This follows successful docking of two satellites - SDX01 (Chaser) and SDX02 (Target) which was achieved in January 2025.
- This made India the fourth nation, after United States, Russia, and China, to demonstrate in-space docking technology.
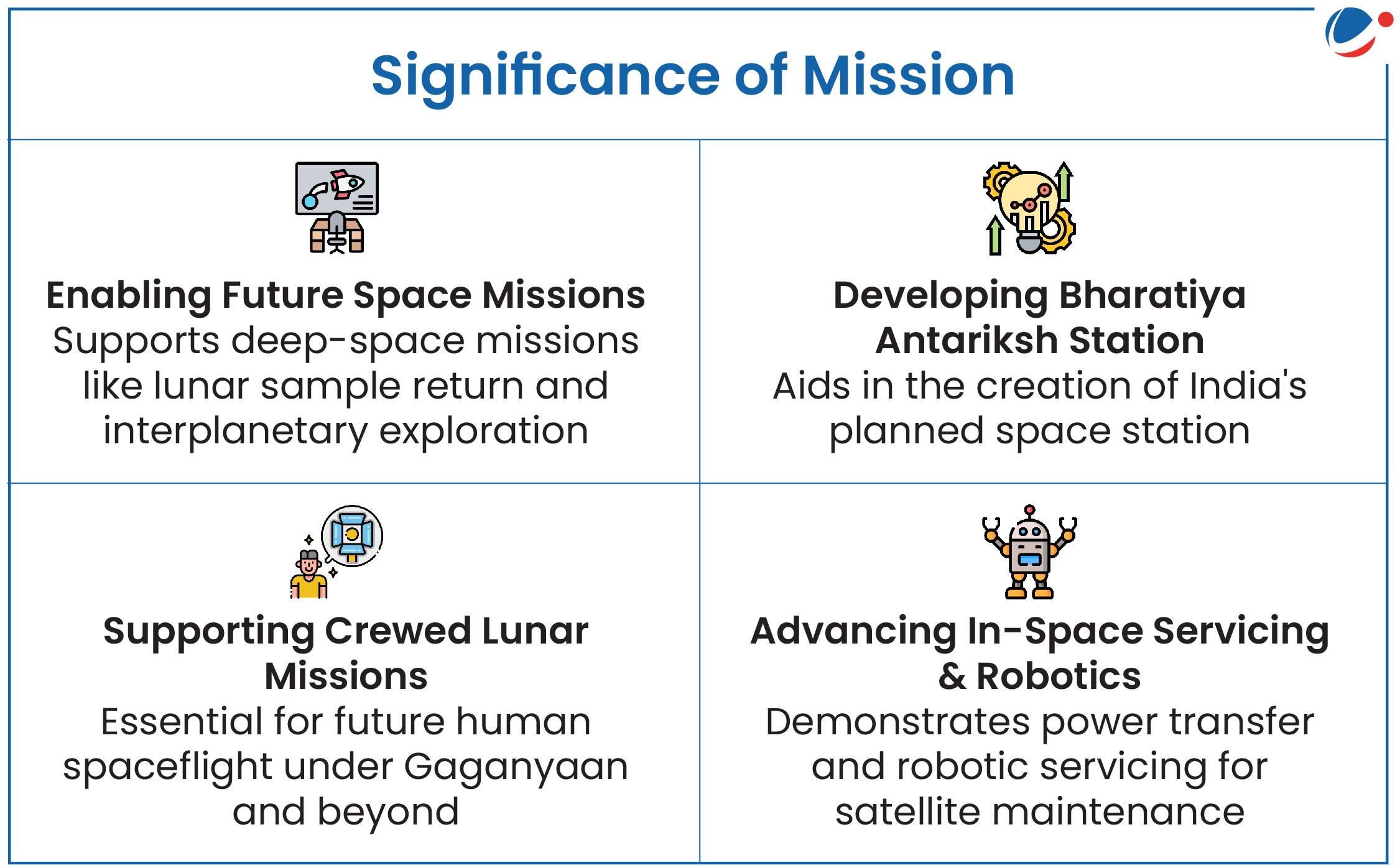
About SpaDeX Mission
- SpaDeX is a technology demonstrator mission designed to develop and showcase in-space docking, rendezvous, and undocking capabilities using two small satellites- SDX01 (Chaser) and SDX02 (Target).
- These satellites were launched aboard PSLV-C60.
- SpaDeX spacecraft were designed and realized by UR Rao Satellite Centre (URSC), Bengaluru with the support of other ISRO centers (VSSC, LPSC, SAC, IISU, and LEOS).
- Established in 1976, URSC is lead centre of ISRO responsible for design, development, assembly & integration of communication, navigation, remote sensing, scientific and small satellite missions.
Technological Innovations in SpaDeX
- Docking Mechanism: A low-impact, androgynous docking system for smooth connection between the spacecraft.
- Inter-Satellite Communication Link (ISL): Enables real-time data transfer between spacecraft.
- GNSS-Based Relative Orbit Determination: Ensures precise navigation and control during docking.
- Power Transfer Technology: Demonstrates energy transfer between docked satellites.
- Autonomous Rendezvous and Docking Algorithms: Used for precise maneuvering of satellites in orbit.
Post-Docking Applications
- After docking and undocking, satellites will continue independent payload operations. These include:
- High-Resolution Imaging (SDX01): Capturing images for Earth observation.
- Multi-Spectral Payload (SDX02): Monitoring natural resources and vegetation.
- Radiation Monitoring (SDX02): Studying space radiation for future human missions.





