About DS of the Lok Sabha
- Background: The office emerged in 1921 under Government of India Act, 1919.
- Sachidananda Sinha first held this office in the Central Legislative Assembly.
- M. A. Ayyangar, became the first elected DS post-independence.
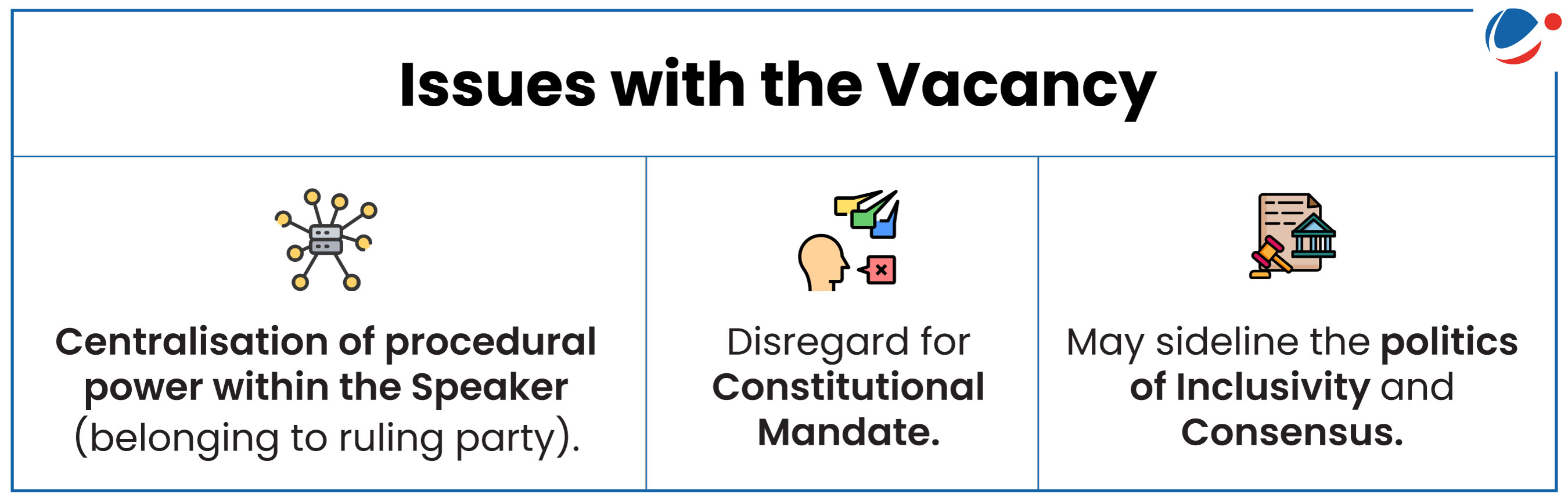
- Election: Article 93 provides that Lok Sabha, as soon as may be, choose two members of the House to be Speaker and DS.
- As per a long-standing convention, the post of DS has been offered to the Opposition.
- Resignation and Removal: Article 94 deals with vacation, resignation and removal (by a resolution passed by a majority of all then members of the House).
- Speaker may resign by submitting a resignation to the DS and vice-versa.
- Duties: As per Article 95, DS performs the duties of Speaker in case of vacancy, absence, etc.
Importance of the office of DS
- Constitutional Imperative: It is not merely ceremonial as the Constitution places it on an equal footing with the Speaker.
- Essential for continuity, stability, and institutional balance: As the DS acts as a second in command in case of emergency.
- M.A. Ayyangar served as the acting Speaker after the sudden death of Speaker G.V. Mavalankar in 1956.
- Legislative Responsibilities: DS chairs key sessions, leads committees, and manages sensitive debates requiring neutrality and authority.
Conclusion
A specific deadline (E.g., 60 days of the first sitting of the new Lok Sabha) or a statutory mechanism could be introduced to ensure appointment within a timeframe.






