Bhabha Atomic Research Centre (BARC) Participated in International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) Scientific Forum ‘Atoms4Food’.
About ‘Atoms4Food’
- Genesis: Jointly launched by IAEA and FAO at the 2023 World Food Forum in Rome (Italy).
- Purpose:
- To provide countries with tailored solutions by harnessing the advantages of nuclear techniques along with other advanced technologies to enhance agricultural and livestock productivity, reduce food losses, etc.
- To help countries boost food security and to tackle growing hunger.
- Nearly 600 million people are projected to be chronically undernourished by 2030 (FAO).
- By 2050 the world’s population will have increased by one-third, mostly in developing countries (UN).
Nuclear Technologies for agriculture
- Irradiation technique: Extends shelf life of foods by reducing or eliminating microorganisms and insects.
- Fallout radionuclide (FRN) technique: Analyzes soil radionuclide concentrations to measure erosion patterns.
- Cosmic-ray neutron sensor (CRNS) technology: Measures soil moisture over large areas by detecting cosmic ray neutrons reflected from soil.
- Radioimmunoassay (RIA) technology: Detects hormone levels in animals enabling precise timing for artificial insemination.
- Sterile insect technique (SIT): Controls pests by releasing sterilized insects to mate with wild populations.
- Other technologies: Nitrogen-15 to measure nitrogen fixation in roots; isotropic tracing techniques for crop nutrition and water management; etc.

Department of Atomic Energy (DAE) inaugurated the Major Atmospheric Cherenkov Experiment (MACE) Observatory at Hanle, Ladakh.
The inaugural of MACE Observatory was a part of the Platinum Jubilee year celebrations of the DAE.
- DAE was set up under the direct charge of the Prime Minister through executive order in 1954 in accordance with Atomic Energy Act, 1948.
- DAE leads Research and development for the peaceful uses of atomic energy.
About MACE Observatory
- It is largest imaging Cherenkov telescope in Asia and 2nd largest in the world.
- Cherenkov Telescope Array (CTA), consisting two arrays located at Spain and Chile, respectively, will be the largest Cherenkov telescope in the world. It is currently under construction.
- It is located at an altitude of ~4,300 m, the highest of its kind in the world.
- Objective: Observe high-energy gamma rays to understand the most energetic phenomena in the universe (such as supernovae, black holes, and gamma-ray bursts).
- It is named after scientist Pavel Alekseyevich Cherenkov, who discovered that charged particles glow when they pass through a non-conducting medium under certain conditions (referred as Cherenkov radiation).
- Indigenously built by Bhabha Atomic Research Centre (BARC) with support from Electronics Corporation of India (ECIL) and other partners.
- It will also complement global observatories such as High Energy Stereoscopic System (HESS), etc.
What are Gamma Rays?
Why Hanle in ladakh is chosen for observatory?
|
NASA’s Europa Clipper embarked on long voyage to Jupiter to investigate its moon Europa.
About Europa Clipper
- Objective: Determine whether Europa has conditions that could support life.
- Evidence suggests presence of enormous, salty ocean with more water than Earth beneath Europa’s ice.
- It is the largest spacecraft NASA has ever developed for a planetary mission.
- It is also the first NASA mission dedicated to studying an ocean world beyond Earth.
- It will begin orbiting Jupiter in 2030 and conduct flybys of Europa from 2031.
- Its instruments include ice-penetrating radar, cameras and a thermal instrument to look for any recent eruptions of water.
Article Sources
1 sourceNational Space Panel Clears India’s 5th Lunar Mission ‘Lunar Polar Exploration Mission (LUPEX)’.
- LUPEX will be a precursor to the country’s lunar sample return mission and for sending the first Indian to the moon by 2040.
About LUPEX Mission
- Purpose: It will investigate the quantity and quality of water on the Moon and is envisaged to explore the dark side of the moon.
- Dark side of the moon refers to the ‘Far side’ of the moon as it is never visible from the Earth due to the ‘Tidal Locking’ of the Moon with the Earth.
- International collaboration project: ISRO is in charge of the lunar rover and Japan’s JAXA is responsible for the lander.
- Observation instruments from NASA and the ESA will also be mounted on the rover.
- Landing Location: Landing point will be the south pole of the moon as this area is believed to have a high-water potential.
- However, landing on the south pole is challenging as there are very few flat, easy landing sites with good illumination and communication conditions.
- The successful landing of the Vikram Lander, onboard Chandrayaan 3, made India the first country to land on its south-pole and the 4th country to land on the Moon (after US, Russia and China).
- However, landing on the south pole is challenging as there are very few flat, easy landing sites with good illumination and communication conditions.
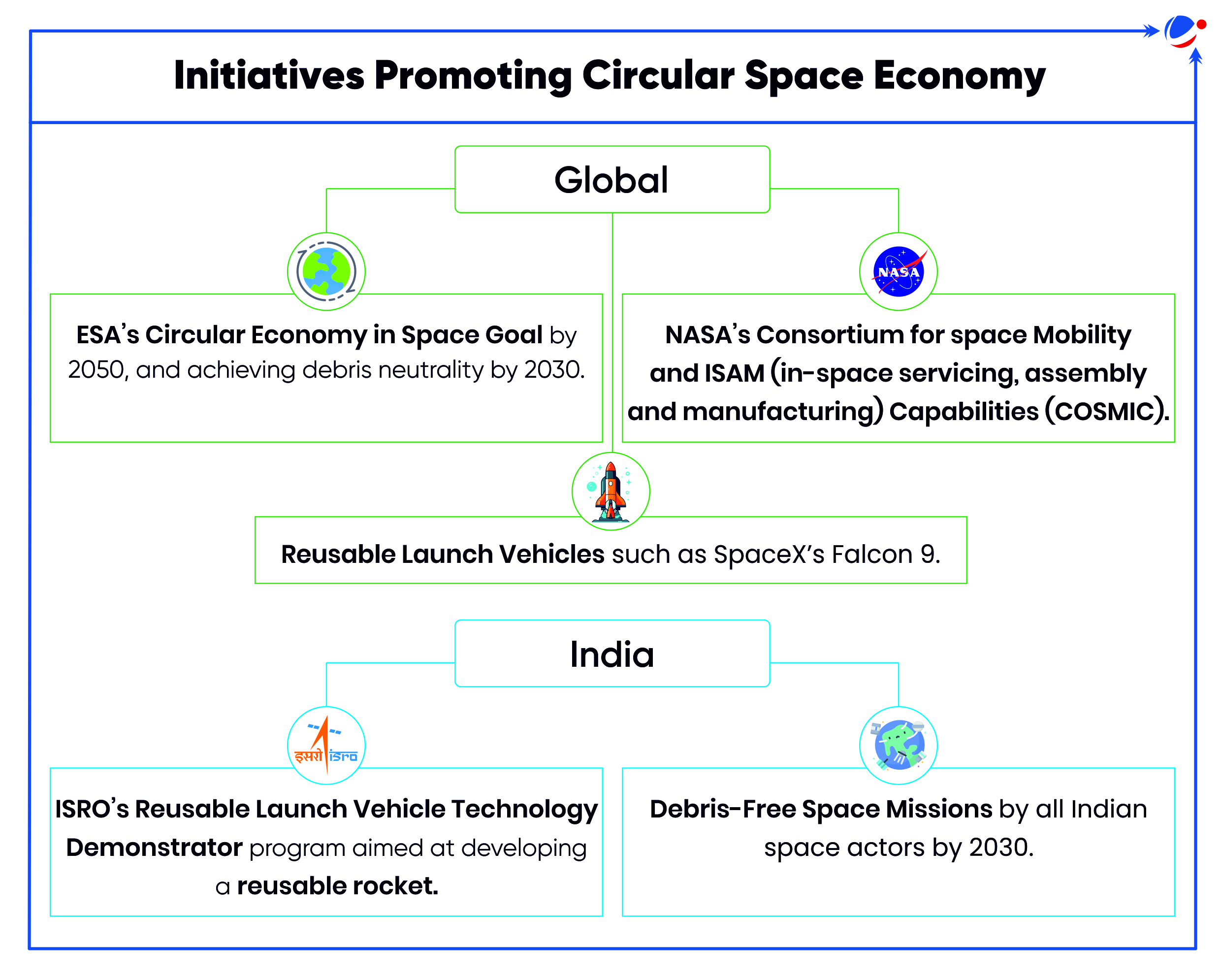
RISE (Remove Debris In-Orbit Servicing) is first in-orbit servicing mission of European Space Agency which is a significant step towards refuelling, refurbishment, and assembling in orbit - all essential elements for creating a circular economy in space.
- It will be launched in 2028 and will have the ability to dock and control orbit of geostationary satellites.
- RISE will rise up to the so-called geostationary graveyard, about 100 km higher, where satellites are ‘parked’ after they have reached the end of their mission.
Circular Space Economy
- Circular space economy draws inspiration from the broader concept of a circular economy, which aims to minimize waste and maximize resource efficiency.
- Key aspects of circular space economy include satellite refurbishment & repair, space debris removal, resource utilization (materials extracted from asteroids or the Moon), etc.
Significance of Space Circular Economy
- Reduced Space debris helps to mitigate the risk of collisions and further debris generation.
- Resource Conservation due to reusing and recycling materials in space.
- Cost Reduction by extending lifespan of satellites.
- Faster development times by assembling and manufacturing space systems directly in orbit.
Challenges to Space Circular Economy
- Technological limitations: Developing necessary technologies for in-orbit servicing, recycling, and asteroid mining.
- Funding: Developing specialized equipment, conducting R&D etc. require significant investment.
- Regulatory Challenges: Establishing global standards & regulations for space sustainability.
Article Sources
1 sourceRecently, European Space Agency has launched the Moonlight Lunar Communications and Navigation Services (LCNS) programme.
About Moonlight Programme
- Objective: To provide services for >400 moon missions planned by space agencies and private companies over the next two decades.
- It will be a constellation of five lunar satellites (satellites that orbit the moon).
- Benefits: Enable precise, autonomous landings and surface mobility, facilitate high-speed communication and data transfer between Earth and Moon, offer coverage at the Moon’s South Pole, etc.
- Initial services are expected to begin by the end of 2028, and the system is to be fully operational by 2030.
Recently, the LUX-ZEPLIN (LZ) (USA) dark-matter detector failed to identify any definite particle behind the dark matter due to presence of ‘Neutrino Fog’.
- Other similar experiments in the past such as, PandaX-4T (China) and XENONnT (Italy), have also failed to detect the ‘unknown particles’ behind the dark matter.
- Dark matter is the invisible stuff making up most of the mass in the universe, responsible for giving the cosmos its current looks.
- The LZ detector is located 1.5 km below the earth’s surface at the Sanford Underground Research Facility in South Dakota, USA.
About Neutrino Fog
- Neutrino fog refers to the background noise (interference) created by the vast number of neutrinos produced in the universe, particularly from cosmic sources like the Sun, supernovae, and other astrophysical phenomena.
- These neutrinos interact very weakly with matter, making them difficult to detect, but they are everywhere, permeating the universe.
- As a result, distinguishing between the signals from potential dark matter and those from neutrino interactions becomes a critical task.
Scientists have detected carbon dioxide and hydrogen peroxide on Charon (Pluto's moon) using NASA's James Webb Telescope.
Significance of Findings
- Understanding the origin of Charon and other moons of Plato.
- Could help in understanding origins and evolution of icy bodies in the outer Solar System.
About Charon
- It is largest among five moons of Plato.
- It is so big that Pluto and Charon orbit each other like a double planet.
- Pluto is a dwarf planet located in a distant region of our solar system beyond Neptune known as the Kuiper Belt.
World Health Organization (WHO) launched SPRP.
About SPRP
- Aim: To tackle dengue and other Aedes-borne arboviruses (Zika and chikungunya) by fostering a global coordinated response.
- Tenure: Over one year until September 2025.
- 5 key components:
- Emergency coordination
- Collaborative surveillance
- Community protection
- Safe and scalable care
- Access to countermeasures
- Aligns with other Global initiatives: SPRP is aligned with the Global Vector Control Response 2017–2030 and Global Arbovirus Initiative.
Switzerland joins European Sky Shield Initiative (ESSI)
About ESSI
- Genesis: Founded in 2022 after Russia invaded Ukraine
- It is a German led European Iron Dome-style defence system.
- Aim: Bolstering Europe’s defence against air strikes as it will strengthen NATO’s integrated air and missile defence.
- Members: 21 member states, including the UK
- At the heart of this initiative is the Arrow 3, an Israeli-American missile defence system that can intercept long-range ballistic missiles.
Department of Pharmaceuticals (DoP) modified Revamped Pharmaceutical Technology Upgradation Assistance Scheme (RPTUAS).
- It has increased incentive for pharmaceutical companies to Rs 2 crore (from Rs 1 crore).
- Added "production equipment," a new category to the list of eligible expenses for subsidy calculation.
About RPTUAS
- Objective: To support the pharmaceutical industry's upgradation to Revised Schedule-M & WHO’s good manufacturing practices standards.
- Introduced more flexible financing options, emphasizing subsidies on a reimbursement basis.
Recently, Central Drugs Standard Control Organization under Union Ministry of Health & Family Welfare has become an affiliate member of the International Medical Device Regulators Forum (IMDRF).
About IMDRF
- Established in 2011, it is a collaborative group of global medical device regulators dedicated to accelerating the harmonization and convergence of international medical device regulations.
- Members include national regulatory authorities from different countries and the World Health Organization (WHO).
India is the third country in the South-East Asia Region after Nepal and Myanmar that eliminated this Neglected Tropical Diseases (NTD).
- Previously WHO declared India free from two other NTDs (Guinea Worm disease (2000) and Yaws (2016)).
About Trachoma
- It is eye infecting disease caused by infection with bacterium Chlamydia trachomatis.
- It is contagious (spreading through contact with eyes, nose etc.) disease and If left untreated can cause irreversible blindness.
- Status in India: In 1971, blindness due to Trachoma was 5% and now it has come down to less than 1%.
- Interventions for Trachoma: National Programme for Control of Blindness & Visual Impairment (NPCBVI), Adoption of WHO SAFE strategy etc.
Article Sources
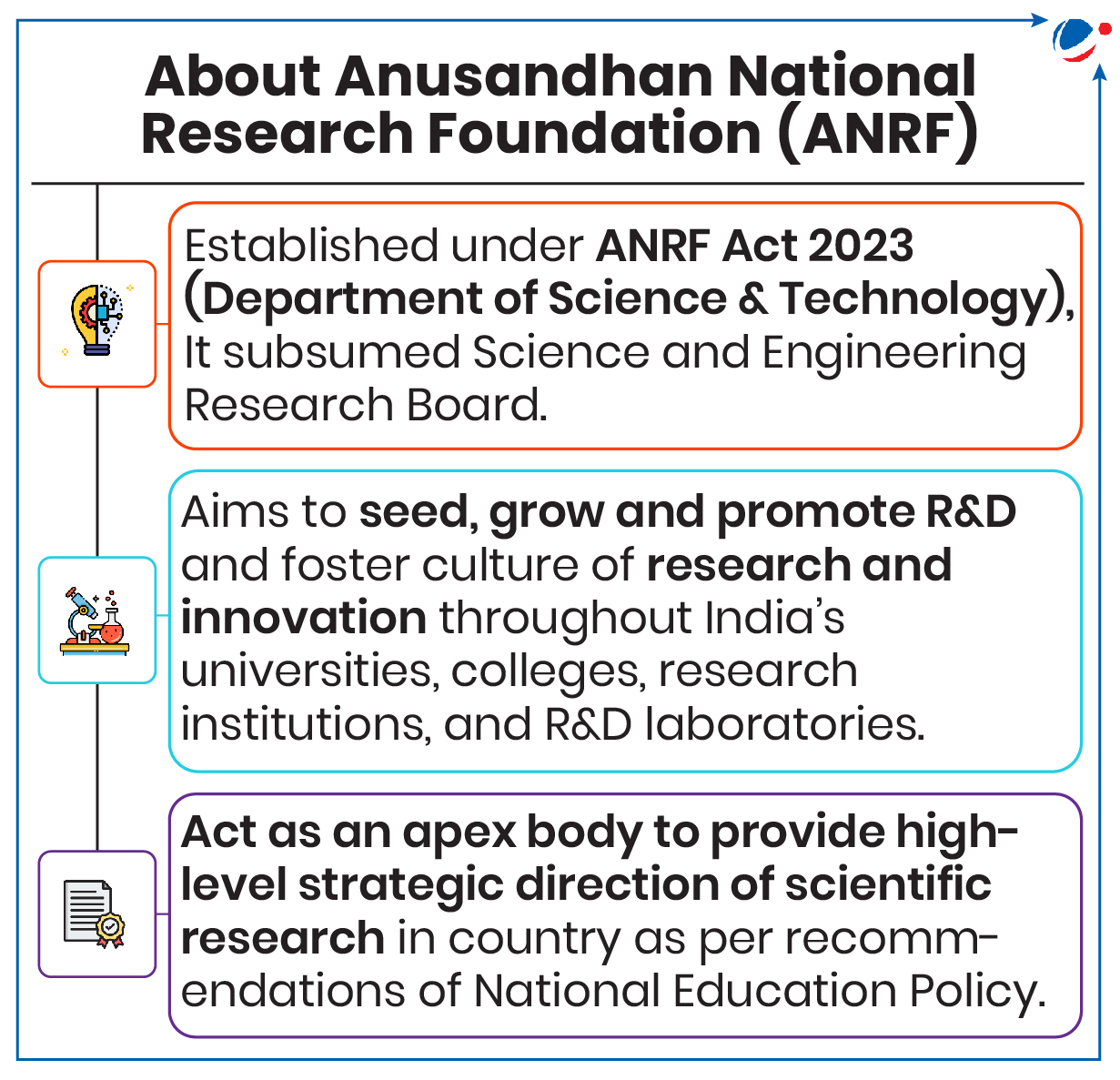
1 sourceThese are first two initiatives of ANRF (Anusandhan National Research Foundation), which plays a transformative role in bridging the gap between academic research and industrial application.
About Prime Minister Early Career Research Grant (PMECRG)
- It aims to position India as a leader in science and technology by providing a flexible budget to facilitate ease of research and invest in early career researchers.
- Significance: Foster high quality innovative research; Enable researchers to expand knowledge boundaries and drive technological progress.
About Mission for Advancement in High-Impact Areas -Electric Vehicle (MAHA-EV)
- It focuses on development of key EV technologies to reduce dependency on imports and promote domestic innovation. It is aligned with government’s Atmanirbhar Bharat (self-reliant India) vision.
- Concentrating on three critical technology verticals i.e. Tropical EV Batteries and Battery Cells, Power Electronics, Machines, and Drives and EV Charging Infrastructure, mission will enhance domestic capabilities in design and development of essential EV components.
- Significance:
- Position India as a hub for EV component development, driving global competitiveness and innovation.
- By accelerating the shift towards electric mobility, it will contribute to a greener and sustainable future
Article Sources
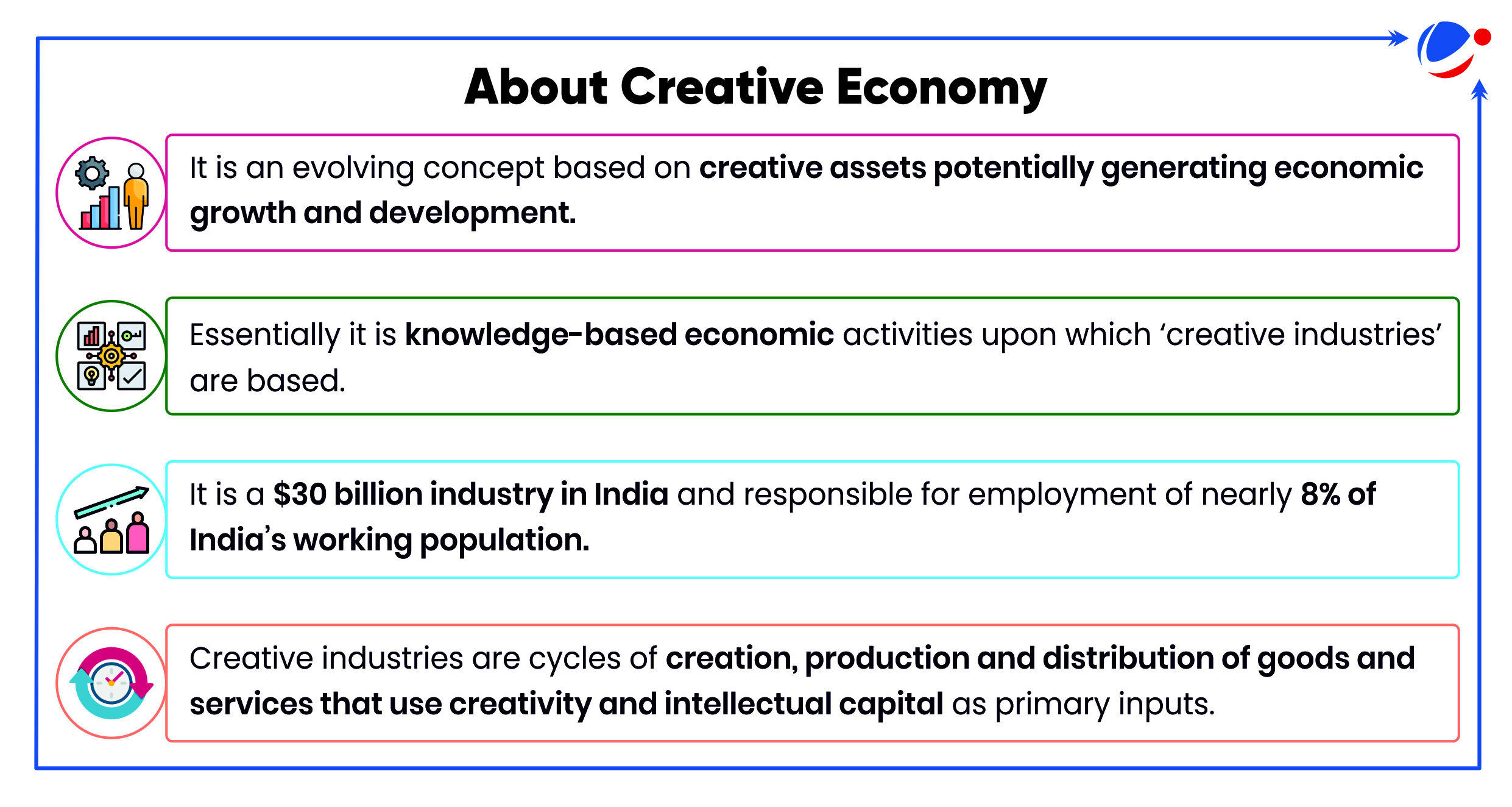
1 sourceFormation of NCoE for Animation, Visual Effects, Gaming, Comics, and Extended Reality (AVGC-XR) follows the 2022-23 budget announcements, which proposed the creation of an AVGC task force.
- It will boost the creative economy in India.
Features of NCoE
- It will be set up as a Section 8 Company under the Companies Act, 2013.
- Provisionally named the Indian Institute for Immersive Creators (IIIC).
- It will function as an incubation center for nurturing startups in the AVGC-XR field.
Benefits
- Exponential growth potential: e.g. animation industry in India has a growth rate of 25% and has an estimated value of ₹46 billion (2023) (as per FICCI-EY Report 2023).
- Playground of various immersive technologies. e.g. Virtual Reality (VR), Augmented Reality (AR), Mixed Reality (MR) and 3D modeling.
- Creation of indigenous intellectual property (IP): for both domestic consumption and global outreach and nurturing of the future of India’s digital creative economy.
- Employment Opportunities: It is expected to generate 5,00,000 jobs with an integrated focus on education, skilling industry, development, innovation.
- Enhance India's soft power globally and attract foreign investment.