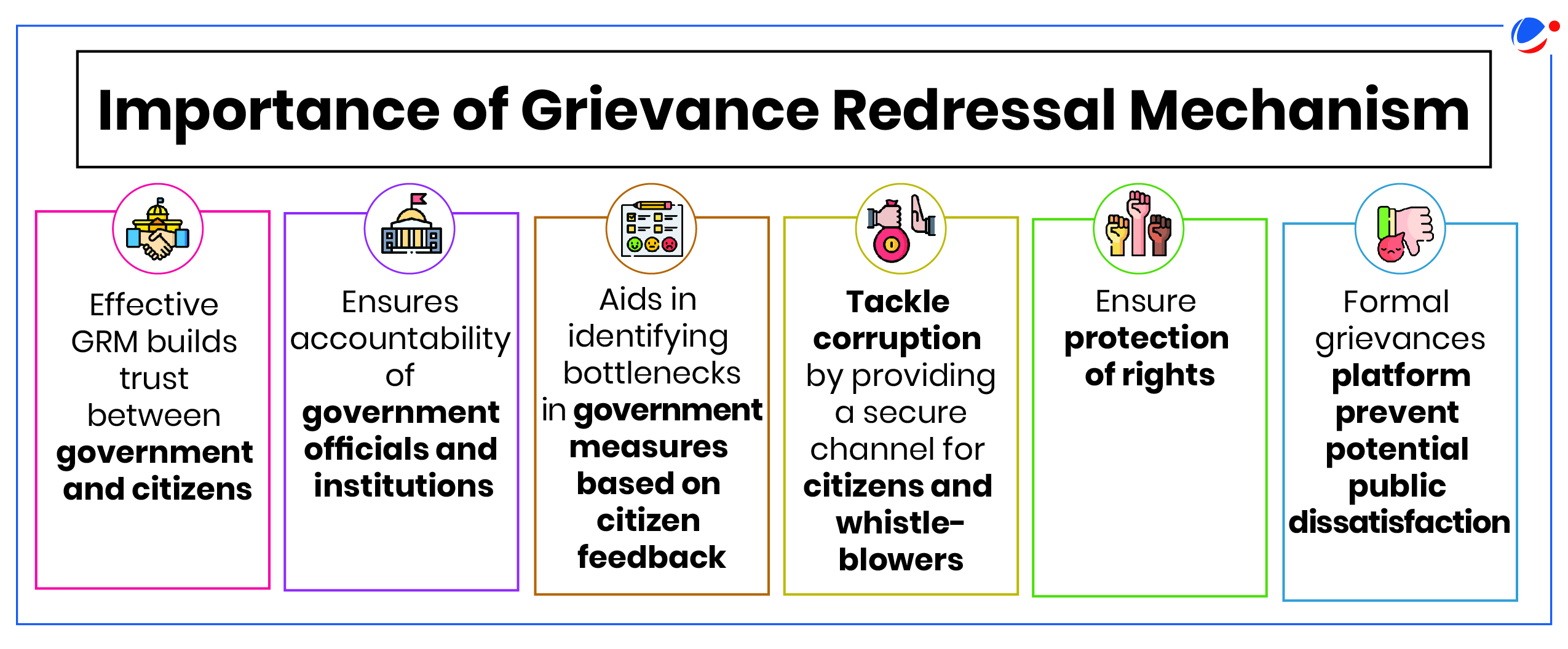
- GRM of an organisation is an important instrument to measure its effectiveness as it provides feedback on the working of the organisation.
- Its basic principle is that if promised level of service delivery is not achieved or if a right of a citizen is not honoured then citizen should be able to take recourse to a mechanism for grievance redressal.
- Two designated nodal agencies in Union Government handling grievances are:
- Department of Administrative Reforms and Public Grievances, DARPG (under MoPPG&P).
- Directorate of Public Grievances, Cabinet Secretariat.
- Status of Grievance Redressal: CPGRAMS portal has redressed nearly 60 lakh Public Grievances in period 2022-2024 and has mapped 1.01 lakh Grievance Redressal officers of Ministries/ Departments and States/ UTs.
- CPGRAMS is an online platform available to citizens 24x7 to lodge their grievances to public authorities on any subject related to service delivery.
- It is a single portal connected to all Ministries/Departments of Government of India and States through role-based access to the officers in portal.
Other Initiatives taken for Grievance Redressal
|
Issues associated with Grievance Redressal Mechanism
- Delays: Delays in grievance redressal due to bureaucratic hurdles, limited resources, or inefficient workflows undermines public confidence in the government.
- Corrupt Practices: In some instances, grievance redressal mechanisms themselves are subject to corrupt practices, where officials allegedly delay or manipulate outcomes in exchange for bribes.
- Lack of Integration: Multiplicity of grievance redressal platforms across different sectors (e.g., public distribution systems, consumer rights), across states, makes it difficult for citizens to lodge and track their complaints.
- Digital divide: Many citizens, particularly in rural areas, lack access to internet or digital literacy required to use online redressal platforms effectively.
Way ahead
- 2nd ARC Recommendations:
- States may be advised to set up independent public grievances redressal authorities to deal with complaints of delay, harassment or corruption.
- Government organizations should analyse complaints received and identify areas wherein interventions would be required to eliminate underlying causes that lead to public grievances.
- Recommendations of Parliamentary Standing Committee on Personnel, Public Grievances, Law and Justice, (25th Report):
- Grievance-handling system should be accessible, simple, quick, fair, responsive and effective.
- Public Grievance Redressal Mechanism should be envisaged in statutory form on line of RTI Act, 2005 which would make it mandatory on all State Governments/UTs/etc. to pursue grievance till their final disposal.
- Decentralized redressal: Decentralize GRM so that local or regional offices are empowered to resolve issues, reducing the burden on central authorities and ensuring faster resolutions.
- Reduce bureaucratic layers: Simplify the process of filing complaints by minimizing paperwork and formalities, focussing on making system accessible, and citizen friendly.
- For example, setting up and effective operationalization of Information & Facilitation Counters.
- Review and monitoring: Establish a robust monitoring system to analyse performance of grievance-handling departments and officials through periodic audits and evaluations.
- Feedback mechanism: Establish key performance indicators for online grievance management system like response times, resolution rates, and citizen satisfaction.
- Integrating Technology: AI can be employed to categorize/prioritize grievances and utilize data analytics to identify trends/patterns in grievances, helping in allocation of resources and policy adjustments.







