Why in the News?
Recently, India joined the US-led Minerals Security Partnership (MSP) Finance Network to secure sustainable supply chains for critical minerals.
More on the News
- India's participation in MSP Finance Network is part of its broader effort to diversify and secure its supply of critical minerals.
- It also aims to reduce dependency on China, which currently dominates global critical mineral supply chains.
What is MSP Finance Network?
About Mineral Security Partnership
|
- An initiative of the Minerals Security Partnership, it is a joint financing body designed to fund critical minerals projects across the globe.
- Objectives: To unite institutions from the Indo-Pacific region and Europe to strengthen cooperation, promote information exchange and co-financing among participating institutions, with the aim of advancing diverse, secure, and sustainable supply chains for critical minerals.
- It will also drive sustainable investmentin global critical mineral supply chains, including by mobilizing private sector capital, in production, extraction, processing, recycling, and recovery projects.
- Members: 14 countries including India and the European Commission.
- It also includes the US International Development Finance Corporation (DFC), European Investment Bank (EIB), Japan International Cooperation Agency (JICA), among others.
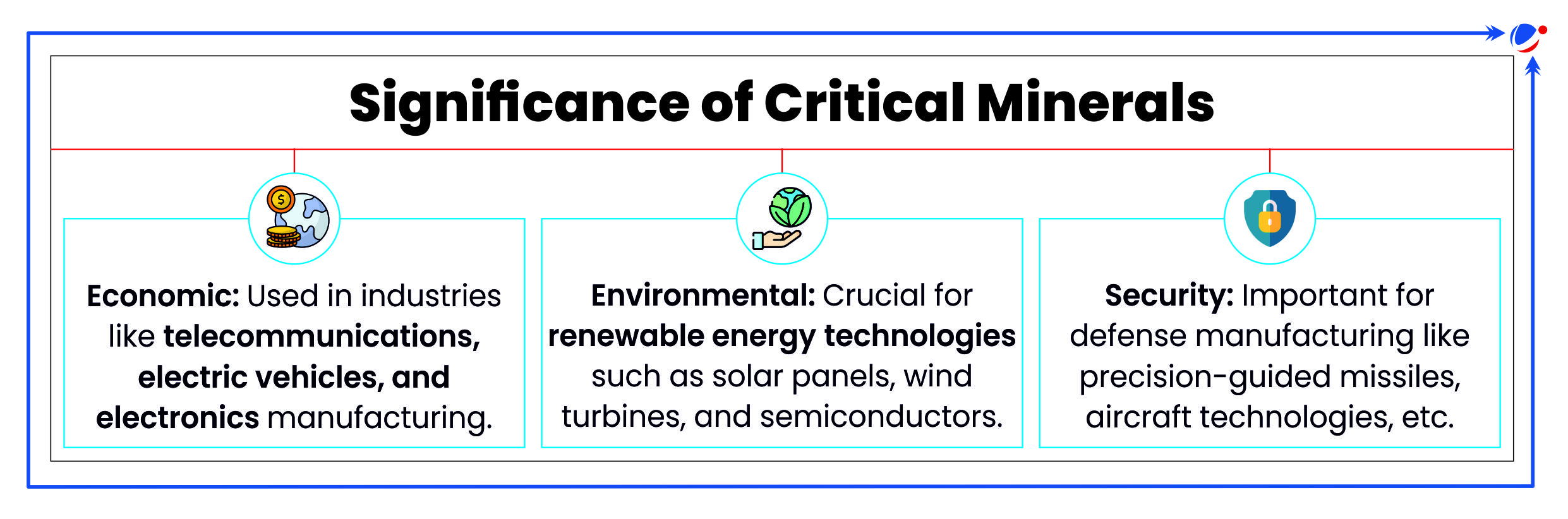
What are Critical Minerals?
- These minerals are building blocks of essential modern-day technologies and are at risk of supply chain disruptions due to limited global production and geopolitical factors.
- e.g., Lithium, cobalt, nickel, copper, rare earth elements, etc.
- Government of India has released a list of 30 critical minerals for India.
- These minerals are - Antimony, Beryllium, Bismuth, Cobalt, Copper, Gallium, Germanium, Graphite, Hafnium, Indium, Lithium, Molybdenum, Niobium, Nickel, PGE, Phosphorous, Potash, REE, Rhenium, Silicon, Strontium, Tantalum, Tellurium, Tin, Titanium, Tungsten, Vanadium, Zirconium, Selenium, and Cadmium.
What are the challenges in securing Critical Minerals for India?
- Limited domestic reserves: India lacks significant deposits of many critical minerals within its territory necessitating heavy reliance on imports and exposing to supply chain vulnerabilities.
- Low private investment, limited technological expertise, and evolving regulations further hinder domestic production of critical minerals.
- Geopolitical complexities: e.g., Democratic Republic of Congo supplies ~70% of the world's cobalt, but political instability there has led to supply disruptions affecting industries relying on cobalt for batteries and alloys.
- Global competition and supply chain vulnerabilities: e.g., China controls ~85% of global rare earth element processing capacity and ~60% of critical minerals production, resulting in a virtual monopoly over critical minerals for high-tech manufacturing.
- Environmental Concerns: Mining and processing of critical minerals often have significant environmental footprint resulting in protests from local population and environmental groups.
- Inadequate recycling infrastructure: Recycling of critical minerals from e-waste and spent technologies is underdeveloped, with the sector remaining largely unorganized and inefficient.

Way Forward
- Establish a National Institute/Centre of Excellence on Critical Minerals: Set up a Centre of Excellence for Critical Minerals (CECM) under the Ministry of Mines to focus on critical mineral research, discovery, and innovation, modeled after Australia's CSIRO.
- Boost domestic processing capabilities: Establish Special Economic Zones (SEZs) focused on critical mineral processing and value addition.
- Implement a "Green Channel" for quick approvals of critical mineral projects, with stringent but efficient environmental and social impact assessments, etc.

- Promote Circular Economy in critical mineral recovery: Setting up state-of-the-art e-waste recycling facilities in urban centres, introducing a nationwide "Recycle for Resources" campaign to increase public awareness and participation in e-waste recycling, urban mining, etc.
- Public-Private Partnerships: Establish joint ventures with global Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) and mining companies to build resilient value chains and achieve India's green energy goals.







