Perpetual Bonds
India's first additional Tier I (AT-1) perpetual bond was issued after recent rule changes to make them more appealing.
Perpetual bonds:
- They are fund-raising instruments that do not carry any maturity date as bonds usually do.
- Instead, they offer to pay their buyers a coupon or interest at a fixed date for perpetuity.
- Investors can get the principal back by selling the bond in the secondary market, or when the issuer decides to redeem the bonds.
- These bonds have an obligation only to pay interest and are not required to repay the debt.
- Tags :
- Perpetual Bonds
- Bond Market
Windfall Tax
The Centre has reduced the windfall tax on domestically produced crude oil.
About Windfall Tax
- A windfall tax is a tax imposed by governments on certain industries that experience significantly above-average profits due to favorable economic conditions.
- The purpose is to redistribute excess profits in one area to raise funds for the greater social good.
- Governments justify the tax by asserting that these profits are not solely due to the taxed entity's efforts but also due to external factors.
- Tags :
- Windfall Tax
- Crude Oil
Agriculture Infrastructure Fund
Union Cabinet approved progressive expansion in Central Sector Scheme of financing facility under ‘Agriculture Infrastructure Fund (AIF)’ to make it more attractive, impactful, and inclusive.
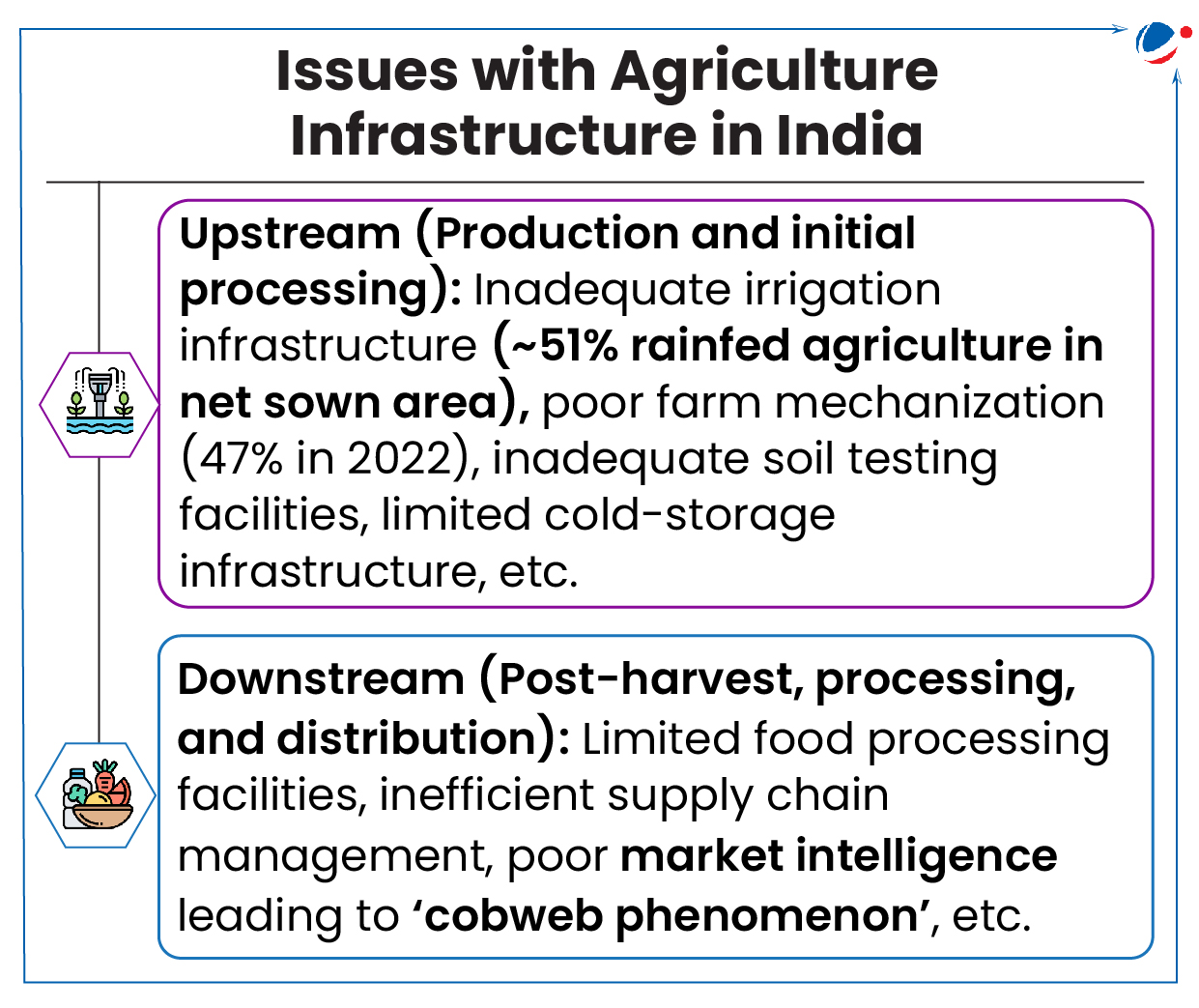
Key highlights of the recent expansion of AIF
- Viable Farming Assets: To allow all eligible beneficiaries of scheme for creation of infrastructure covered under 'viable projects for building community farming assets'.
- Integrated Processing projects: To include integrated primary and secondary processing projects in list of eligible activities under AIF.
- PM KUSUM Component-A: To allow convergence of Component-A of PM-KUSUM with AIF for farmer/group of farmers/ Farmer Producer Organizations/ Cooperatives/ Panchayats.
- In addition to Credit Guarantee Fund Trust for Micro and Small Enterprises (CGTMSE), now NABSanrakshan (wholly owned subsidiary of NABARD) has also been proposed to extend AIF credit guarantee coverage of FPOs.
About Agriculture Infrastructure Fund (AIF)
- It is a medium - long term debt financing facility for investment in viable projects for post- harvest management infrastructure and community farming assets through interest subvention and credit guarantee support.
- ₹ 1 Lakh Crore will be provided by banks and financial institutions as loans with interest subvention of 3% per annum and credit guarantee coverage under CGTMSE for loans up to ₹ 2 Crores.
- Tags :
- PM-KUSUM
- Agriculture Infrastructure Fund
- NABSanrakshan
Articles Sources
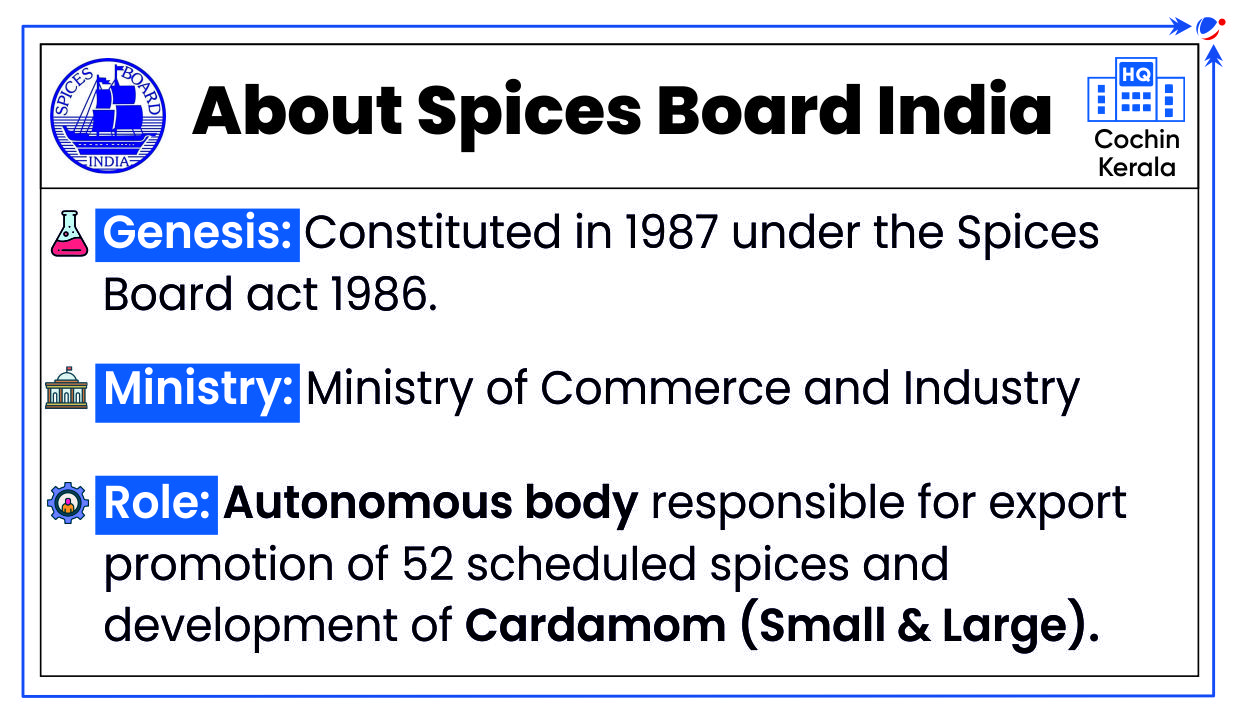
SPICED Scheme
The Union Ministry of Commerce and Industry recently approved SPICED Scheme.
About SPICED Scheme
‘Sustainability in spice sector through progressive, innovative and collaborative interventions for export development’ (SPICED) is a Spices board scheme.
- Aim: To expand the area under cardamom and increase productivity of small and large cardamom, export promotion, capacity building & skill development of stakeholders, etc.
- Major components of the scheme: Improving productivity, post-harvest quality upgradation, market expansion efforts, trade promotion, technology interventions, research and capacity building, and skill development.
- Implementation during the remaining term of the 15th Finance Commission (from 2023-24 to 2025-26).
About Cardamom
- Cardamom is commercially cultivated for its dried fruits (capsules)
- Small Cardamom:
- Native: Indigenous to the evergreen forests of Western Ghats of South India.
- Major producers of small cardamom: Kerala, Karnataka and Tamil Nadu
- Favorable conditions for Small Cardamom
- Thick shady areas with loamy soil which are usually acidic are ideal.
- Elevation: 600 to 1500 m.
- Adequate drainage must be provided
- Large Cardamom
- Distribution: Sub-Himalayan region of North Eastern India, Nepal and Bhutan.
- Favorable conditions for Large Cardamom: average precipitation of 3000-3500 mm spread over about 200 days.
- Temperature ranging from 6-30 degree C.
- Tags :
- Cardamom
- SPICED Scheme
- Spices Board of India
Delhi Declaration on Civil Aviation
2nd Asia Pacific Ministerial Conference on Civil Aviation (APMC) concluded with unanimous adoption of Delhi Declaration.
- APMC which also celebrates 80 years of International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) has been organized by Ministry of Civil Aviation and ICAO.

Key commitments under Delhi Declaration:
- Reaffirming Asia and Pacific Ministerial Declaration on Civil Aviation (Beijing): Pursue implementation of State Safety Programme, Asia/Pacific Seamless Air Navigation Service Plan
- Aviation Safety & Security: Achieve aspirational goal of Global Aviation Security Plan
- Gender Equality: Take necessary measures to strengthen gender equality
- Aviation Environment Protection: Reduce emissions and other environmental impacts of aviation
- Ratification of International Air Law Treaties: Encourage Asia & Pacific States to ratify Amendments to Convention on International Civil Aviation
Civil Aviation Sector in India
- India is fastest growing aviation market in world and is currently 3rd largest in domestic segment.
- Number of aircraft in India is more than 800 and airports have exponentially grown to 157.
- Gender Equality: 15% of the pilots in India are women (global average is 5%).
- Schemes for Aviation Sectors: Regional Connectivity Scheme (RCS) –Ude Desh ka Aam Nagrik (UDAN), Digi Yatra & Greenfield Airports Policy, 2008(To prioritize carbon neutrality).
- Tags :
- Civil Aviation
- Delhi Declaration
- International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO)
Financialisation
Chief Economic Advisor raised concerns about excessive ‘financialisation’ in India.
- Financialization is a process whereby financial markets, financial institutions, and financial elites gain greater influence over economic policy and economic outcomes.
- Thus, financial intermediaries and technologies gain unprecedented influence over our daily lives.
- It also describes moving investments away from traditional, ‘physical’ asset (like real estate, gold) towards ‘financial assets’ (like mutual funds).
Factors Driving Financialisation | |||
Rising middle class with higher disposable income | Inflation due to which households are seeking higher returns beyond fixed deposits | Government incentives on these instruments | Increasing digitisation and financial inclusion |
Why is excessive financialisation a concern?
- Increased Inequality: Financial income is funneled to top 1% of population through equity ownership.
- Distorts functioning of economy: Profits flow increasingly from financial investments, rather than trade in goods and services.
- Thus, movements of stock market primarily determines functioning of economy instead of production of employment or rising standards of living.
- Rising Household debts: Stagnation of real wages may increase Households’ reliance on loans (as seen in U.S economy).
- Adverse impacts on policies: Fincialisation may push for policies favouring predatory lending, higher risk-taking and erosion of worker protections.
Developing countries often face debilitating crises when financial market ‘innovations’ and growth run ahead of economic growth for e.g the Asian crisis of 1997-98. Therefore, India needs to have an orderly and gradual evolution of the financial market.
- Tags :
- Inequality
- Financialisation
- Financial Intermediaries
Average household spending on food falls below half since 1947: EAC-PM Paper
It was highlighted by Economic Advisory Council to the Prime Minister (EAC-PM) in paper titled "Changes in India's Food Consumption and Policy Implications: A Comprehensive Analysis of Household Consumption Expenditure Survey 2022-23 and 2011-12”.
Other Key Highlights
- Regional Variations: Household spending has increased across India, though the extent varies by state and region. E.g. West Bengal saw a 151% rise and Tamil Nadu 214%, between 2011-12 and 2022-23.
- Rural vs. Urban Spending: Consumption expenditure growth for rural households (164%) was higher than that for urban households (146%).
- Nutrients and Dietary Diversity: Shift from cereal-based consumption towards a diet that includes fruits, milk & milk products, eggs, fish & meat.
- Processed Foods: Household spending on served and packaged processed foods has increased across all income groups. But it’s most noticeable among top 20% of households and is significantly higher in urban areas.
Policy Implications due to changing consumption patterns
- Government should focus on policies promoting production of diverse food items, mainly fruits, vegetables, and animal-source foods etc.
- Policy addressing micronutrient deficiency must be well-targeted due to variation in micronutrient intake across region.
- Agricultural policies should focus beyond cereals, as their consumption is dropping. Support measures like MSP, which target cereals, will only have limited benefits for farmers.
- Tags :
- Changes in India's Food Consumption and Policy Implications
- Average Household Spending
- Economic Advisory Council
BHASKAR Initiative for India's Startup Ecosystem
DPIIT will launch Bharat Startup Knowledge Access Registry (BHASKAR) initiative for India's Startup Ecosystem
About BHASKAR Initiative
BHASKAR initiative (of Ministry of Commerce and Industry) is a platform designed to centralize, streamline, and enhance collaboration among key stakeholders within entrepreneurial ecosystem, including startups, investors, etc.
- Its primary goal is to build world’s largest digital registry for stakeholders within startup ecosystem.
- It is under Startup India program, which aims to build a strong ecosystem for nurturing innovation and encouraging investments.
Key Features of BHASKAR
- Networking: It will bridge gap between startups and other stakeholders, allowing for seamless interaction across sectors.
- Centralized Access to Resources: By providing startups immediate access to critical tools and knowledge, it will enable faster decision-making and more efficient scaling.
- Creating Personalized Identification: Every stakeholder will be assigned unique BHASKAR ID, ensuring personalized interactions and tailored experiences across platform.
- Enhancing Discoverability: Through powerful search features, users can easily locate relevant resources, collaborators, and opportunities, ensuring faster decision-making and action.
- Supporting India’s Global Brand: It will promote India’s global reputation as a hub for innovation, making cross-border collaborations more accessible to startups and investors alike.
India’s Startup Ecosystem
- India has 3rd largest startup ecosystem in world and has over 1,46,000 DPIIT-recognized startups.
- Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT) recognize business as a startup.
- Tags :
- Startup India
- India's Startup Ecosystem
- BHASKAR Initiative
Priority Sector Lending
RBI study titled "Priority Sector Lending (PSL): The Indian Experience" released
PSL was formalized in 1972 to facilitate flow of credit to such sectors, which though creditworthy, are unable to access credit from formal financial institutions.
Key findings of the study
- Improved asset quality: PSL is responsive to asset quality, with higher PSL growth enhancing overall bank asset quality.
- Developing niche in specific PSL segments: Since introduction of Priority Sector Lending Certificates (PSLCs), share of PSL in total bank credit has increased, enabling certain banks to specialize in specific PSL segments.
- Achieving PSL Targets: Lending to the priority sector has consistently exceeded 40% across various periods and bank categories, influenced by individual banks’ strategies.
- PSBs have frequently met their 18% agricultural lending target.
About PSL
- Objective: To ensure that vulnerable sections of society and underdeveloped areas get access to credit.
- PSL Targets: Banks have to mandatorily allocate a portion of their Adjusted Net Bank Credit (ANBC) or Credit Equivalent of Off-Balance Sheet Exposure (CEOBE), whichever is higher, towards PSL.
- Mandated target differs for different banks and is 40% for Scheduled commercial banks and foreign banks (with 20 or more branches) while it is 75% for Regional Rural Banks and Small Finance Banks.
- Urban Cooperative banks have to allocate 65% to PSL in FY 2024-25 but will have to increase to 75% in FY 2025-26.
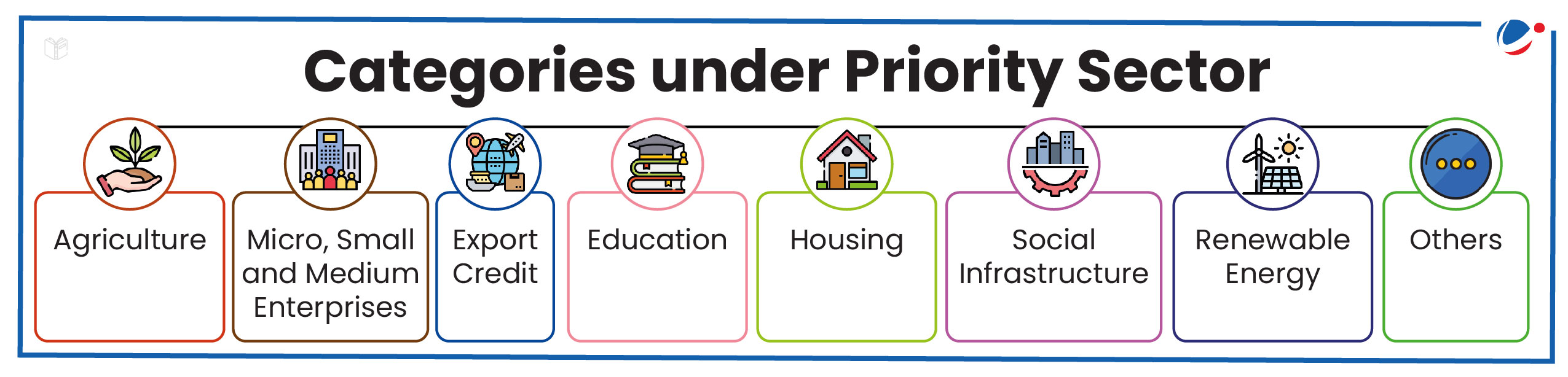
To know more about the Priority Sector Lending, refer to Article 3.1 Revised Priority Sector Lending Norms in June 2024 Monthly Current Affairs Magazine.
- Tags :
- Priority Sector Lending (PSL)
- PSL Targets
- Categories under Priority Sector Lending
Unified Lending Interface (ULI)
About ULI
- It is a technology platform which would enable frictionless credit.
- It will facilitate a seamless and consent-based flow of digital information, including land records of various states, from multiple data service providers to lenders. Consent
- It will have a common and standardised Application Programming Interface designed for a ‘plug and play’ approach.
Benefits of ULI
- Enables borrowers to get benefit of seamless delivery of credit, quicker turnaround time without requiring extensive documentation.
- Addresses credit demand gaps for agriculture and MSME sectors.
- Tags :
- Unified Lending Interface (ULI)
- Frictionless Credit
- Plug and Play Approach
National Bank for Financing Infrastructure and Development (NaBFID)
Central Government, under Companies Act, 2013, notified NaBFID as a Public Financial Institution (PFI).
- Only institutions established under any Central or State Act or whose at least 51% paid up share capital is held by central or state government can be notified as PFI.
National Bank for Financing Infrastructure and Development (NaBFID)
- NaBFID was established as an infrastructure focused Development Financial Institution (DFI) under the National Bank for Financing Infrastructure and Development Act, 2021.
- It was established to support the development of long-term non-recourse infrastructure financing in India including development of bonds and derivatives markets.
- Tags :
- National Bank for Financing Infrastructure and Development (NaBFID)
- Financing Infrastructure
- Development Financial Institution (DFI)
- Public Financial Institution (PFI)



