Study analyzed flood events in HMA from 1950 to 2023 and confirms that temperature rise is the key driver of increased flooding.
- Since 1950, HMA has been warming at 0.3°C per decade.
Other Key observations
- Rising unpredictability in floods timing, while most events continue to occur during monsoon, there is increase in floods happening outside these times.
- Planetary heating from burning of oil, coal, and gas is driving the rise in all four types of floods seen in Asian region.
Four Types of Floods in HMA
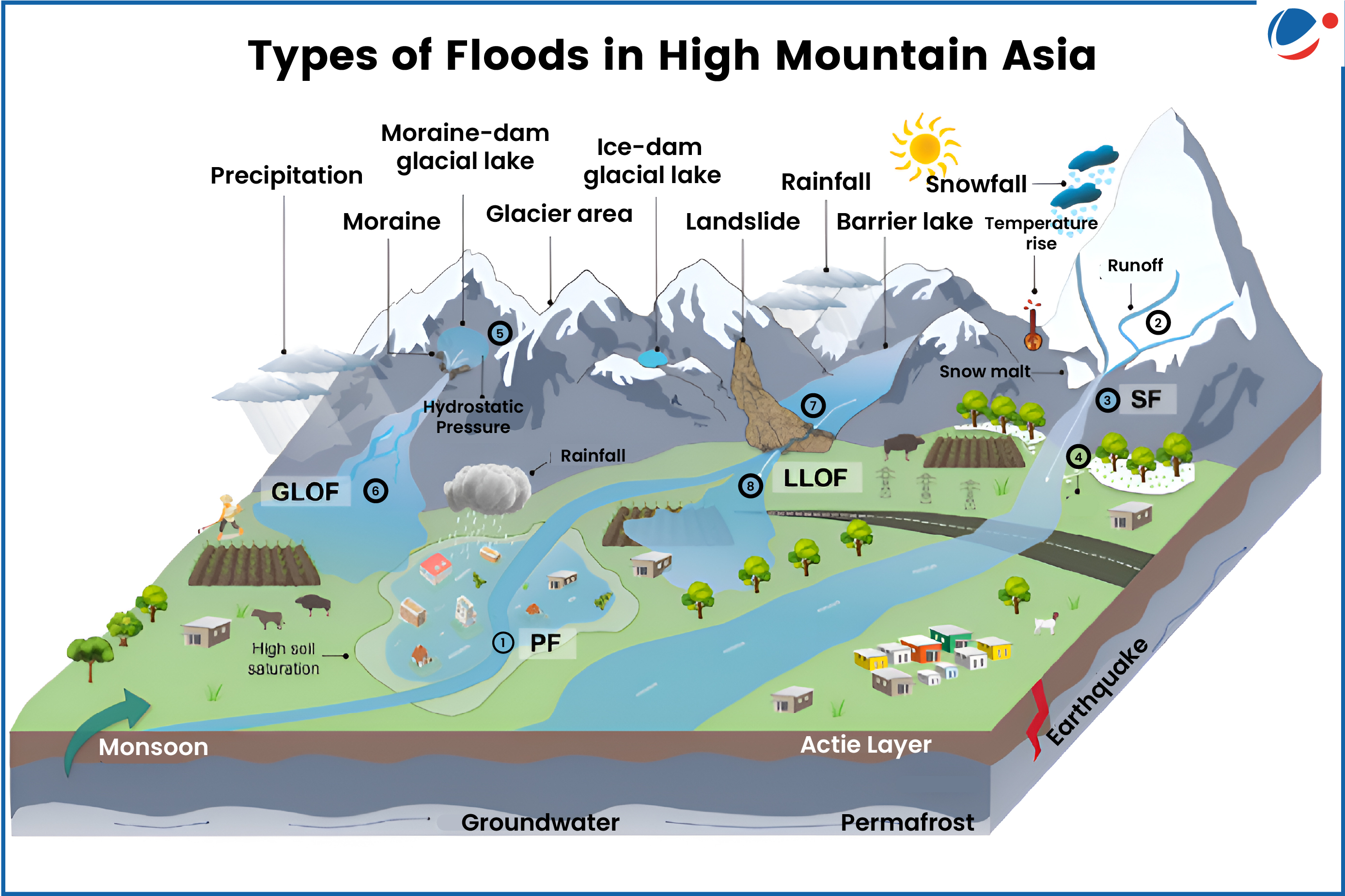
- Rain/Pluvial Floods (PF): Triggered by extreme rainfall, leading to surface runoff and flash floods, common in Himalayas.
- Snowmelt-induced floods (SF): Rising temperatures accelerate snowmelt, increasing river discharge, most frequent in Tien Shan.
- Glacial Lake Outburst Floods (GLOFs): Caused by glacial lakes breaching due to melting glaciers or landslides, common in Karakoram and Himalayas.
- Landslide-Dammed Lake Outburst Floods (LLOFs): Occur when landslides block rivers, forming temporary lakes that later breach, mostly in Hengduan Mountains.
Recommendations
- Prioritise real-time flood monitoring in vulnerable valleys.
- Strengthen data-sharing agreements between HMA nations to address transboundary threats
- Promoting community-based flood mitigation efforts including locally-led construction of protective infrastructure etc.
About High Mountain Asia
|






