Brazil will be the second member of the BRICS after India not to endorse the BRI.
- Previously countries like Italy and Philippines have announced to withdraw from BRI.
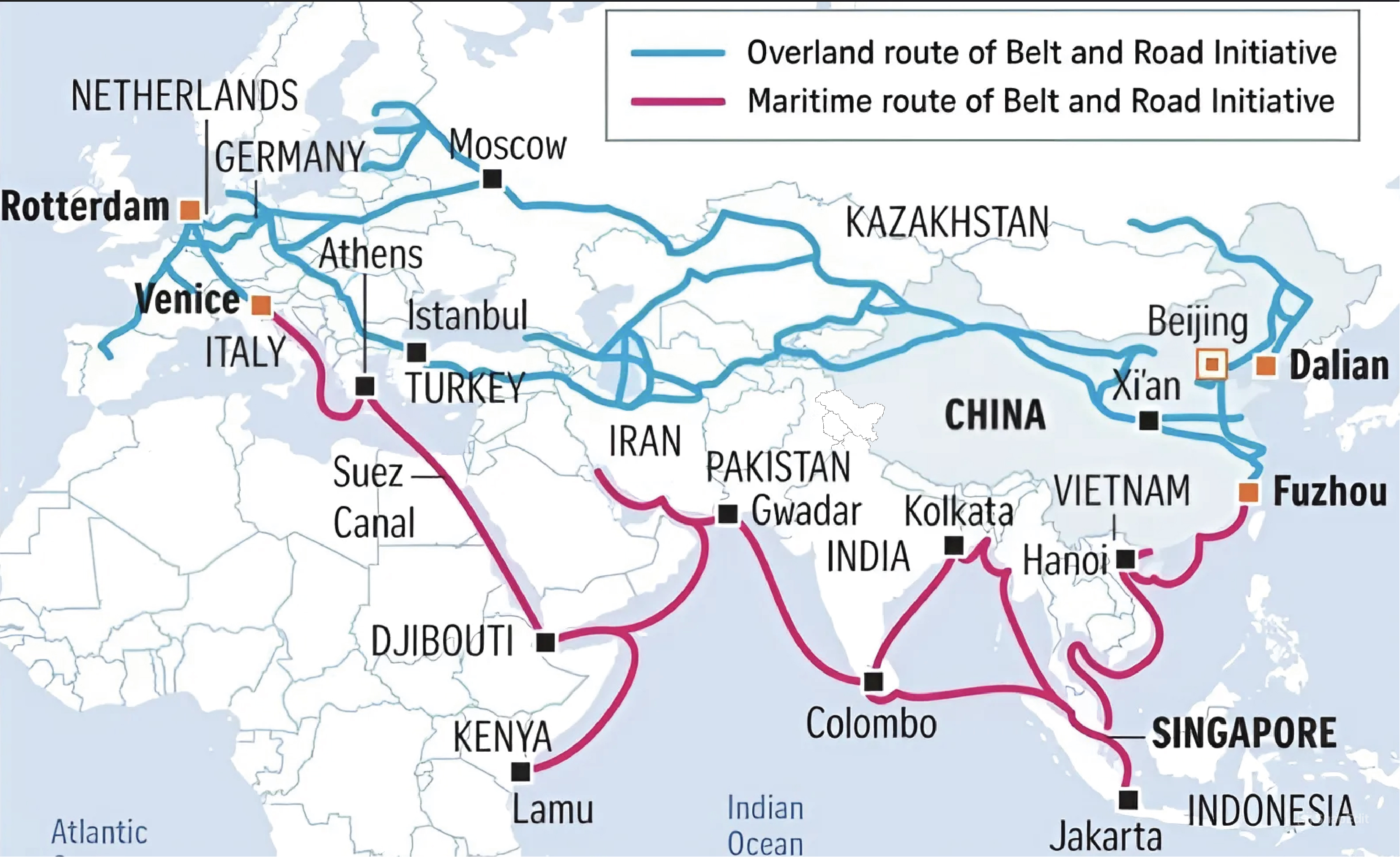
About Belt and Road Initiative (BRI)
- Genesis: Initiated as 'One Belt One Road' in 2013, seeks to connect Asia with Africa and Europe via land and maritime networks.
- Aim: Improving regional integration, increasing trade and stimulating economic growth.
- It comprises:
- Silk Road Economic Belt (A trans-continental passage)
- Maritime Silk Road (A sea route)
- It involves major investments in infrastructure projects such as ports, etc.
Key Concerns of India regarding BRI
- Undermining India's sovereignty and territorial integrity: China's BRI project, the China-Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC) passes through Gilgit Baltistan region of Pakistan-occupied Kashmir
- Competition: BRI’s financial incentives and low-interest loans for infrastructure may undercut Indian influence in South Asia.
- Unsustainable debts by China to partner countries lead to debt trap making them vulnerable to China’s influence.
- Security: China’s growing influence in the Indian Ocean region is perceived by India as a security threat (String of Pearls Policy).
Key Steps taken to counter BRI
|







