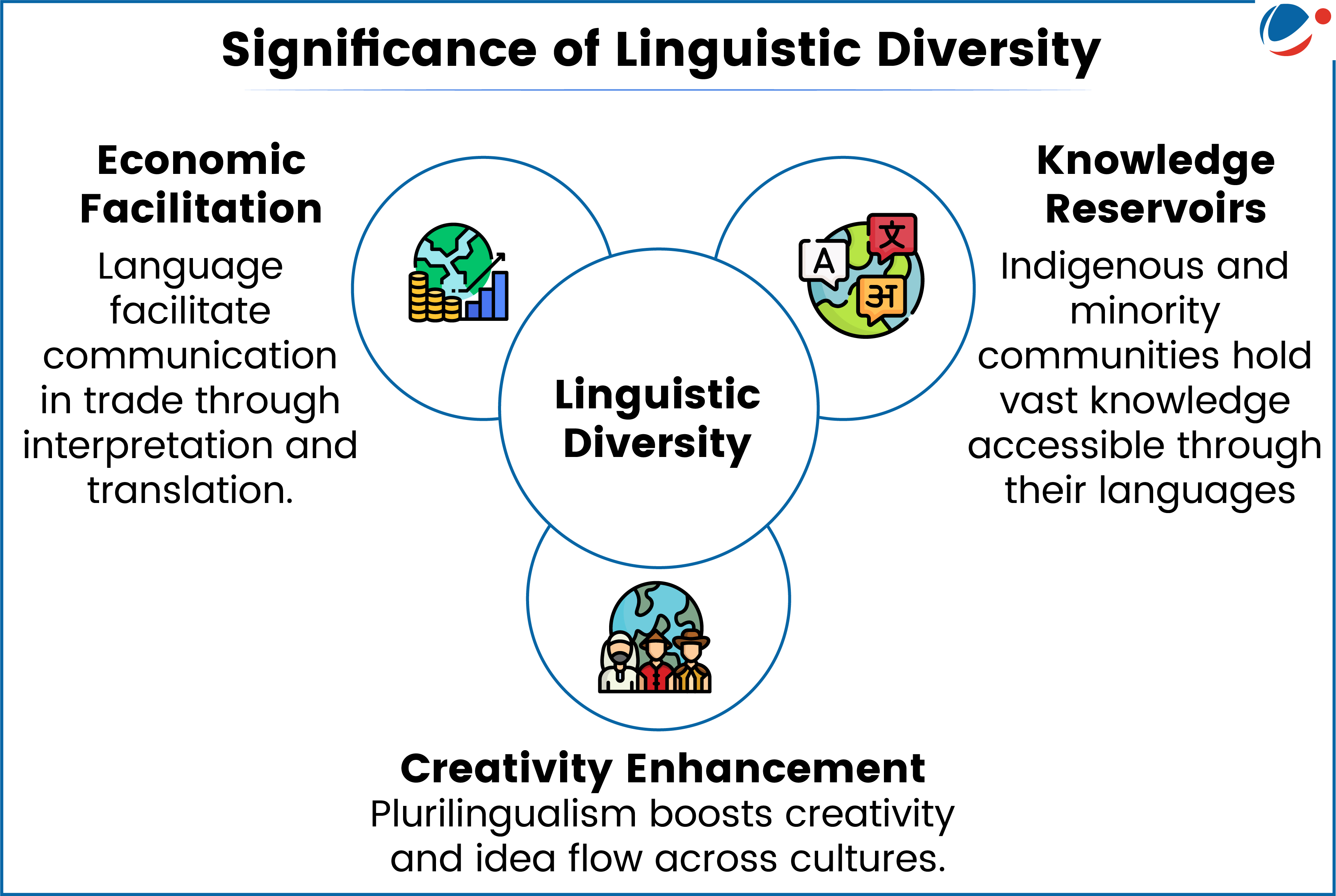
Linguistic Diversity can be understood both as the absolute number of languages and the percentage of the population speaking any single language in a country.
Linguistic Diversity In India
- Status: As per Census 2011, there are more than 99 Non-scheduled languages, 22 Scheduled languages and 121 other languages.
- Peoples Linguistic Survey of India (2010) identified 780 languages, of which 50 are extinct in past five decades.
- Language Families: Indian Languages belong to Indo-Aryan, Dravidian, Austro-Asiatic, Tibeto-Burmese and others.
- Constitutional Provisions promoting Linguistic Diversity in India
- Eighth Schedule: Recognizes 22 scheduled languages.
- Article 29: Safeguards the language, script, and culture of any section of citizens.
- Article 350-B: Provides for a Special Officer for Linguistic Minorities to protect minority language interests.
Some Initiatives taken to enhance Linguistic Diversity in India
- National Education Policy (NEP) 2020: Provides for medium of instruction to be in mother tongue/ local language upto at least class 5.
- Sahitya Akademi: Supports and preserves Indian languages through awards, publications, and research.
- Technology Initiatives: Bhashini, AI-driven translation tools, and regional language support in digital platforms.
- Classical Languages: Designation accorded to a language based on its historical significance, linguistic contribution, etc.
- Committee: Bharatiya Bhasha Samiti, a High Powered Committee for Promotion of Indian Languages constituted in 2021.





