According to US Energy Information Administration, India’s LNG imports from U.S rose by more than 71% Y-o-Y during first eleven months of 2024.
About LNG
- It is created by transforming natural gas into a liquid state, by cooling it to -162°C (-260°F).
- Since it is composed primarily of methane (around 90%), LNG is odourless, colourless, non-toxic and non-corrosive.
- India is fourth-largest LNG importer globally.
Why is India’s LNG dependence increasing?
- Diversify Energy basket: Coal reduction efforts drive transition to cleaner LNG fuel.
- Government targets to raise natural gas share in energy mix to 15% by 2030.
- Gas-based Economy: Transitioning towards a gas-based economy to reduce reliance on imported crude oil.
- Climate Change target: LNG produces 40% less CO2 than coal and 30% less than oil, making it cleanest of fossil fuels.
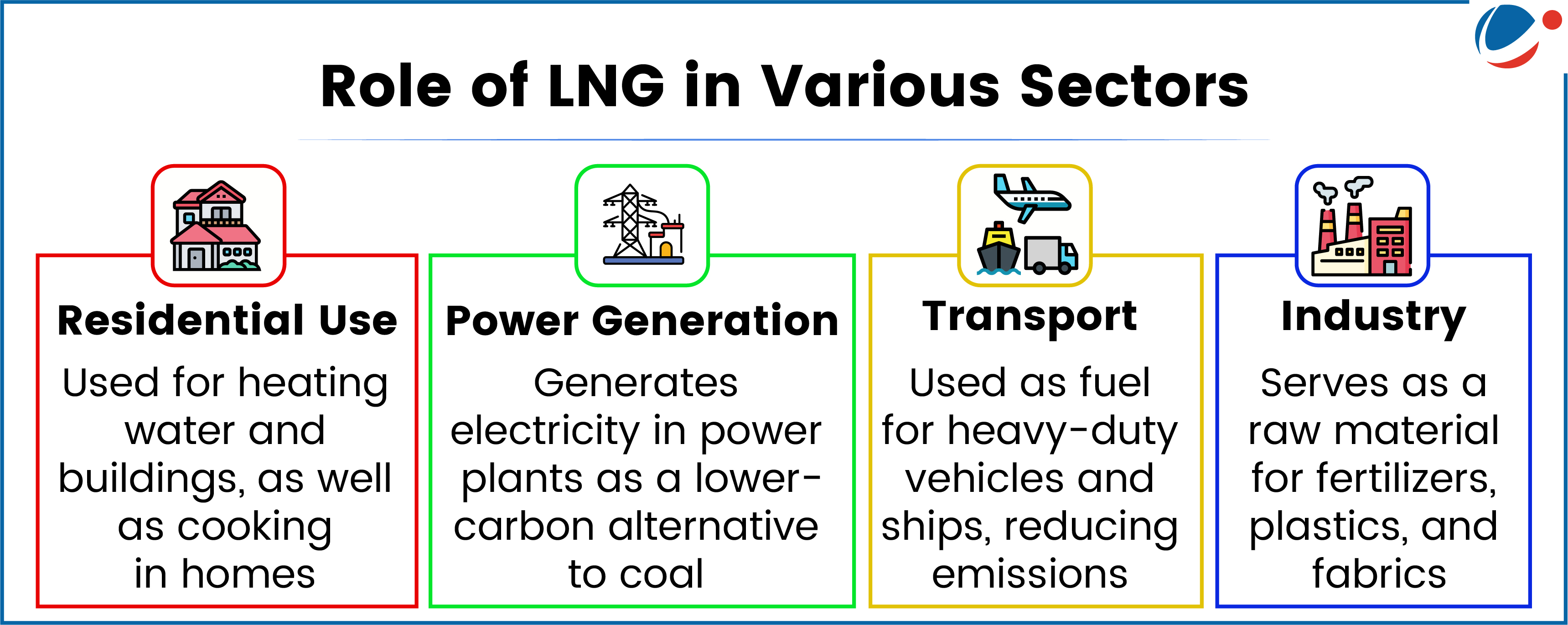
Challenges associated with LNG
- High prices and extreme price volatility: Due to demand-supply imbalances (Russia-Ukraine war) etc.
- Inadequate Pipeline Network: To move LNG from terminals to areas of its application, hindering distribution and availability of LNG throughout nation, especially in isolated regions.
- Limited storage capacity: It makes India vulnerable to price fluctuations in global LNG market.
India’s Initiatives for LNG
|



