According to the UN Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC), extradition means the surrender of any person who is sought by the requesting State for criminal prosecution for an extraditable offence.
- Extraditable offence refers to an offence provided for in extradition treaty with that State or the offence is punishable with at least 1 year of imprisonment either in India or in foreign State (in case of no treaty).
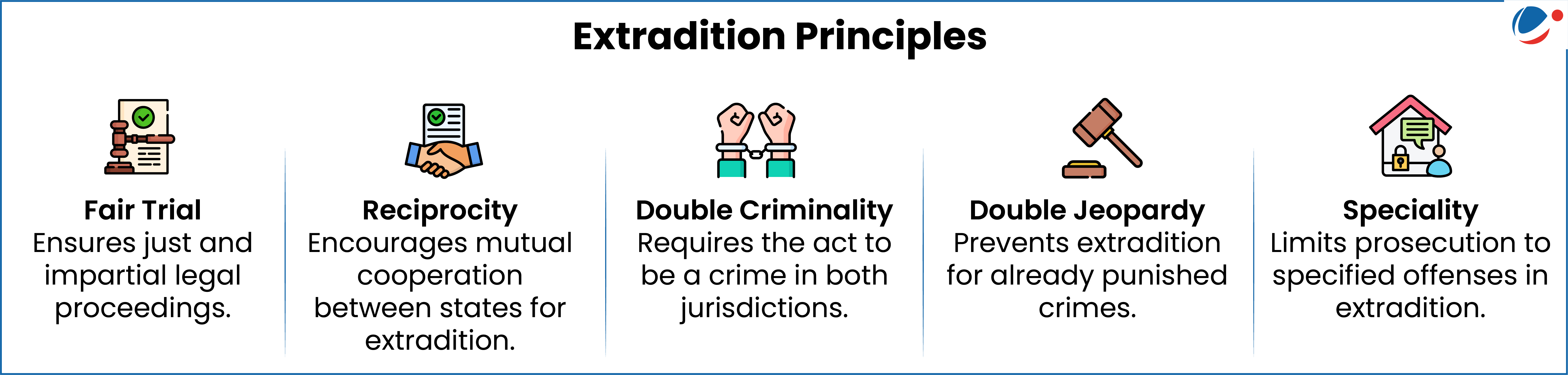
What is the framework for Extradition?
- In India:
- The Extradition Act 1962 (substantially modified in 1993) consolidated the law relating to the extradition of criminal fugitives from India to foreign states.
- The Ministry of External Affairs is the nodal authority for Extradition in India.
- India has extradition treaties with 48 nations, including Bangladesh and the USA.
- The Government of India finally decides on Extradition and this decision can be appealed in a higher court.
- The Extradition Act 1962 (substantially modified in 1993) consolidated the law relating to the extradition of criminal fugitives from India to foreign states.
- Globally: United Nations Model Treaty on Extradition (1990), UN Model Law on Extradition (2004), United Nations Convention against Transnational Organized Crime (2000), etc. are some of the international frameworks which deal with various principles of extradition.
Challenges in Extradition Law
|







