Why in the News?
Recently, USA and Egypt co-hosted the Gaza Peace Summit in Sharm El-Sheikh, Egypt to advance peace in Gaza and overall stability in the Middle East.
More on the News
- During the summit, four ceasefire mediators—the United States, Egypt, Qatar, and Turkey signed a declaration to inaugurate the USA's 20-point peace plan or the Trump Declaration for Enduring Peace and Prosperity.
- Peace plan declares that future disputes will be resolved via diplomatic engagement and negotiation, not through force or protracted conflict.
- Plan calls for Hamas's disarmament and an internationally supervised reconstruction of Gaza.
- Long term, Trump's twenty-point plan stipulates that no Palestinians will be militarily forced to leave Gaza, and that Israel will agree not to occupy or annex the Gaza Strip.
- Importantly, 20-point plan for Gaza does not guarantee a two-state solution or the creation of the state of Palestine.
- India's Minister of State for External Affairs attended the summit and appreciated the efforts towards a lasting peace in the region.
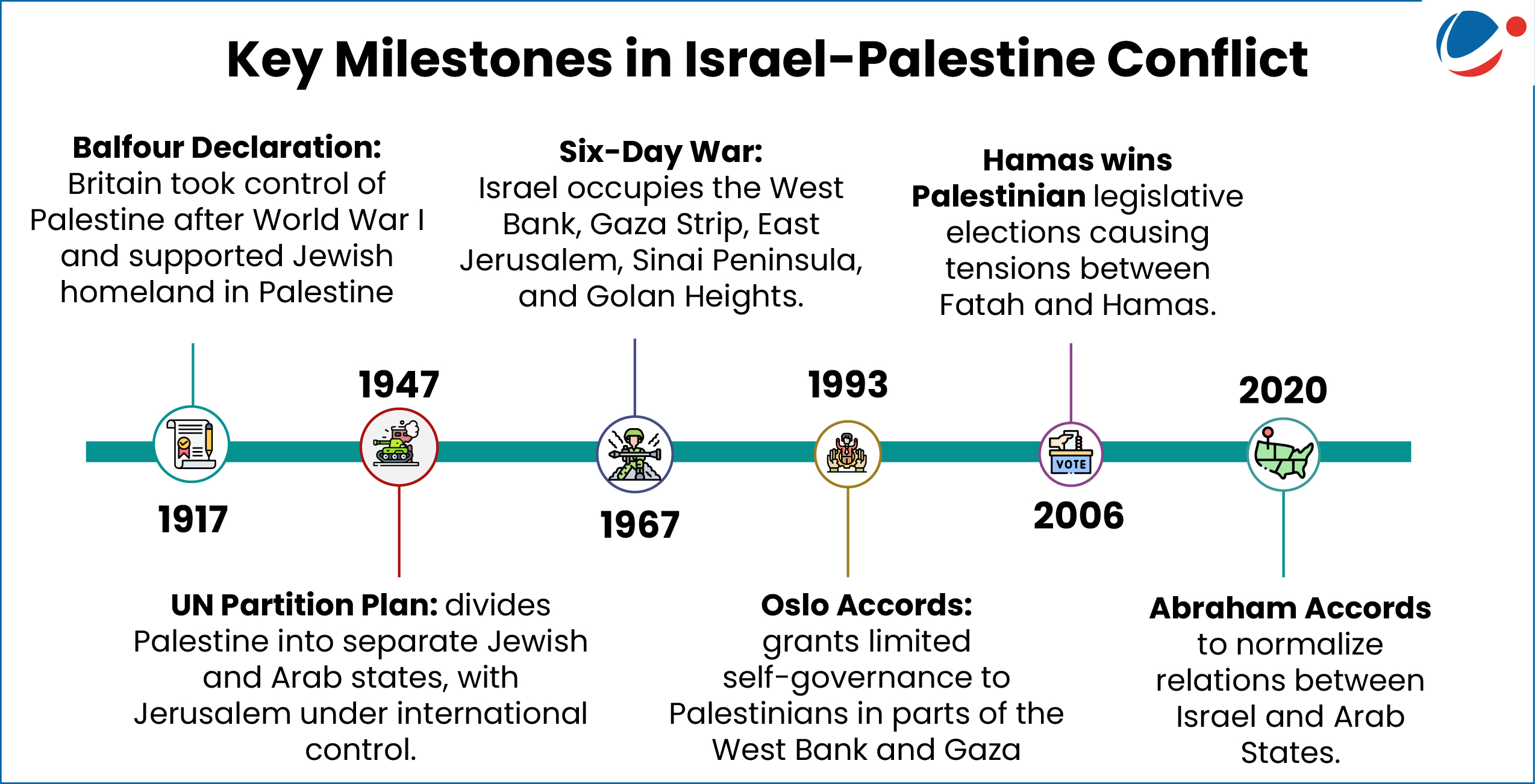
Significance of Peace in the region
- Regional Prosperity: The peace plan could aid in the expansion of Abraham Accords and unlock broader peace and prosperity.
- The Abraham Accords are a feature of U.S. Middle Eastern diplomacy involving peace agreements between Israel and the United Arab Emirates, Bahrain, Morocco, etc.
- Strategic Location: The region, rich in oil and gas resources is strategically located at the juncture of critical global lines of communication involving Red Sea, Strait of Hormuz, and Suez Canal.
- Contemporary Geopolitics: Great power competitions can lead to regional fragmentation in the absence of peace. E.g., Russia is showing security interest while China has economic interests in the region.
- Global Trade: The region houses one of the youngest and fastest-growing populations expected to reach around 580 million people by 2030, serving as a market for goods and services in times of peace.
- Importance for India: Energy and remittances from the Indian workforce in the region are of vital strategic interest for India.
- India imports nearly 70% of its annual oil from the region and is gaining importance through initiatives/groupings like India–Middle East–Europe Economic Corridor, I2U2, etc.
India's Stance on the Palestinian issue | ||
1947-1991 | 1991-2014 | 2014- Present |
|
|
|
Conclusion
India's present foreign policy toward Israel has witnessed strategic recalibration. From historical support for Palestine to increased engagement with Israel, India has gradually shown pragmatic shift in its priorities aligning with its moral commitments, strategic imperatives, and regional geopolitics.
 Key Strategic Locations in the Region
|





