Report highlights the growing complexity of the cyber landscape (refer to the infographic) and its wide-ranging implications for organizations and nations.
- The report also highlighted that cybercrime disrupted global economies, costing $12.5 billion in 2023.
What factors are increasing the complexities of cybersecurity?
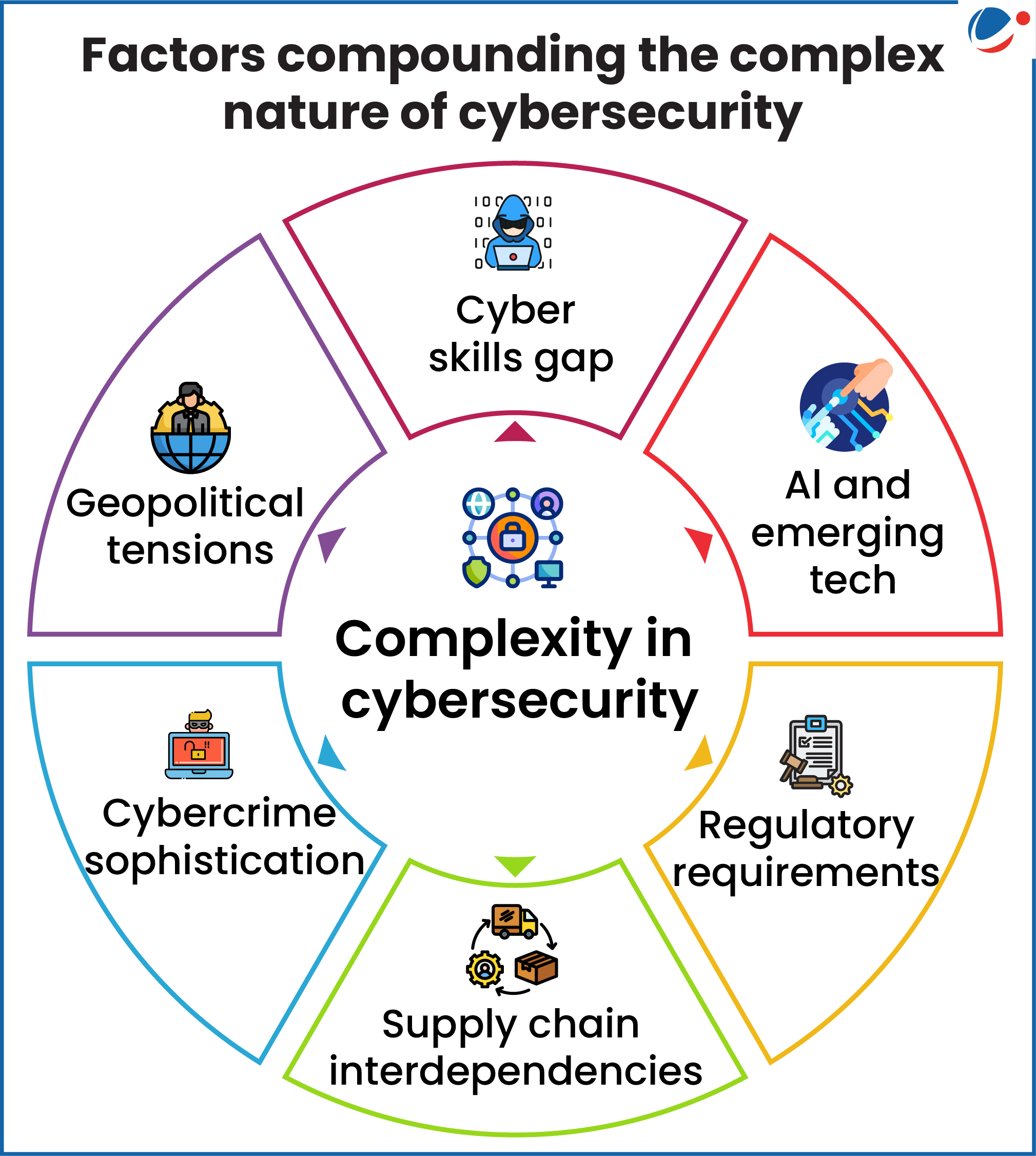
- Supply Chain Vulnerabilities: Increasing complexity of supply chains and limited oversight create risks, with third-party software flaws enabling cyberattack propagation throughout the ecosystem.
- Geopolitical Tensions: Conflicts drive advanced cyber strategies, threatening critical infrastructure like energy and telecommunications.
- AI-Driven Threats: Generative AI enables cost-effective, scalable malware deployment and sophisticated multilingual social engineering (manipulating people to gain control over a computer system) attacks.
- Cyber Skills Gap: A growing 8% skills gap leaves two-thirds of organizations unable to address security needs effectively.
- Convergence of Cybercrime and Organized Crime: Rising cyber-enabled fraud has drawn violent organized crime groups into the cyber domain, amplifying the scale and social impact of cybercrime.
- Climate-Linked Cyber Risks: Energy grids face heightened risks due to reliance on evolving energy systems.
- Quantum Vulnerabilities: Quantum computing pose the ability to break public-key encryption critical for securing digital systems.
The report underscores Overcoming cyber challenges demands a shift in perspective, recognizing cyber resilience as a collective responsibility. Leaders must treat cybersecurity as a strategic investment to counter emerging threats.







