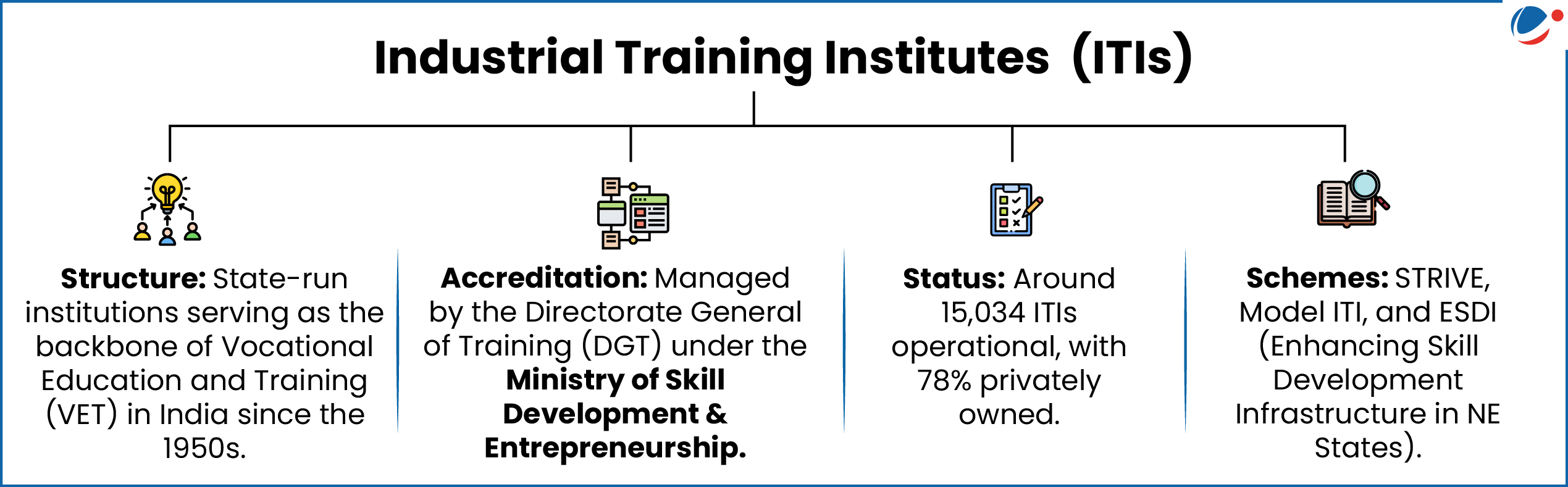
The scheme will be implemented under the Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship.
About PM-SETU
- Type: ₹60,000 crore centrally sponsored scheme.
- Aim: To transform 1,000 Government Industrial Training Institutes (it is) across India into modern, industry-aligned training institutions.
- Implementation: PM-SETU will follow a hub-and-spoke model, with 200 hub ITIs linked to 800 spoke ITIs.
- Each hub will be equipped with advanced infrastructure, innovation and incubation centres, production units, training of trainer facilities, and placement services, while the spokes will extend access and outreach.
- Main Components:
- Introduce new, demand-driven courses and revamp existing ones in collaboration with industry;
- Set up Special Purpose Vehicles (SPVs) with credible Anchor Industry Partners to manage clusters and ensure outcome-based training;
- Create pathways for long-term diplomas, short-term courses, and executive programs;
- Strengthen 5 National Skill Training Institutes in - Bhubaneswar (Odisha), Chennai (Tamil Nadu), Hyderabad (Telangana), Kanpur (Uttar Pradesh), Ludhiana (Punjab), as Centres of Excellence with global partnerships.
Article Sources
1 sourceRemission of Duties and Taxes on Exported Products (RoDTEP) Scheme has been extended till March 2026.
About RoDTEP Scheme
- Launched: January 2021 by Ministry of Commerce and Industry.
- Objective: To reimburse taxes, duties, and levies at central, state, and local levels that are not refunded under any other mechanism.
- Reduces hidden costs and make Indian exports more competitive in global markets.
- Scope: Covers taxes incurred during manufacture and distribution of exported products
‘We Rise’ (Women Entrepreneurs Reimagining Inclusive and Sustainable Enterprises) initiative was launched recently.
About We Rise Initiatives
- Launched by: NITI Aayog’s Women Entrepreneurship Platform (WEP) under its Award to Reward (ATR) initiativealong with DP World.
- Objective: To help women entrepreneurs, including women-led MSMEs, to scale their businesses globally through trade facilitation, mentorship, and strategic partnerships.
Article Sources
1 sourceMinistry of Petroleum and Natural Gas informed about the occurrence of natural gas in the Sri Vijayapuram 2 well at 17 km from the shoreline on the east coast of the Andaman Islands.
- India’s Hydrocarbon Resource Assessment Study (HRAS) estimates hydrocarbon resources of 371 million Metric Tons of Oil Equivalent (MMTOE) in the Andaman-Nicobar (AN) Basin.
- Geologically, the AN basin lies at the intersection of the Andaman and Nicobar Basins, part of the Bengal-Arakan sedimentary system.
- Tectonic setting at the boundary of the Indian and Burmese plates have created numerous stratigraphic traps conducive to hydrocarbon accumulation.
- Earlier, gas has been discovered in adjacent basins along North Sumatra (Indonesia) and Irrawaddy-Margui (Myanmar).
- The discovery aligns with India’s vision of establishing a Gas Based Economy by 2030 and increasing share of natural gas in its primary energy basket to 15 percent by 2030.
- Currently, India’s natural gas production meets only around 50% of its demand with rest demand being fulfilled through imports.
- Qatar, US and UAE are major sources of India’s Liquified Natural Gas (LNG) imports.
- Currently, India’s natural gas production meets only around 50% of its demand with rest demand being fulfilled through imports.
Initiatives for Natural Gas Exploration
|
Ministry of Mines releases State Mining Readiness Index (SMRI)
About State Mining Readiness Index
- Objective: To capture State’s relative contribution in developing the country’s mining sector, promote mining sector reforms and assess State performance.
- Basis: The index evaluates States based on auction performance, early mine operationalization, exploration thrust, and sustainable mining practices related to non-coal minerals.
- Classification: States are classified into three categories based on their mineral endowment.
- Top Performers in these categories are:
- A: Madhya Pradesh, Rajasthan, and Gujarat
- B: Goa, Uttar Pradesh, and Assam
- C: Punjab, Uttarakhand, and Tripura
- Top Performers in these categories are:
Ministry of Mines classified limestone as a major mineral completely.
- Earlier limestone was classified as minor mineral as well as major mineral depending upon the end use.
About Major and Minor minerals
- Under the Mines and Minerals (Development and Regulation) (MMDR) Act, 1957, minerals are broadly classified in two categories, i.e. major minerals and minor minerals.
- The major minerals cover fuel minerals consisting of coal, lignite, petroleum & natural gas and metallic minerals including atomic minerals and non-metallic minerals.
- Minor minerals consist of materials such as marble, slate, shale etc.
- MMDR Act gives State Governments the power to make rules for minor minerals.
Article Sources
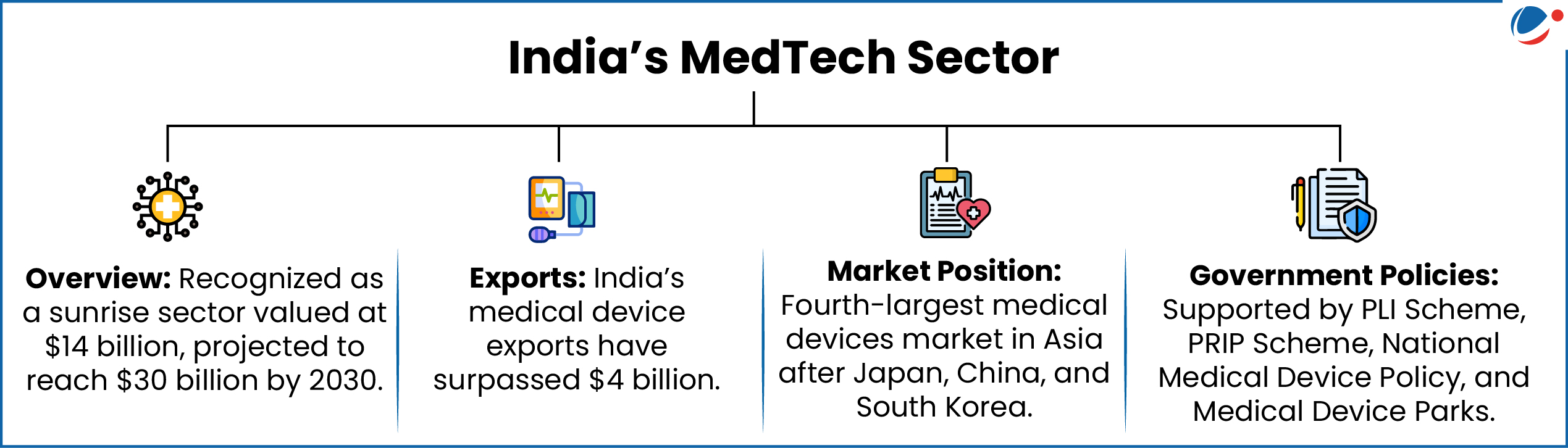
1 sourceMAHA-MedTech Mission has been launched by the Anusandhan National Research Foundation (ANRF), in collaboration with the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) and the Gates Foundation.
- ANRF has been established, through ANRF Act, 2023, as an apex body to provide high-level strategic direction of scientific research as per recommendations of the National Education Policy.
About MAHA-MedTech Mission
- Aim: To accelerate innovation in India’s medical technology sector, reduce reliance on high-cost imports, and promote equitable access to affordable and high-quality medical technologies.
- Funding: Provide funding support to a wide range of entities including Academic and R&D institutions, Hospitals, Startups, MSMEs, MedTech industry and collaborations between entities.
- Milestone-linked funding of ₹5–25 crore per project (and up to ₹50 crore in exceptional cases).
- Enabling Support: Through national initiatives such as Patent Mitra (IP protection and technology transfer), MedTech Mitra (regulatory guidance and clearances), a Clinical Trial Network (for clinical validation and evidence generation) etc.
- Technology Areas: Innovative medical devices and IVD (In vitro diagnostics) including High-end Frontier Technologies (Deep Tech like Imaging, Radiotherapy equipment, Robotics, minimal invasive technologies, implants, AI/ML enabled platforms & devices etc.).
Article Sources
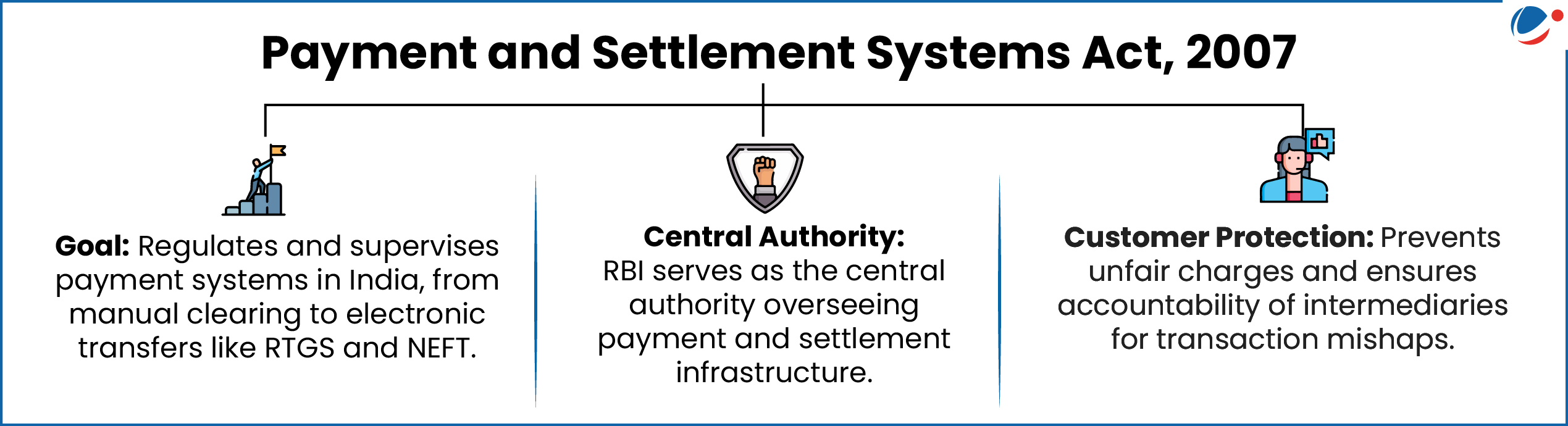
1 sourceThe 6-member Board will be responsible for the regulation and supervision of payment systems under the Payment and Settlement Systems Act, 2007.
- It has replaced the earlier Board for Regulation and Supervision of Payment and Settlement Systems (BPSS).
About the Payments Regulatory Board
- Composition & Structure:
- As per Section 3 of the Payment and Settlement Systems Act, the Board shall consist of
- Governor of the Reserve Bank as ex officio Chairperson;
- Deputy Governor of the Reserve Bank (in-charge of the Payment and Settlement Systems) as ex officio member;
- One officer of the Reserve Bank, nominated by the Central Board of the Reserve Bank as ex officio member;
- Three central government nominated persons, expert in payment systems, IT, cybersecurity, law.
- Tenure: 4 years, not eligible for re-nomination; resignation allowed with 6 weeks’ notice.
- Disqualifications: Age >70; insolvency; criminal conviction ≥180 days; MPs/MLAs, etc.
- As per Section 3 of the Payment and Settlement Systems Act, the Board shall consist of
- Principal Legal Adviser of RBI is a permanent invitee.
- RBI may also invite experts (permanent/ad hoc) for meetings.
- Meetings: At least twice a year with a Quorum of 3 members including Chairperson (or Deputy Governor in his absence) and a nominated member.
- Decision-making: Decisions by majority of votes of the members present and voting;
- Chairperson (or Deputy Governor in his absence) has a casting vote in case of tie.
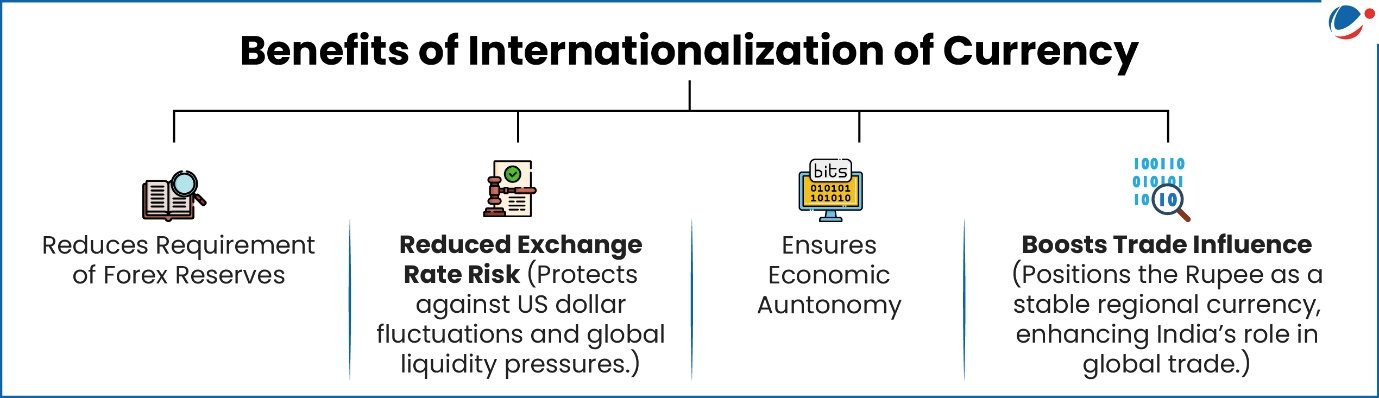
The RBI has unveiled new measures to promote wider international use of the Indian Rupee (INR), expanding both trade and investment avenues.
- Internationalisation of the Rupee means allowing the Indian Rupee to be used for global trade and financial transactions.
Key Measures Announced
- Loans in Indian Rupees to Non-Residents: Authorised dealer banks in India and their overseas branches will be permitted to lend in INR to persons resident in Bhutan, Nepal, and Sri Lanka, including a bank.
- Establishing Transparent Reference Rates: Financial Benchmarks India Limited (FBIL) will develop transparent reference rates for the rupee against major global currencies.
- Currently, the RBI publishes reference rates for the U.S. dollar, euro, Japanese yen, and sterling.
- Widening Use of Special Rupee Vostro Accounts (SRVAs): SRVA balances can now be used to invest in corporate bonds and commercial papers.
- Previously, surplus vostro balances were allowed to be invested in central government securities.
Special Rupee Vostro Account
|
Article Sources
1 sourceRBI granted Self-Regulatory Organisation status to Finance Industry Development Council (FIDC) to oversee NBFCs.
- FIDC is a representative body of non-banking financial companies (NBFC) registered with the RBI.
- Granting SRO status to FIDC will ensure better governance for NBFCs.
About Self-Regulatory Organisation
- Objective: SRO is expected to adhere to a set of overarching objectives for betterment of the sector they represent, foster advancement and address critical industry concerns within the broader financial system.
- Legal Backing: RBI’s Omnibus Framework for recognising Self-Regulatory Organisations (SROs) for Regulated Entities (REs), 2024
- Eligibility of SROs:
- An SRO shall be setup as a not-for-profit company registered under Section 8 of the Companies Act, 2013.
- It should have adequate net worth, sufficiently diversified shareholding (no entity shall hold 10% or more of its paid-up share capital) and must represent the sector.
- Responsibilities of SROs:
- Towards members: Frame a code of conduct, establish a grievance redressal and dispute resolution/ arbitration framework, etc.
- Towards Regulator: Ensuring regulatory compliance, promote sector development, foster innovation and detect early warning signals.
- Governance framework:
- Articles of Association (AoA)/bye-laws shall provide for manner of functioning of Governing Body and specify the functions of SRO.
- At least one-third of members in Board of Directors including Chairperson shall be independent.
The Central and State Co-operative Banks have been brought under the ambit of Reserve Bank - Integrated Ombudsman Scheme, 2021.
About Reserve Bank - Integrated Ombudsman Scheme, 2021 (RB-IOS, 2021)
- Objective: Provide customers of regulated entities (REs) a speedy, cost-effective and expeditious alternate grievance redress mechanism.
- Coverage: Until now it covered-
- All Commercial Banks, Regional Rural Banks, Scheduled Primary (Urban) Co-operative Banks, and Non-Scheduled Primary (Urban) Co-operative Banks with deposits size of ₹50 crore.
- All Non-Banking Financial Companies (excluding Housing Finance Companies) which are authorised to accept deposits or have customer interface, with an assets size of ₹100 crore
- All System Participants (includes System Provider which participate in a payment system in accordance with the Payment and Settlement Systems Act, 2007).
- Credit Information Companies
- It integrated the three Ombudsman schemes of RBI, namely,
- the Banking Ombudsman Scheme, 2006;
- the Ombudsman Scheme for Non-Banking Financial Companies, 2018; and
- the Ombudsman Scheme for Digital Transactions, 2019.
- It adopted the ‘One Nation One Ombudsman’ approach by making the RBI Ombudsman mechanism jurisdiction neutral.
- Power: The Ombudsman can award up to ₹20 lakh in compensation, plus up to ₹1 lakh for the complainant’s time, expenses, and any mental distress or harassment.
Recently, RBI unveiled key initiatives like the Unified Lending Interface (ULI), Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC) retail sandbox, pilot for tokenisation of Certificates of Deposit (CDs).
About Initiatives
- ULI: It is envisioned as a Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI).
- It aggregates data from multiple data sources which would be made available to lenders for better credit assessment.
- It aims to enhance the delivery of credit.
- CBDC Retail sandbox- for fintech firms to innovate and test solutions.
- CBDC is a digital version of fiat currencies issued by Central Banks.
- Tokenisation of CDs: Facilitates faster settlements, improves liquidity, enhances transparency, etc.
- Tokenization is the process of creating a digital representation, called a "token", of a real-world asset like stocks on a distributed ledger or blockchain.
- CD is a negotiable money market instrument and issued in dematerialised form or as a Promissory Note against funds deposited at a bank or other eligible financial institution.
- Its maturity period is up to one year (min- 7 days).
RBI has exempted SWAMIH (Special Window for Affordable and Mid-Income Housing) Fund, a government-backed fund from its tightened rules of Alternate investment fund (AIF).
- The RBI prescribes the regulatory guidelines in respect of investment by the regulated.
- entities in AIF.
About SWAMIH, 2019
- It is a Category II AIF.
- AIF means any fund established or incorporated in India which is a privately pooled investment vehicle which collects funds from sophisticated investors, whether Indian or foreign, for investments.
- SEBI regulates AIF. E.g., Venture capital funds (Including Angel Funds)
- Objective: Provide priority debt financing for completion of stalled housing projects.
- Fund Manager: SBI Ventures Limited.
Geoffrey Hinton who was awarded the 2024 Nobel Prize, warned that AI could trigger a modern Engels’ pause.
About Engels’ Pause
- It is a term coined by Oxford economist Robert Allen, based on Friedrich Engels’ observations of 19th-century Britain.
- It refers to the paradox during early Industrial Revolution in Britain (c. 1780–1840) when industrial output rose sharply but real wages of workers remained stagnant.
- There are concerns that AI driven Economy could replicate Engels’ pause, where economic growth exists but the gains are unequally distributed, leaving many behind.
Aspect | Historical (Industrial Revolution) | Modern (AI-driven Economy) |
Driver of Change | Mechanization and steam power | Artificial Intelligence, automation, machine learning |
Timeframe | 1780–1840 | 2020s–2030s (projected) |
Productivity Trend | Sharp industrial growth | Rising output through AI automation |
Wage Response | Real wages stagnant | Wages of low/mid-skill workers stagnate or decline |
Distribution of Gains | Capital and inventors enriched | Tech firms, investors, and high-skilled AI workers benefit |
Social Outcome | Urban inequality, worker unrest | Skill polarization, job displacement, inequality across sectors and countries |
Article Sources
1 sourceRBI would continue to use the overnight weighted average call rate (WACR) as the operating target for monetary policy.
About WACR
- It is the average interest rate at which banks lend and borrow money from each other overnight, just for one day.
- Significance:
- It reflects the short-term cost of money in the banking system.
- It helps the RBI monitor how easy or difficult it is for banks to get funds.
- If WACR goes up, it means money is becoming costlier; if it goes down, it means money is easier to get.
IMF projected India’s GDP growth rate for 2025-26 to 6.6% (6.4% earlier) and 6.2% for 2026-27 in its WEO.
- Global growth is projected to slow from 3.3% in 2024 to 3.2% in 2025 and 3.1% in 2026.
About World Economic Outlook
- Published by: International Monetary Fund (IMF)
- Purpose: It presents analyses and projections of the world economy in the near and medium term.
- It is usually published twice a year with updates in between.
Article Sources
1 sourceInternational Monetary Fund (IMF) recently released the Global Finance Stability Report (GFSR), April 2025.
About GFSR
- Purpose: Provide a regular assessment of global financial markets and identify potential systemic weaknesses before they lead to crises.
- Key Findings
- Tightened Global Financial Conditions: Have caused significant increase in the Global financial stability risks.
- Role of Major geopolitical risk events: Especially military conflicts, can lead to substantial decline in stock prices and increases in sovereign risk premiums.
- Other Key Reports by IMF: World Economic Outlook, Fiscal Monitor.






