The RBI has issued direction in the exercise of its powers under Section 45L(1)(b) of the Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934.
- RBI action is based on material supervisory concerns observed in the pricing policy regarding their weighted average lending rate (WALR) and the interest spread charged over their cost of funds.
About Non-Banking Financial Company (NBFC)
- It is a company registered under the Companies Act, 1956, primarily engaged in lending activities, but excludes institutions mainly involved in agriculture, industrial activity, trading goods (except securities), and providing any services and sale/purchase/construction of immovable property.
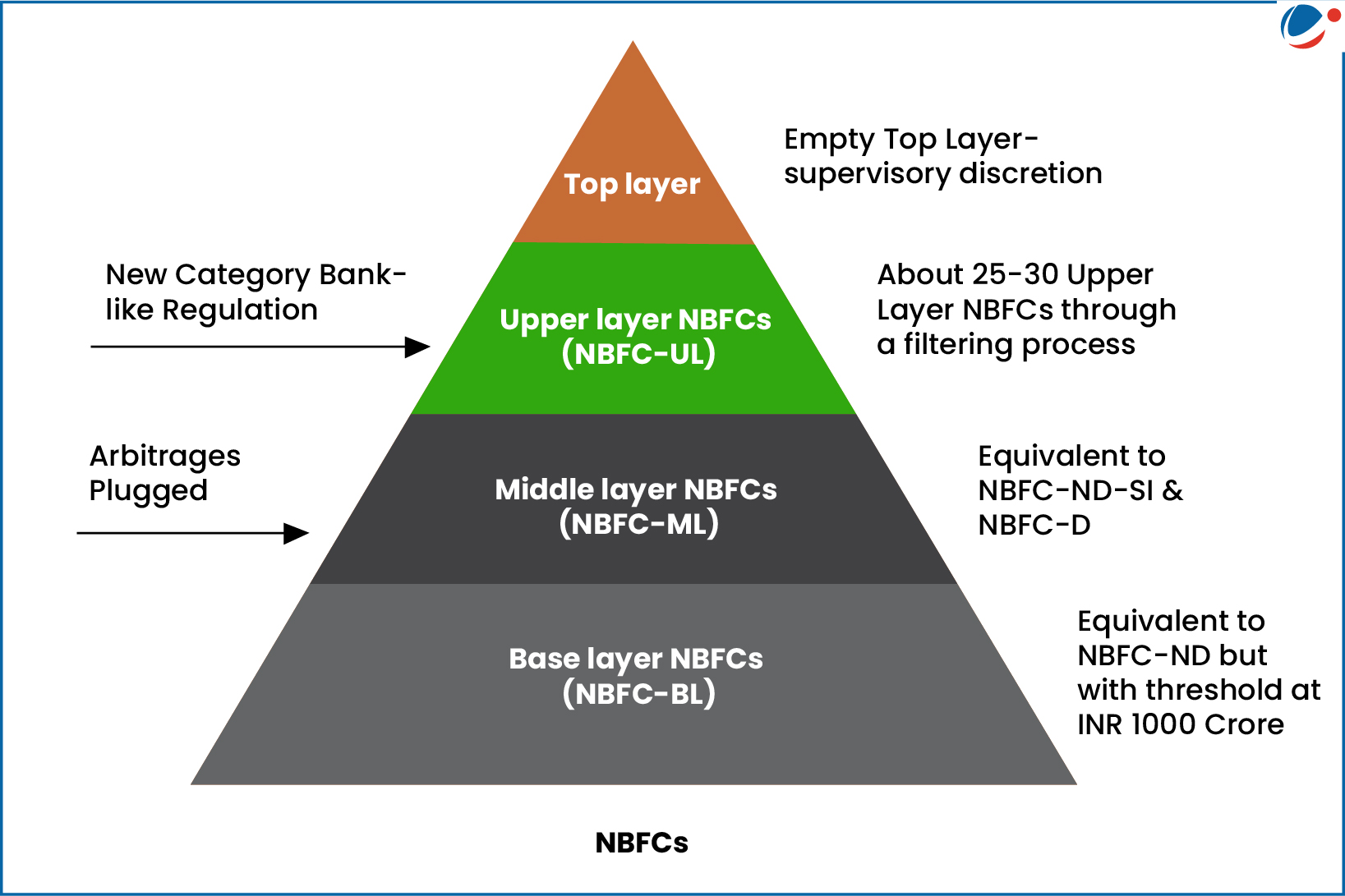
- The RBI regulates NBFCs in four layers based on their size, activity, and perceived riskiness (See Infographic).
- NBFCs are different from Banks as
- They cannot accept demand deposits.
- Do not form part of the payment and settlement system and cannot issue cheques drawn on itself.
- The deposit insurance facility of Deposit Insurance and Credit Guarantee Corporation is not available to depositors of NBFCs.
- Issues with NBFCs: Multiple regulatory bodies (SEBI, IRDAI, etc), funds borrowed for short term and lending take place for long tenures, Non-Performing Assets, etc.



