The case concerns the encroachment of 'Singampatti Zamin forests lands,' cleared for plantation cultivation (tea, coffee, rubber).
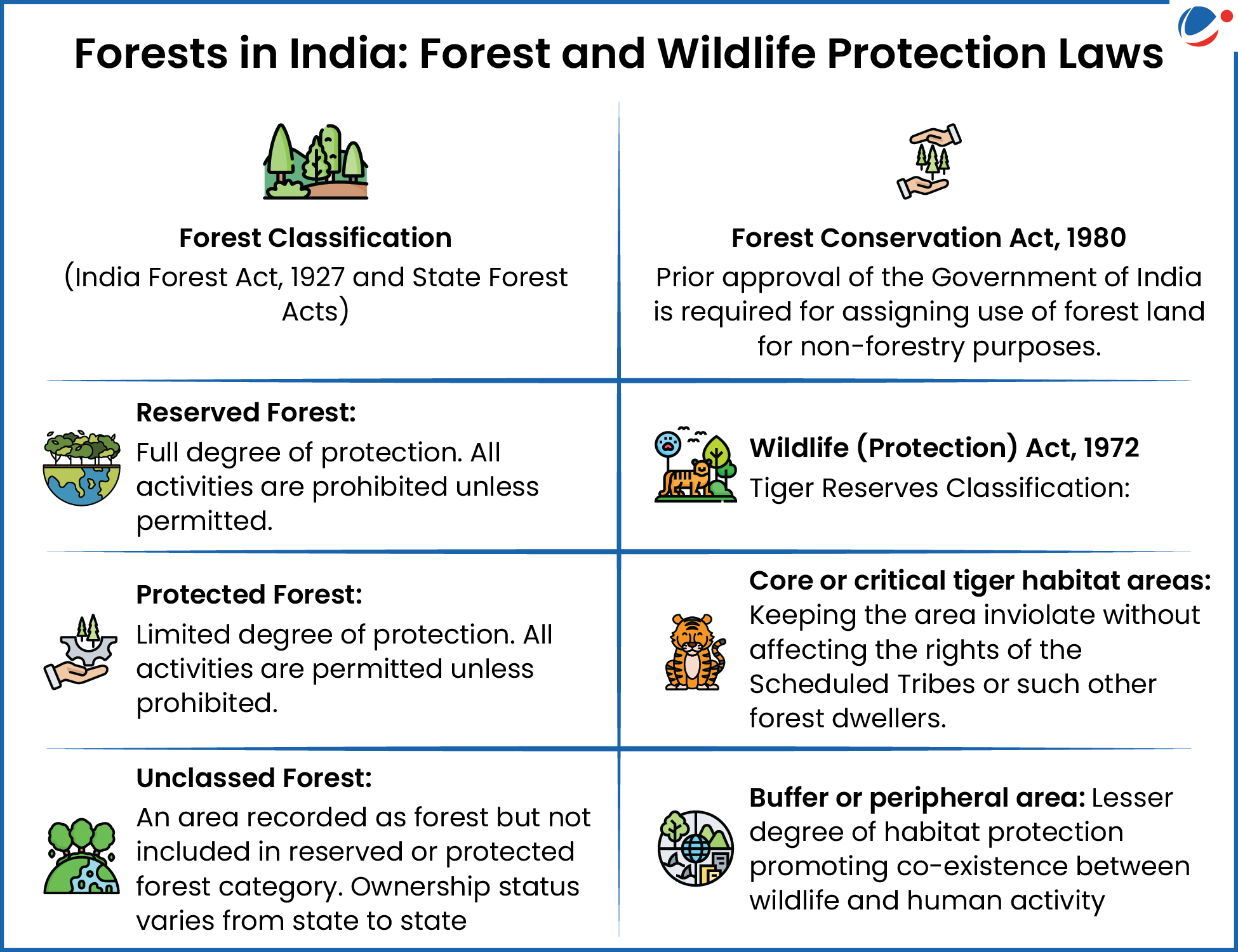
- The land was declared part of Kalakkad-Mundanthurai Reserved Forest (1978), Core Critical Tiger Habitat (2007), Wildlife Sanctuary, and Tiger Reserve (2012) which led to the eviction of tea estate workers.
Key Observations from SC Order in A. John Kennedy v. State of Tamil Nadu & Others
- Forests are the "lungs of the ecosystem: Their depletion directly impacts climate change and biodiversity.
- Around 13,000 sq. km of forest land in India is under encroachment (Environment Ministry)
- A healthy tiger population is vital for ecosystem balance: Court cited T.N. Godavarman case to stress that "the tiger perishes without the forest, and the forest perishes without its tigers."
- The Court endorsed an "ecocentric approach" (over anthropocentric) from State of Telangana v. Mohd. Abdul Qasim (2024).
About Agastyamalai Landscape
- It includes Periyar Tiger Reserve, Srivilliputhur Grizzled Squirrel WLS, Meghamalai and Thirunelveli WLS.
- 14 rivers flow through the landscape including the Thamirabarai river.
- Agasthyamala Biosphere Reserve is included in the World Network of Biosphere Reserve under the Man and Biosphere (MAB) Program of UNESCO.
- Located in the southern Western Ghats in Tamil Nadu and Kerala.
- The reserve includes 3 WLSs, Shendurney, Peppara and Neyyar (Kerala), and the Kalakad Mundanthurai Tiger Reserve (Tamil Nadu).







