Why in the News?
Recently, Union Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) has launched the 'Vishvasya: National Blockchain Technology Stack'.
More on the News
Additionally, MeitY has also launched:
- NBFLite: A Blockchain sandbox platform, developed especially for startups/academia for rapid prototyping of applications, carrying out research and capacity building.
- Praamaanik: A solution that harnesses Blockchain technology to verify mobile app origins and is powered by the National Blockchain Framework.
- National Blockchain Portal: It is developed on the theme based on Content Management System to manage the contents related to the National Blockchain Framework initiative.
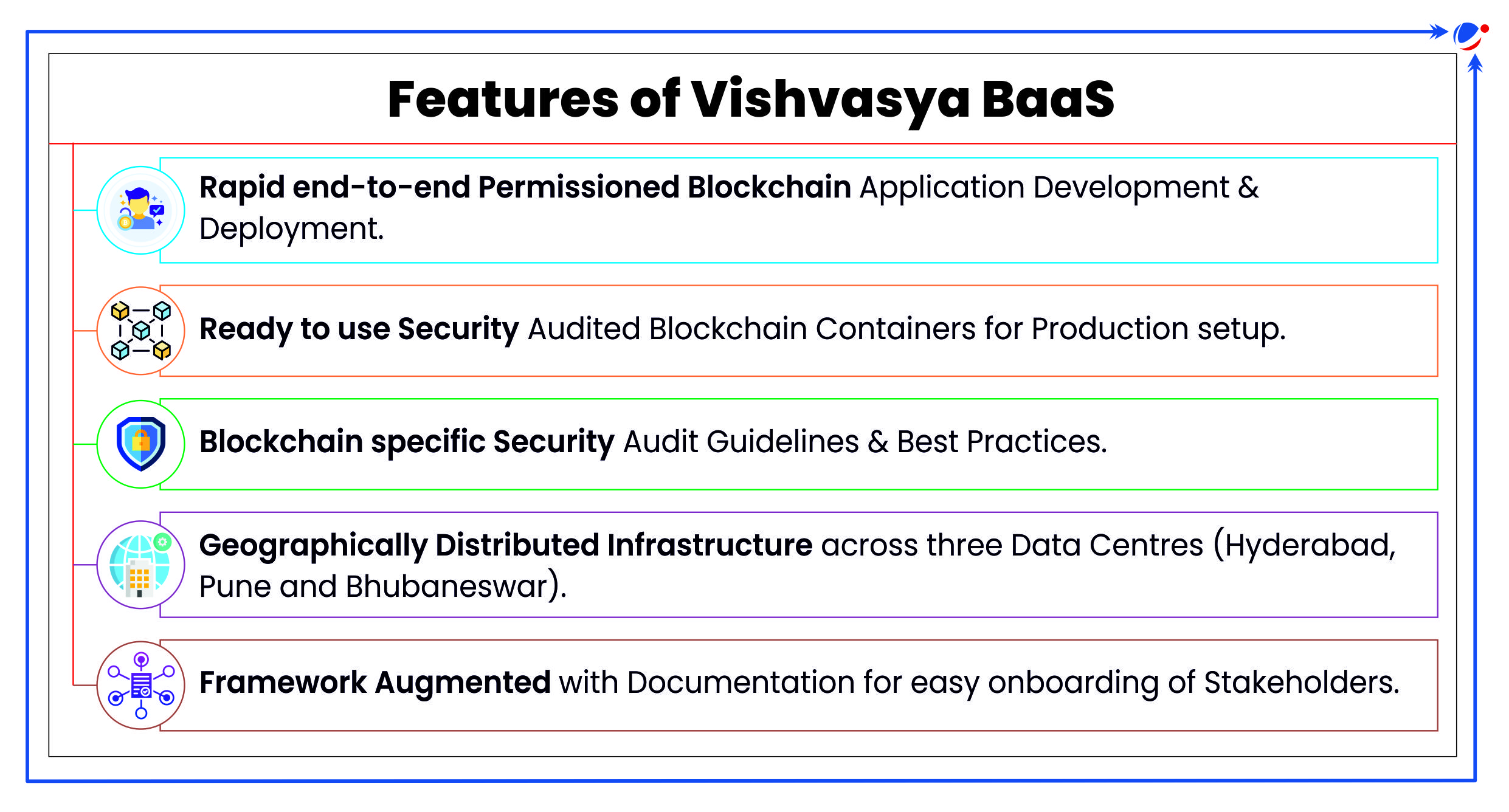
About Vishvasya: National Blockchain Technology Stack
- It offers Blockchain-as-a-Service (BaaS) with a geographically distributed infrastructure designed to support various permissioned Blockchain based applications.
- BaaS is third party cloud-based infrastructure and management that organizations and businesses use for developing and managing blockchain applications.
- It is a part of the broader National Blockchain Framework (NBF) provided under the National Strategy on Blockchain.
- NBF is meant for effectively utilize the Blockchain technology in different domains such as health, agriculture, education, finance, etc.
- Significance of BaaS
- Facilitates in enabling trust by developing new types of distributed software architectures, capable of finding consensus on their shared states and providing a single source of truth.
- Addresses the challenges of Blockchain adoption across various stakeholders including Infrastructure Providers, Smart Contract Developers and Application Developers.
- Provides security assurance of various Blockchain components across the stack.
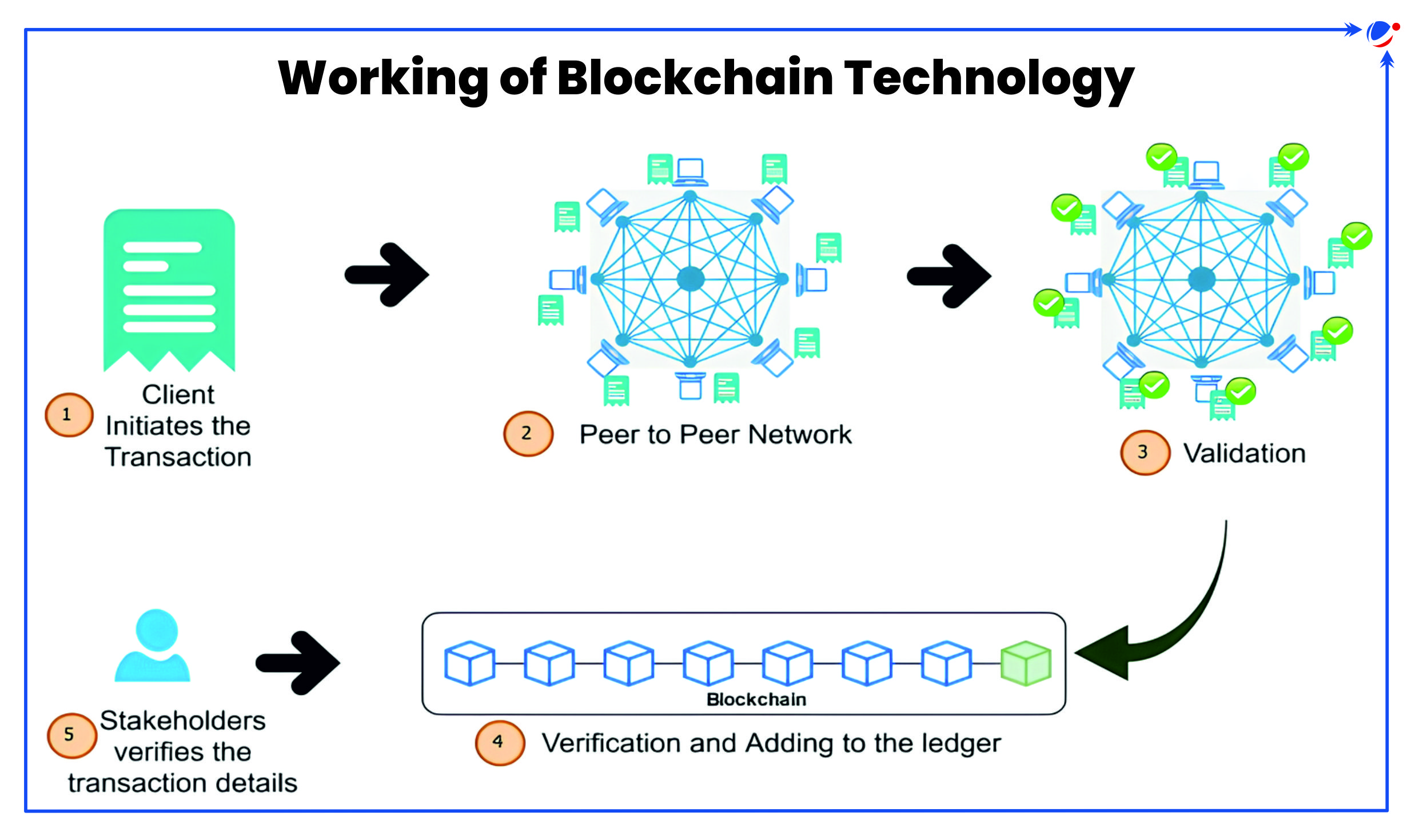
What is Blockchain technology?
Working Mechanism
 Properties of Blockchain
Types of Blockchain
|
Potential applications of Blockchain Technology
- Cryptocurrencies: Cryptocurrencies (e.g., Bitcoin, Ethereum, Litecoin, Ripple, etc.) uses blockchain to record and verify transactions, which makes them secure and transparent.
- Supply Chain Management: It enables more efficient communication and collaboration between suppliers, manufacturers, distributors, and customers.
- Voting Systems: It can include features such as voter identification, eligibility checks, and ballot tracking, all of which can Identity Verification.
- Intellectual Property Protection: For e.g., companies can use blockchain technology to manage their trademarks and patents, ensuring that their intellectual property is protected and not used without their permission.
- Records Management: For e.g., Blockchain-based healthcare record management can also help improve data accuracy and integrity by providing a single source of truth for patient data.
- Others: Law Enforcement, banking, Internet of Things, crowd funding, etc.
Challenges in Blockchain Technology implementation
- Performance: Replication of data on each node leads to performance issues and slows down the performance as compared to traditional centralized systems.
- Scalability: Poor scalability due to factors such as complex architecture and configuration of the Blockchain platform, variable requirements for processing power, network bandwidth, etc.
- Storage: Demands heavy storage as data stored is replicated at all the nodes and becomes perpetual.
- Energy Consumption: Blockchain networks often require significant computational power, leading to high energy consumption.
- Interoperability: Interoperability between different blockchain platforms can be a challenge, especially in environments where multiple networks coexist.
- Legal: Section 43A of the Information Technology Act, 2000 currently does not have safeguards mentioned from the perspective of Privacy when applied to Blockchain.
- Localization requirements: Since public Blockchain automatically store data redundancies across all nodes on a network, it may hit a hurdle with localization requirements.
Other Initiatives taken to promote Blockchain Technology
India
- National Strategy on Blockchain by MeitY.
- Centre of Excellence in Blockchain Technology
- Future Skills PRIME: For upskilling and reskilling in emerging technologies including Blockchain by NASSCOM and MeitY
Global
- World Economic Forum's Presidio Principles: A Blockchain Bill of Rights issued by World Economic Forum's Global Blockchain Council.
- IBM's Blockchain World Wire: A global payment network using blockchain to facilitate cross-border transactions.
- Global Blockchain Business Council (GBBC): An industry association promoting blockchain technology adoption across various sectors.
Conclusion
India's path to blockchain adoption requires a balanced approach that combines skill development, regulatory clarity to provide enabling, practical implementation through identification of specific use-cases, and robust security measures. By addressing these key areas simultaneously, India can create an environment conducive to blockchain innovation and adoption, positioning itself as a global leader in this transformative technology.





