The assessment classified the Tiger as ‘Critically Depleted,’ reflecting the severe historical and ongoing threats.
- Threats include habitat loss, prey depletion, poaching, and regional extinctions.
Key Findings
- Population Trend: Decreasing (Current estimate (mature individual)- 2608-3905)
- Tigers are now extinct in 9 of the 24 areas evaluated and are threatened in all spatial units where they still persist.
- Status of Conservation Legacy and Recovery Potential: High and Medium, respectively.
About IUCN Green Status of Species
- Launched in 2012, it builds upon the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.
- In 2020, it became an optional part of Red List assessments.
- Provides a tool for assessing the recovery of species’ populations and conservation impact alongside extinction risk.
- Categories: It includes Largely Depleted, Moderately Depleted, Slightly Depleted, Fully Recovered, etc.
How Green Status defines Species Recovery?
- A species is fully recovered if :
- It is present in all parts of its historical range (including areas lost due to human impact).
- It is viable (not at risk of extinction) across its range.
- It performs its ecological functions in all parts of its range.
- These factors together give a "Green Score" (0–100%), indicating how close a species is to full recovery.
 About Tiger (Panthera tigris)
|
SAIEE is India’s first DNA-based count of elephants conducted by the Wildlife Institute of India, under the aegis of Project Elephant, Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change.
Key Findings of the report
- It estimates total Asian Elephant population at 22,446 and India harbours the largest wild population – approximately 60% of global total.
- Currently, wild elephants persist mainly in four forested hill regions— Himalayan foothills, Northeastern states, East-central India, and Western/Eastern Ghats—with a small feral population in Andaman Islands.
- Western Ghats hosts the largest population of wild elephants followed by North Eastern Hills and Brahmaputra Flood Plains.
- Among states, Karnataka supports highest population, followed by Assam, Tamil Nadu and Kerala.
- Threats:
- Habitat Shrinkage & Fragmentation: Once-contiguous elephant population in the Western Ghats is rapidly disconnecting due to changing land use, including expanding commercial plantations (coffee and tea), invasive plants, farmland fencing, human encroachment and mushrooming developmental projects.
- Human–Elephant Conflict (HEC): Rising sharply in Central India and Eastern Ghats.
- Linear Infrastructure: Roads, railways, and power lines disrupt corridors and cause fatalities via electrocution and collisions.
- Recommendations: Strengthening corridors and connectivity, restoration of habitat, improving protection strategies and mitigation of developmental projects.
Asian Elephants
|
International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) for the first time evaluated Indian Wolf separately as potential distinct species within the Canis genus.
- The genus currently has seven species recognized by the IUCN. With the inclusion of the Indian wolf, this will be the eighth recognized species of the genus.
About Indian Wolf
- Habitat: Thorn forests, scrublands, arid and semi-arid grassland habitats in India (few found in Pakistan).
- It is one of the common large carnivores found in the agro-pastoral regions of semi-arid India.
- Threats: habitat loss, conflict with humans, and diseases.
- Conservation Status: Vulnerable (IUCN).
Draft policy paper has been prepared by Ministry of Fisheries, Animal Husbandry and Dairying in consultation with the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO).
Key Highlights of Draft Policy Paper
- India’s camel population has declined by more than 75% since the 1970s.
- Drivers of Population Decline: Decline in traditional economic utility, loss of grazing lands, environmental stress (desertification, invasive species, prolonged droughts etc.), restrictive legal framework, underdeveloped markets for camel products etc.
- Strategic Recommendations: Launching National Camel Sustainability Initiative (NCSI), securing grazing rights, strengthening camel dairy value chains, reviving camel-based tourism, and introducing veterinary and genetic conservation programs.

About Camels
- Once revered as “Ship of the Desert”, camels are exceptionally suited to dryland ecosystems and are primarily reared (90%) in Rajasthan and Gujarat.
- Pastoralist communities associated with camel rearing include Raika, Rabari, Fakirani Jat, and Manganiyar communities.
- Characteristics: Survive days without drinking water, travel long distances, feed on thorny desert plant species.
- Camels' humps store fats providing them energy when food is scarce and they store water in their blood cells, not their humps.
- Role of Camels:
- Ecological Role: Their low water needs, selective grazing habits, and soft-padded hooves help maintain vegetative diversity and prevent desertification.
- Camel dung enriches soil in arid regions.
- Ecological Role: Their low water needs, selective grazing habits, and soft-padded hooves help maintain vegetative diversity and prevent desertification.
International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) has adopted a motion recognising India’s first Dugong Conservation Reserve in Palk Bay at IUCN World Conservation Congress 2025.
- To promote dugongs (Dugong dugon) conservation, IUCN encouraged extending the Indian model to other parts of the Indian Ocean and similar habitats worldwide.

Dugong Conservation Reserve
- Established in 2022, by the Tamil Nadu government under the Wildlife Protection Act, 1972.
- Covers 448.34 sq. km. in northern Palk Bay.
- The region is home to over 12,250 hectares of seagrass meadows.
- Seagrasses also support a host of other marine species, making the reserve ecologically significant.
- Seagrass plays a vital role in carbon sequestration.
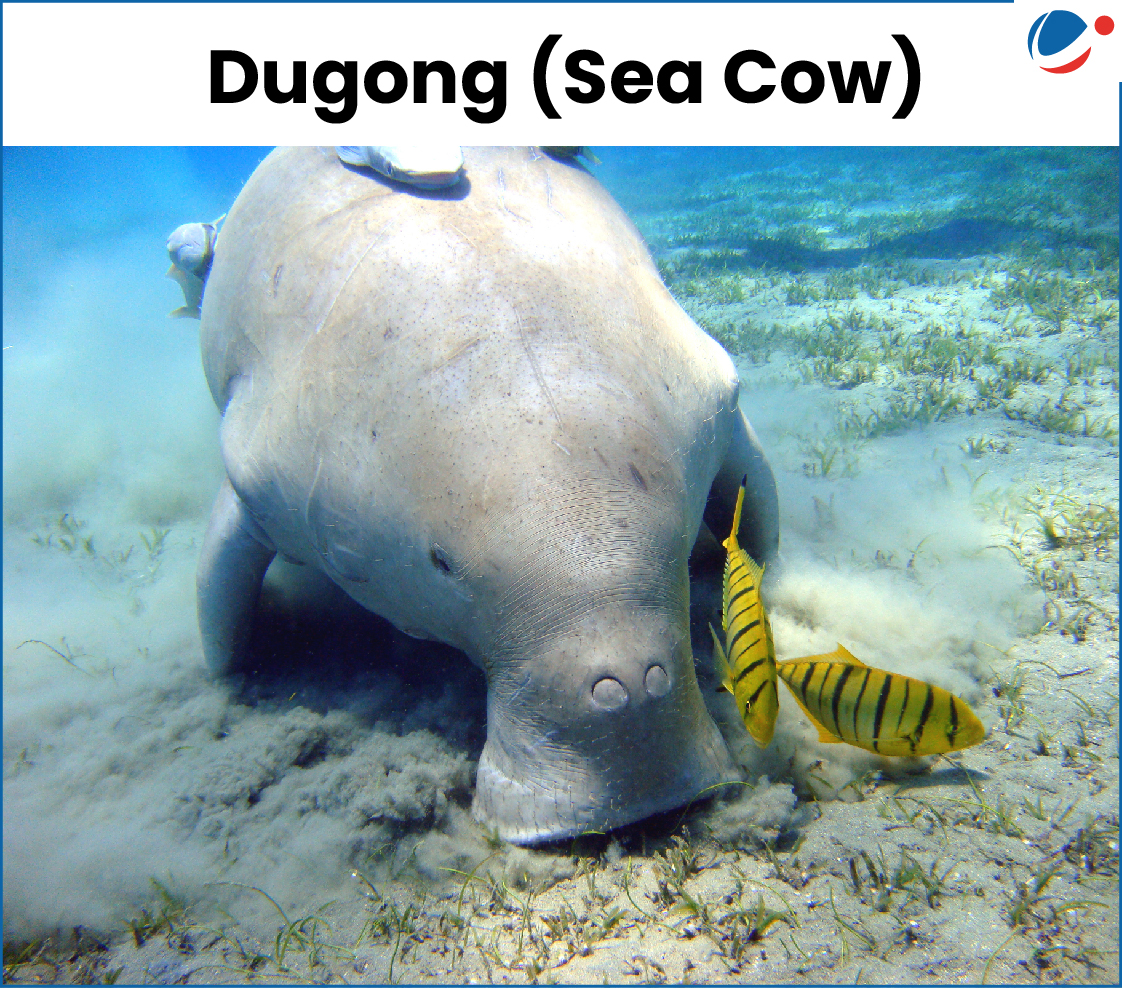
About Dugong (Sea Cow)
- Key Feature: Only marine herbivorous mammals that depend on seagrass.
- Distribution: In India, apart from Palk Bay (highest), it is also found in Gulf of Mannar, Gulf of Kutch, etc.
- Population: Expected about 200.
- Threat: Habitat degradation, hunting and unintentional captures.
- Status:
- IUCN Red list status: Vulnerable
- Listed in Schedule I of the Wild Life (Protection) Act, 1972.
Central Asian countries have come together under CAMI to protect 17 shared species like Saiga, Bukhara Deer etc.
Central Asian Mammals Initiative (CAMI)
- It was launched in 2014 at the 11th Meeting of the Conference of the Parties (COP11) to the Convention on the Conservation of Migratory Species of Wild Animals (CMS).
- Objective: To coordinate conservation efforts for 17 key migratory mammal species in Central Asia.
Early Warnings for All (EW4All) initiative
- Aim: Ensure universal protection from hazardous hydrometeorological, climatological and related environmental events through life-saving multi-hazard early warning systems by 2027.
- Launched: At COP27 of UNFCCC in 2022 by the UN Secretary-General.
- Organizations: It is jointly led by WMO, UNDRR, ITU and IFRC.
- Coverage: Initially focused on 30 high-risk countries, EW4All has since expanded to more than 100 participating nations.

About Early Warning System (EWS)
- EWS is an integrated system of hazard monitoring, forecasting, disaster risk assessment, communication and preparedness which aims at enabling early action to save and protect lives, livelihoods and assets of people at risk.
- Need for Early Warning:
- The damage caused by a disaster can be reduced by 30% if an early warning is issued within 24 hours.
- Disaster mortality is six times higher and the number of people affected is four times higher in countries with limited multi-hazard early warning systems.
- Economic damages from extreme weather events continue to surge, with over US$4 trillion in losses globally since 1970.
Article Sources
1 sourcethe monsoon recover from the disruptions caused by the previous El Niño.
About Arabian Sea Mini Warm Pool (MWP)
- The Arabian Sea MWP is a small patch of unusually warm sea surface temperatures (SST) in the Arabian Sea, especially the southeastern part (near the Kerala coast).
- A warm pool is defined as a body of very warm water, typically with sea surface temperatures exceeding 28.5°C, that plays a significant role in influencing regional climate and weather patterns.
- Duration: Forms every year during April and May, just before the onset of the Indian Summer Monsoon.
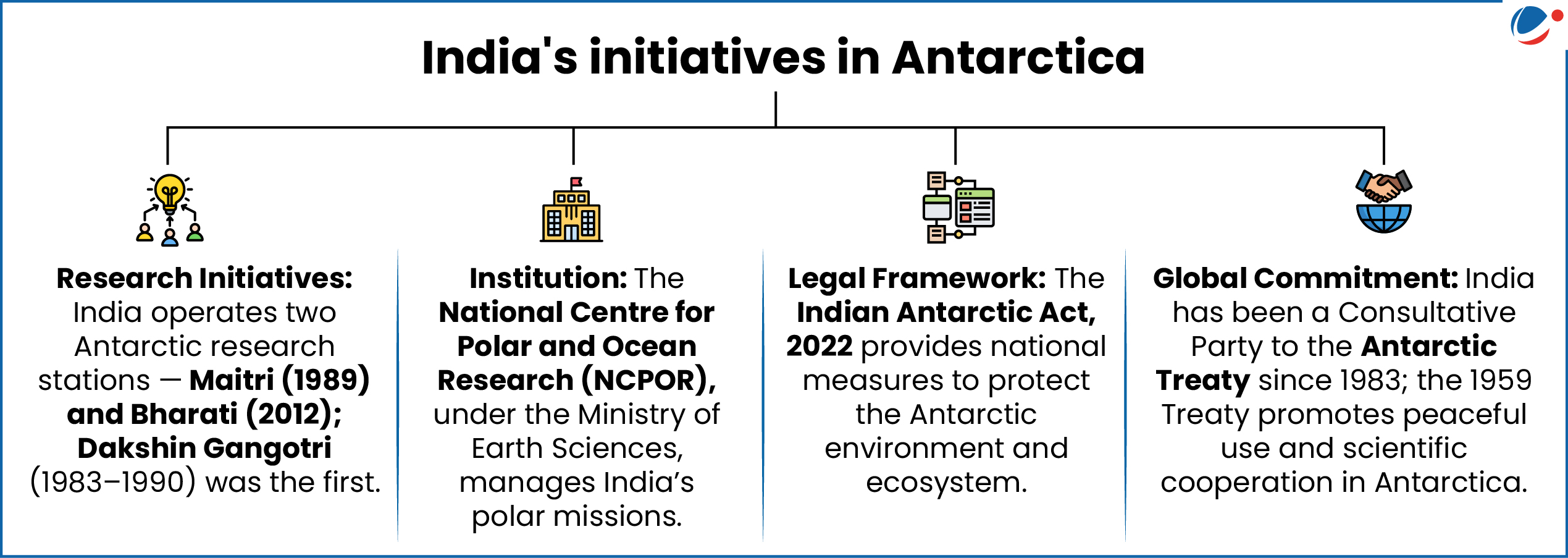
Union Finance Ministry granted approval to Maitri II, new research station in Eastern Antarctica.
- This will be India’s 4th research base expected to be operational by January 2029.
- It would be established as a green research base powered using renewable energy sources (solar and wind) and would house automated instruments.
Importance of the Antarctica Region
- World’s Natural Laboratory: It is the 5th largest continent, holds key to understanding Earth’s climate and ocean systems, acting as a natural tracker of global climate change.
- Natural Resources: Holds nearly 75 percent of the earth’s freshwater reserves and houses abundance of edible algae, more than 200 species of fish including the discovery of iron and copper.
- Geopolitical Significance: Overlapping territorial claims, China’s expansion with dual-use critical infrastructures raises global concerns.
India’s only Mud Volcano in Baratang Island in Andamans and Nicobar Islands erupts after 20 years.
About Mud Volcano
- It is a geological formation where a mixture of mud, water, and gases (mainly methane, sometimes carbon dioxide or nitrogen) erupts to the surface, creating cone-like structures that resemble true volcanoes without molten lava.
- Mud volcanoes are generally encountered in areas where natural gas is present.
- Eruptions are caused by the pressure from Earth’s tectonic forces or by accumulation of hydrocarbon gases.
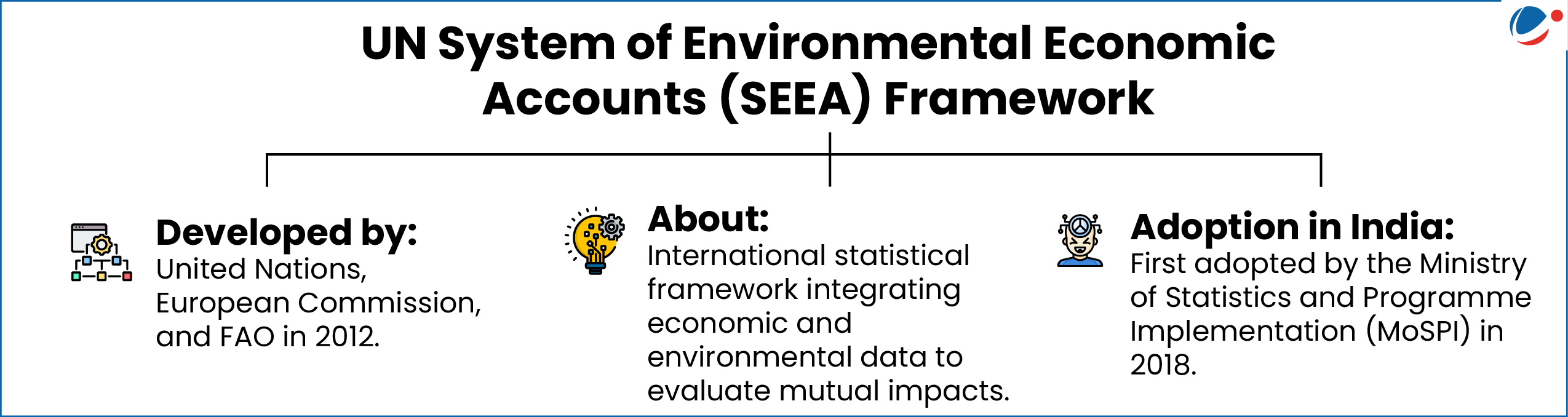
Released by the Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (MoSPI), it is the 8th consecutive issue related to environment accounts.
- It is also the first dedicated publication on forest accounting, based upon the UN System of Environmental Economic Accounts (SEEA) Framework.
Key Findings of the Report
- Physical Asset Account:
- Forest Cover (2010-11 to 2021-22): Increased by 17,444.61 sq. km (22.50%), reaching 7.15 lakh sq. km (21.76% of India’s geographical area).
- Top States in gains: Kerala, Karnataka, Tamil Nadu.
- Extent Account:
- Forest Extent (2013–2023): Net increase of 3,356 sq. km in forest extent due to reclassification and boundary adjustments.
- Top States: Uttarakhand, Odisha, Jharkhand in Recorded Forest Area (RFA).
- Condition Account: Assesses ecosystem quality, focusing on growing stock (volume of usable wood in living trees).
- Growing Stock (2013-23): rose by 305.53 million cum (7.32%).
- Top Contributors: Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Telangana.
- Service Accounts:
- Provisioning Services (timber and non-timber products): Value increased to ~0.16% of GDP in 2021-22.
- Top States: Maharashtra, Gujarat, Kerala.
- Regulating Services (carbon retention): Value rose to ~2.63% of GDP in 2021-22.
- Top States: Arunachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand, Assam.
- Provisioning Services (timber and non-timber products): Value increased to ~0.16% of GDP in 2021-22.
Article Sources
1 sourceFirst legally binding GEI Target Rules, 2025 target four high-emission sectors i.e. aluminium, cement, pulp & paper, and chlor-alkali.
- Each facility must reduce the amount of greenhouse gases emitted per unit of output compared to a 2023-24 baseline.
- GEI is the amount of GHGs that are emitted per unit of product output. For instance, the gases released in the production of a tonne of product, such as cement or aluminium.
What are the rules?
- Issued under: compliance mechanism of Carbon Credit Trading Scheme (CCTS), 2023.
- Compliance Enforced by: Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB).
- Objective: To reduce greenhouse gas emissions per unit of output (tCO2e per tonne of product) in carbon-intensive sectors and facilitate carbon credit trading.

Mechanism:
- Compliant entities reducing emissions below target earn tradable carbon credit certificates.
- The Bureau of Energy Efficiency (BEE) will issue the carbon credits certificate.
- Non-compliant entities must buy additional certificates or pay an environmental compensation, which equals twice the average carbon credit price for that compliance year.
Significance
- Market-based compliance: Earned carbon credits can be traded on the domestic carbon market.
- Rules will help operationalize the country’s domestic carbon market under the Carbon Credit Trading Scheme (CCTS), 2023.
- Transparency: Registration and documentation under Indian Carbon Market portal.
- Revenue for sustainability: Environmental compensation funds support carbon market infrastructure.
- Supports India’s climate goals: Supports commitments under the Paris Agreement.
In its report, Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) found that Delhi-National Capital Region (NCR) is the worst impacted in the country by high Ozone (O3) pollution, followed by Mumbai Metropolitan Region (MMR).
About Ozone
- Ozone (O3) is a variant of oxygen composed of three oxygen atoms. It occurs in two layers of the atmosphere: the stratosphere (upper layer) and the troposphere (ground level up to 10km).
- In the stratosphere, ozone protects life on Earth from the sun’s ultraviolet radiation.
- In the troposphere, it is an air pollutant.
- The safe eight-hourly ozone standard is set at 100 micrograms per cubic metre (µg/m³), while the one-hour limit is 180µg/m³.
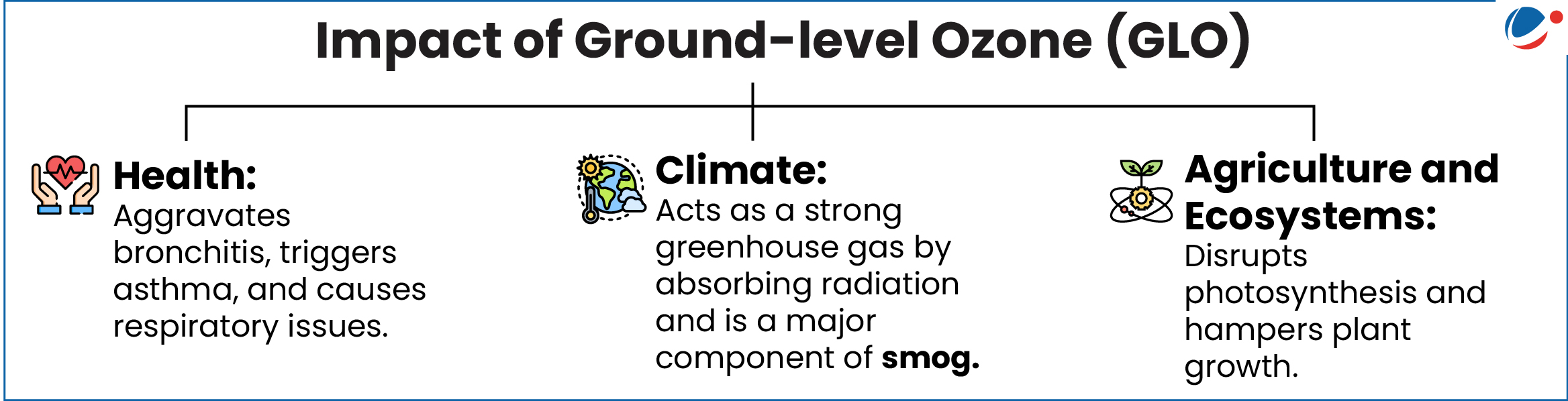
Ground-level Ozone (GLO)
- GLO is a secondary, short-lived pollutant that remains in the atmosphere for only hours to weeks.
- Factor Responsible: Created by chemical reactions between oxides of nitrogen (Nox) and volatile organic compounds (VOC).
- Anthropogenic sources: Transportation, power plants, residential, agricultural activities, etc.
- Natural sources: Soil-based emissions of Nox, and wildfire-induced CO and biospheric methane emissions.
The Indian Coast Guard (ICG) conducted the 10th edition of the National Level Pollution Response Exercise (NATPOLREX-X).
- NATPOLREX is a biennial flagship exercise which aims to evaluate and enhance India’s national preparedness to respond to marine oil spill incidents.
Article Sources
1 source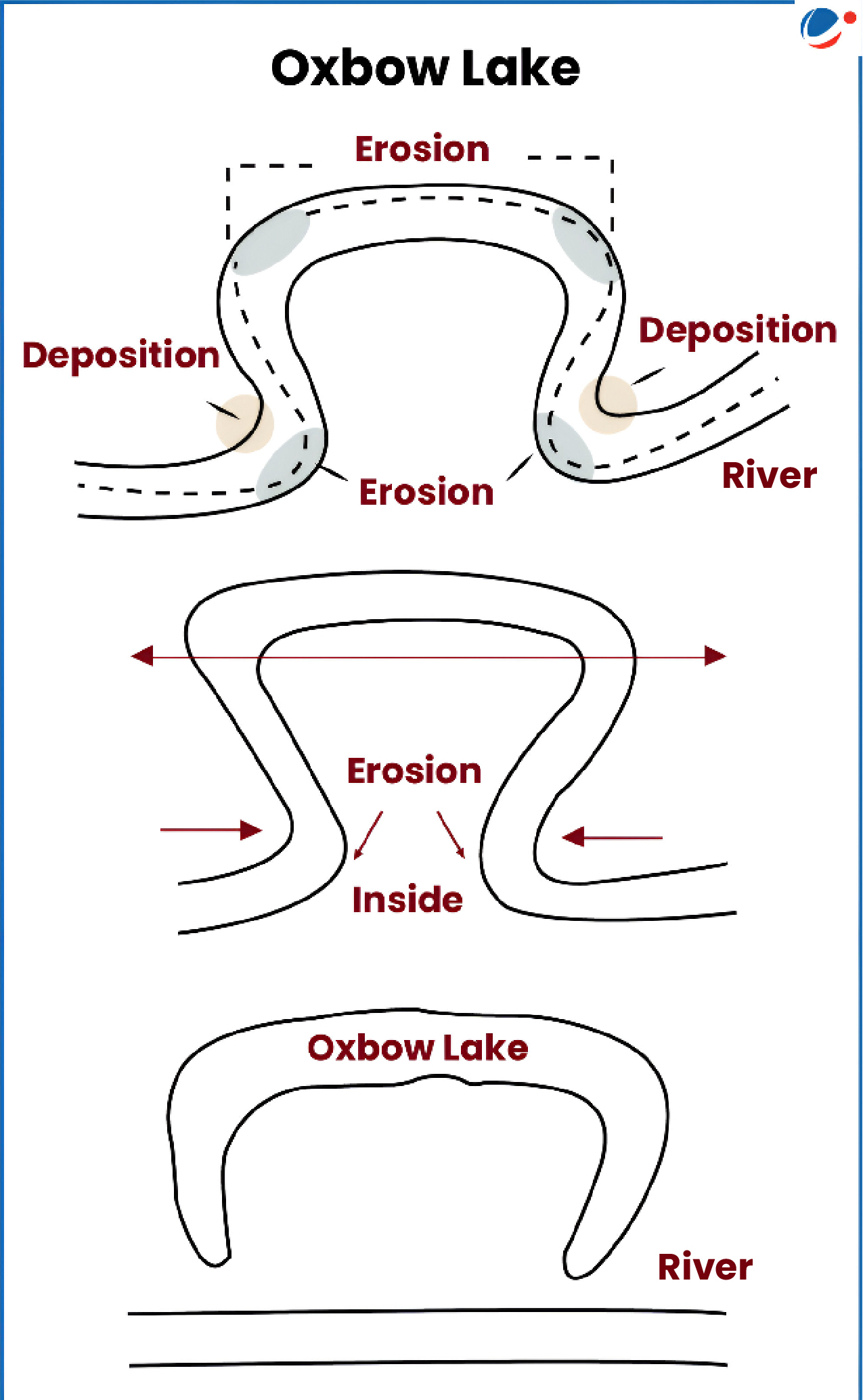
Gokul Reservoir and Udaipur Lake in Bihar have been designated as new Ramsar Sites.
- With these additions, India now has 93 Ramsar sites. They cover total area of 1,360,719 hectares.
- Bihar already had three Ramsar sites – Kabar Jheel (Kabar Taal) in Begusarai and Nagi and Nakti bird sanctuaries in Jamui district.
About New Wetlands
- Both Wetlands are oxbow lakes.
- An oxbow is a crescent-shaped lake lying alongside a winding river.
- Gokul Reservoir (Buxar district) is located on the southern edge of the Ganga River.
- Udaipur Lake in West Champaran district is surrounded by the Udaipur Wildlife Sanctuary.
- It is an important wintering ground for many migratory bird species, including pochard (Aythya ferina).
About Ramsar Convention (Convention on Wetlands)
- Adopted in 1971.
- An intergovernmental treaty under UNESCO.
- Objective: Provides the framework for the conservation and wise use of wetlands and their resources.
- Criteria: A wetland must meet at least 1 of 9 criteria such as regularly supporting 20,000 or more water birds, or conserving biological diversity etc.
- India ratified the Convention in 1982.
Article Sources
1 sourceIt includes 5 initiatives launched for Species Conservation and Conflict Management:-
Initiatives | Details |
Project Dolphin (Phase-II): Implementation of the Action Plan to strengthen conservation measures for both riverine and marine cetaceans across India. |
|
Project Sloth Bear: Launch of the national implementation framework for the conservation of the Sloth Bear. |
|
Project Gharial: Launch of the implementation action plan for the conservation of Gharials. |
|
Tigers Outside Tiger Reserve: A project to address conflicts involving tigers outside protected areas, employing a landscape approach, technological interventions, capacity building, and community support. |
|
Centre of Excellence for Human–Wildlife Conflict Management (CoE-HWC) |
|
GFRA, released every five years by FAO, was published during Global Forest Observations Initiative (GFOI) Plenary in Bali, Indonesia.
- GFOI is a flagship programme of the Group on Earth Observations (GEO), which is a network of governments, academia, organizations, civil society and private sector aiming to harness the power of Earth Intelligence.
- India is a member of GEO.
Key highlights of GFRA 2025
- Forest extent: Forests cover 4.14 billion hectares, or 32% of the global land area.
- Nearly half of the world’s forests are located in the tropics, followed by boreal, temperate and subtropical domains.
- Europe has the largest forest area, accounting for 25% of world’s total.
- India’s Forest Extent: India moved up one rank to 9th position in terms of total forest area globally, accounting for 2% of global forest area.
- India ranks 5th in terms of rubber plantation.
- Deforestation and expansion: Deforestation slowed to 10.9 million hectares per year in 2015–2025, down from 17.6 million in 1990–2000.
- Natural Regeneration: More than 90% of world’s forests are regenerating naturally.
- Carbon Stock: Forest carbon stocks have increased, reaching 714 gigatonnes, with soil holding majority forest carbon stock, followed by living biomass, and litter and deadwood.
- Disturbances: Fire is prevalent forest disturbance in subtropics while insects, diseases and severe weather affect mainly the temperate and boreal domains.
Article Sources
1 sourceThe UN Environment Programme released the first State of Finance for Forests 2025 report, providing a global overview of public and private forest finance in 2023.
Major Findings
- Report finds an annual forest finance gap of US$ 216 billion between current financial flows and the investment required to achieve global forest goals by 2030.
- Governments were the primary source of forest funding, accounting for 91% of total flows in 2023.
Article Sources
1 sourceInternational Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) World Conservation Congress 2025 concluded in Abu Dhabi, UAE.
Held once every four years, the IUCN World Conservation Congress hosts the Members’ Assembly, which is the IUCN’s highest decision making body.
Key Resolutions at Member’s Assembly
- Abu Dhabi Call to Action: Accelerate action across five key areas – reaffirming nature as foundation of well-being, strengthening multilateralism, ensuring justice and inclusion, advancing knowledge and innovation, and scaling up resources for nature and climate action.
- New Members: Over 100 new members including six states – Armenia, Tajikistan, Marshall Islands, Gabon, Tuvalu, and Zimbabwe.
- First-ever Policy on Synthetic Biology and Nature Conservation: Synthetic biology may carry both substantial benefits (e.g. to restore lost genetic diversity or to locally eradicate invasive alien species) and significant risks (e.g. unintended ecological cascades), necessitating balanced policy.
- Crime of Ecocide: Recognizes ecocide (deliberate environmental harm) as international crime under the International Criminal Court.

Released by IUCN World Conservation Congress latest update modified the conservation status of 12 Indian bird species, downlisting eight species, signaling positive trends in their conservation while uplisting four species.
- Four species that have been uplisted include:
- Indian Courser, Indian Roller and Rufous-tailed Lark uplisted to Near Threatened;
- Long-billed Grasshopper-warbler uplisted to Endangered.
- All these four species depend upon open natural ecosystems, which include habitats like grasslands, semi-arid landscapes, desert, croplands, hilly scrublands, and fallow lands.
- Threats to these ecosystems: Expansion of power infrastructure, intensification of agriculture, introduction of invasive species, and conversion of grasslands into woodlands through afforestation.
Update to IUCN Red List
- More than half of bird species globally are in decline primarily due to habitat loss and degradation, driven by agricultural expansion and intensification and logging.
- Birds play vital roles in ecosystems and for people, serving as pollinators, seed dispersers, pest controllers, scavengers and ecosystem engineers.
- Three species of Arctic seal have moved closer to extinction with primary threat being sea ice loss driven by global warming.
- Seals, a keystone species, play a central role in food web, consuming fish and invertebrates and recycling nutrients.
- Green Sea Turtle, a keystone species,has improved in status from Endangered to Least Concern, due to sustained conservation efforts.







