Why in the news?
In a major push to transform India's dairy cooperative sector, Ministry of Cooperation launched Standard Operating Procedure for 'White Revolution 2.0.'
Key Objectives of White Revolution 2.0
- Increase milk procurement by dairy cooperative societies: Aim is to increase the procurement by 50% over the next five years increasing the milk procurement to 1,000 lakh kilograms per day by 2029.
- Strengthen women Farmer: To make women self-reliant and empoweredin rural areas through employment, and fight against malnutrition etc.
- Strengthen Dairy Infrastructure: The targets of White Revolution 2.0 have been subsumed under the Central Sector Scheme National Programme for Dairy Development (NPDD) 2.0.
- Financial assistance under NPDD is provided for setting up of village level milk procurement system, milk chilling facilities for quality milk procurement to strengthen dairy infrastructure
- Boost Dairy Exports: Through indigenous production of testing equipment, bulk milk collection and dairy infrastructure.
- Financial Inclusion: Announcement of nationwide expansion of the 'Cooperation among Cooperatives' Initiative, was also done which has been successfully piloted in Gujarat.
- The programme will provide interest-free cash credit to dairy farmers through RuPay-Kisan Credit Cards and distribute micro-ATMs to dairy cooperative societies, bringing banking services to farmers' doorsteps.
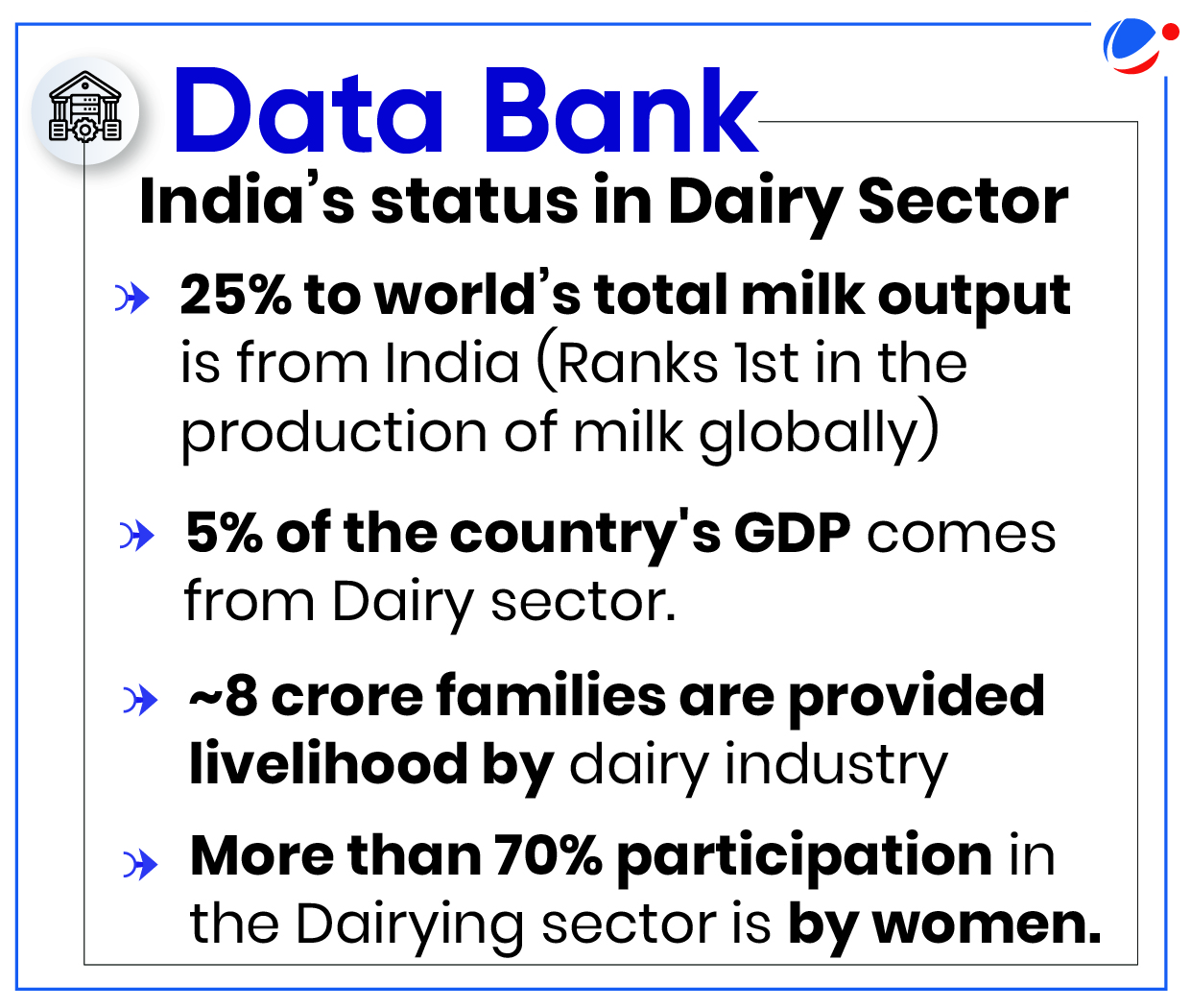
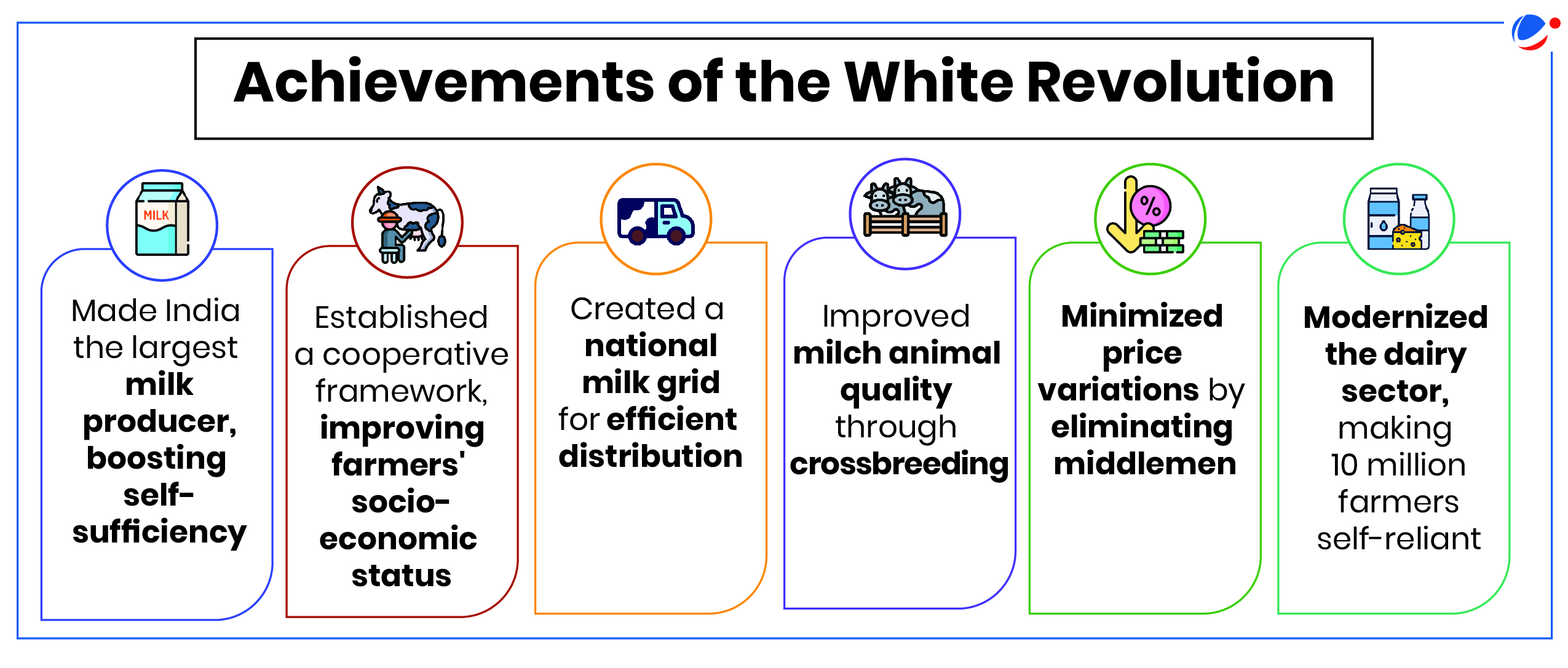
About White Revolution
|
Importance of Cooperatives in Dairy Sector
- Promoting Economic Empowerment of Farmers: Cooperative societies like Amul and Nandini have provided equitable wealth distribution, reducing economic inequality among farmers.
- Market Access: Cooperatives facilitate market access for small farmers, enhancing their collective bargaining power and enabling them to reach consumers more effectively.
- Supporting Women's Empowerment: By increasing women's representation in the dairy sector, cooperatives contribute to their economic independence. 35% of participants in dairy cooperatives are women.
- Facilitating Financial Inclusion: Cooperative banks offer low-interest loans, improving access to credit for farmers and members.
- Crisis resilience and risk mitigation: Cooperatives offer crisis resilience and risk mitigation by providing a support network during economic downturns and reducing vulnerability to market fluctuations.
Challenges Faced by India's Dairy Cooperatives
Successful cooperative models are primarily found in Maharashtra, Gujarat, and parts of Kerala. Other regions have struggled to replicate this success. Some of the key reasons for this are as follows
- Financing: Huge constraints are faced by cooperatives in alluring investments since cooperatives rely upon member contributions or loan capital, unlike firms/corporations that primarily rely on equity capital.
- Hurdles in creating milk grid: Domestic milk production units are scattered and partitioned by uneven terrain, constraining the development of a grand superstructure for a milk grid. The procurement price received by rural producers is further eroded by inefficiencies and diseconomies of scale. The cost of transportation and processing too is higher
- Challenges faced by dairy farmers: low milk prices, high feed costs, unstable markets, inadequate veterinary services, equipment for milking, cow dung management, and tracking and storing of records.
- Farmers who have tracts of irrigated land possessed greater comparative advantages, to the many disadvantages of the landless.
- Consumer preference and market dynamics: Changing consumer needs, increased regulation, competition in the market, and volatile weather are some other challenges faced by milk cooperatives.
Initiatives taken to strengthen Dairy Sector
|
Way ahead
Following initiatives could make India's dairy cooperatives more efficient and competitive
- Technological Integration: Milk cooperatives should integrate with information and communication technologies (ICT) for smoother operations.
- Establish cyber stores at key locations and create customer databases to segment the market and improve sales targeting.
- Introduce a web-based business-to-business system for rural cooperatives, enabling easier transactions with dealers and stockists.
- Efficient Milk Processing
- Focus on Quality & Safety: Ensure quality milk procurement while maintaining high food safety and quality standards.
- Cold Chain Infrastructure: Develop a robust cold chain infrastructure to maintain milk quality and ensure smooth transportation.
- Brand Building & Promotion: Improve brand recognition through online promotion strategies, interactive websites, and creative marketing, such as food preparation guides or quizzes to capture consumer interest.
- Boosting Exports
- Competitiveness: Build confidence in domestic dairy brands by improving their competitiveness against international brands.
- Business Approach: Farmers should manage dairy cooperatives with a business mindset, focusing on profitability and sustainability.
- Exclusion from FTAs: Advocate for the exclusion of dairy from free trade agreements (FTAs) to protect domestic producers from international competition.
Conclusion
By leveraging the cooperative model, India's dairy sector can transform its potential into reality, positioning the nation as a leading exporter of dairy products on the global stage.






