Report titled ‘Dependency and depopulation? Confronting the consequences of a new demographic reality’ provides comparative analysis of demographic dynamics of first wave (developed) and later wave (developing) countries.
Key Highlights of Demographic Transition
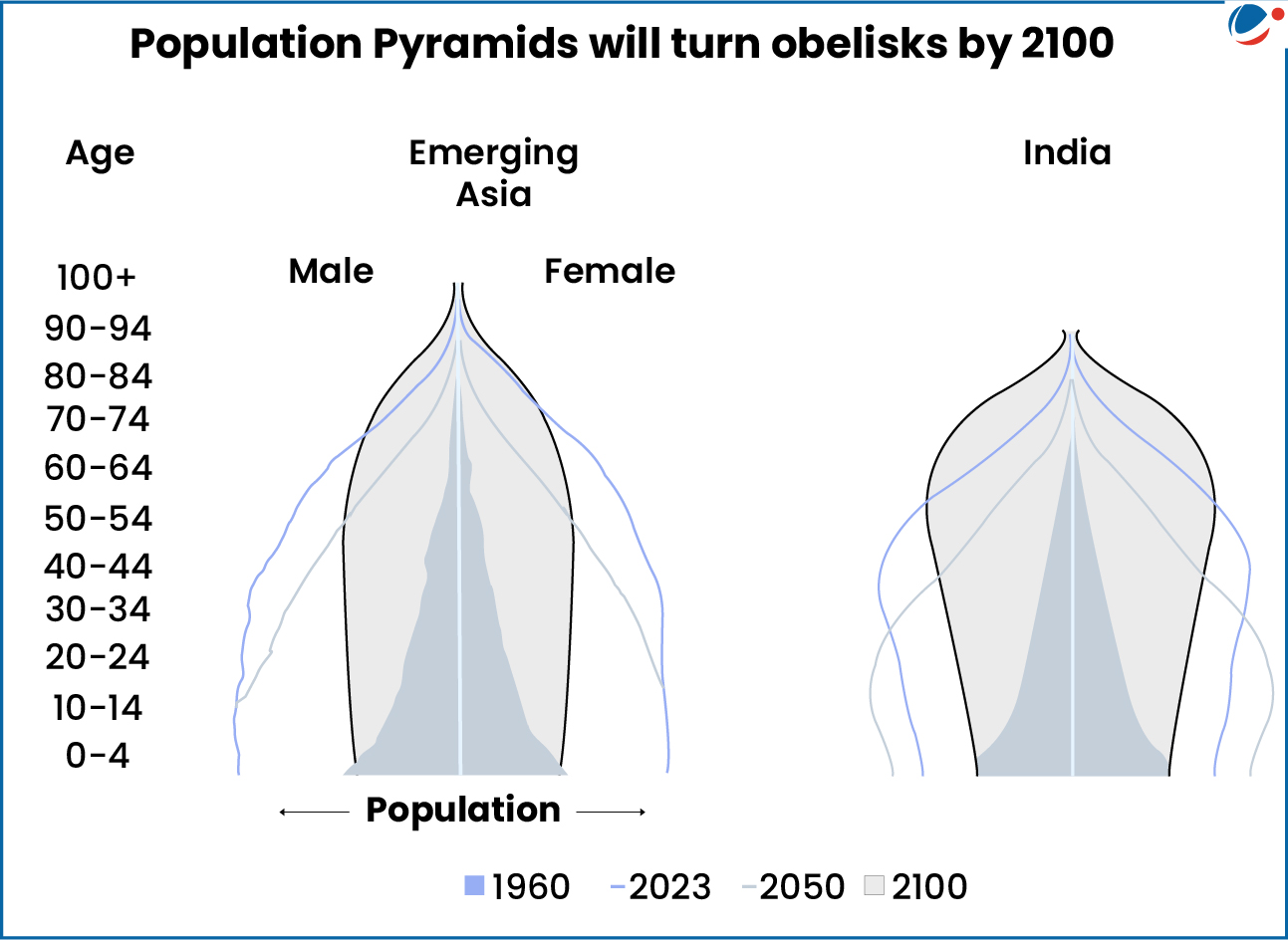
- Depopulation: 2/3rd of humanity lives in countries with fertility below the replacement rate of 2.1 children per family.
- Age structures are inverting from pyramids to obelisks as the number of older people grows and the number of younger people shrinks.
- By 2100, populations in some major economies will fall by 20%-50% (UN).
- Falling Support Ratios: Support ratios are falling (from 6.5 today to 3.9 in 2050).
- The support ratio is the number of people aged 15-64 years (working age), relative to the number 65 years and older.
- In advanced economies and China, retirement systems might need to channel 50% of labor income to fund a 1.5-time increase in the gap between the aggregate consumption and income of seniors.
- India’s Diminishing Demographic Dividend
- India has 33 years to capitalize demographic dividend (as it reaches support ratios at par developed countries).
- The dividend added 0.7 percentage points per year to GDP per capita growth. Through 2050, it will shrink to just 0.2% points per year.







