The report has been coordinated by the World Meteorological Organization (WMO).
- WMO is a specialized agency of United Nations responsible for promoting international cooperation in atmospheric science and meteorology.
Key Findings
- Hydrological extremes: Year 2023 was the hottest year on record.
- Levels of soil moisture were predominantly below or much below normal across large territories globally.
- 2023 was driest year for global rivers in 33 years.
- Lake Coari in the Amazon faced below-normal water levels, leading to extreme water temperature.
- Glaciers: Glaciers suffered the largest mass loss ever registered in the last five decades.
Article Sources
1 sourceRecently, President of India presented fifth NWA in New Delhi.
About National Water Awards
- Nodal Ministry: Ministry of Jal Shakti.
- Aim: To create awareness among people about importance of water and motivate them to adopt the best water usage practices.
- Presented in nine categories: Best State, Best District, Best Village Panchayat, Best Urban Local Body (ULB), Best School/College, Best Industry, Best Water User Association, Best Institution (other than school/college), and Best Civil Society.
- Odisha is best state and Surat, Gujarat is Best ULB.
Article Sources
1 sourceCentral Consumer Protection Authority (CCPA) has issued guidelines for ‘Prevention and Regulation of Greenwashing and Misleading Environmental Claims,2024’.
- These guidelines are in the furtherance to the Guidelines for Prevention of Misleading Advertisement, 2022 and prohibits Greenwashing.
Key provisions of the guidelines
- Defines greenwashing clearly: Greenwashing means any deceptive or misleading practice, which includes concealing, omitting, or hiding relevant information, by exaggerating, making vague, false, or unsubstantiated environmental claims.
- Applicability: All environmental claims, a manufacturer, service provider, product seller, advertiser, or to an advertising agency or endorser whose service is availed for the advertisement of such products.
- Substantiation of Environmental claim:
- Use consumer friendly language and explain meaning or implication of technical terms like Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA).
- All environmental claims shall be supported by accessible verifiable evidence on independent studies and third-party certification.
- Adequate Disclosures:
- Ensure all environmental claims in ads or communications are fully disclosed, either directly or through technology like QR codes or web links (for easy accessibility).
- Claims must specify whether it refers to the good as a whole or part of it or manufacturing process, packaging, etc.
- Avoid selectively presenting data to favorably highlight environmental claims.
- Aspirational or futuristic environmental claims: Such claims may be made only when clear and actionable plans have been developed for achievement of objectives.
Article Sources
1 sourceUnion Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (MoSPI) released the 7th issue of the “EnviStats India 2024: Environment Accounts”
- EnviStats (Environment Statistics) have been compiled in accordance with the SEEA (System of Environmental- Economic Accounting) Framework.
- EnviStats provide information about environment, its most important changes over time and across locations and main factors that influence them.
- Publication includes Four areas- Energy Accounts, Ocean Accounts, Soil Nutrient Index and Biodiversity.
Key Highlights of EnviStats India 2024
- India emerged as world leader in energy transition.
- Around 72% increase in number and around 16% increase in area for Total Protected Area during 2000 to 2023.
- Coverage of Mangroves has increased around 8% during 2013 to 2021.
Significance of EnviStats
- Sustainable management of natural resources, key to long-term development.
- Balance economic growth with environmental sustainability.
- Provide alternate means of measuring prosperity and progress and go beyond GDP.
- Data-driven policymaking.
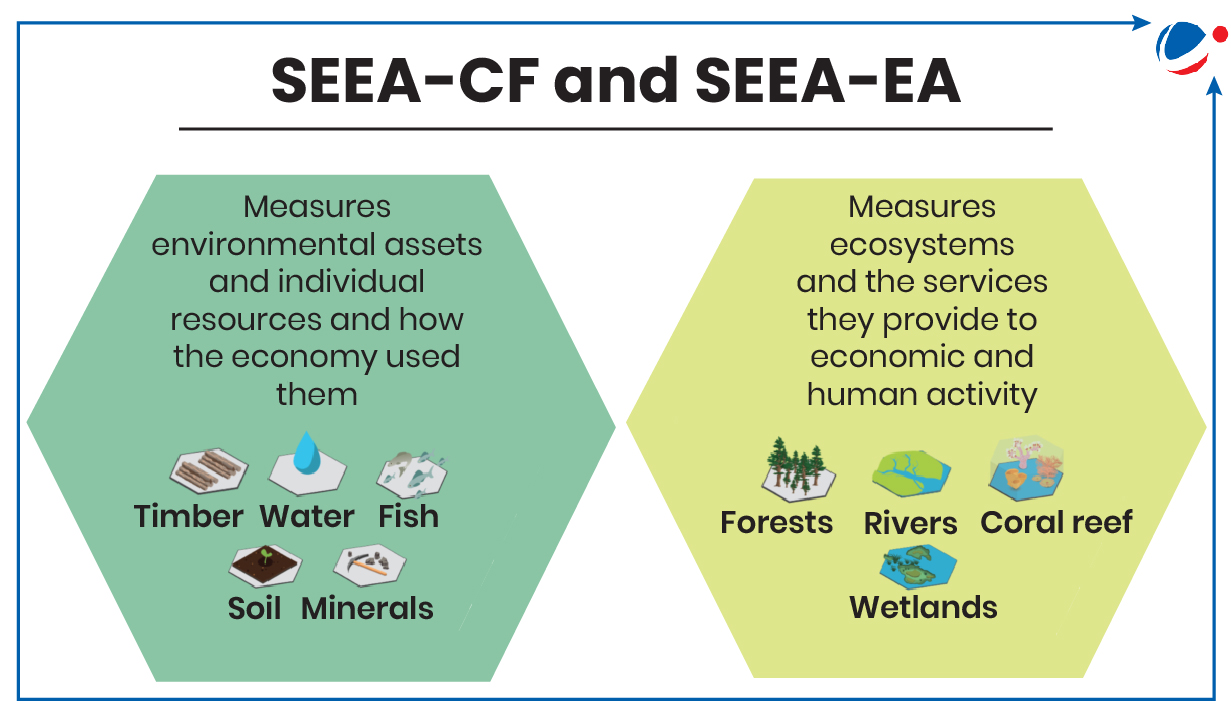
About System of Environmental-Economic Accounting (SEEA)
- It is an agreed international framework for the compilation of the Environment Economic accounts.
- It describes the interaction between the economy and the environment, as well as the stocks and changes in stocks of environmental assets.
- There are two sides of SEEA- SEEA-Central Framework (SEEA-CF) and SEEA-Ecosystem Accounting (SEEA-EA) (refer infographic).
Environment Accounts in India
|
Article Sources
1 sourceReport focuses on tracking the overarching forest goals: eliminating deforestation and forest degradation, and restoring 30% of degraded forest area by 2030.
- These goals have been established by international commitments such as New York Declaration on Forests (2014), Glassgow Leaders’ Declaration (2021), and Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework (2022).
Global Forest Goals and Progress
- Eliminate deforestation by 2030: Around 6.37 million hectares deforested in 2023 much greater than the targeted 4.38 million hectares.
- 3.8 billion metric tons of CO2 equivalent in 2023 making deforestation fourth-highest emitter after China, US and India.
- Eliminate tree cover loss in forested Key Biodiversity Areas (KBAs): Over 1.4 million hectares of forests were lost within forested KBAs in 2023.
- Controlling Forest Fire: Nearly one-third of area lost to fires since 2001 was burned from 2019-23.
- Restore 30% of degraded and deforested landscapes by 2030: Only around 18% of the Bonn Challenge’s 2020 target of 150 million hectares was restored from 2000-19.
Drivers of Deforestation
- Commodity Production: Agricultural commodities responsible for 57% of global deforestation over past two decades.
- Shifting agriculture in primary forests: Responsible for loss of 15.9 million hectares of primary forests from 2015-23.
- Mining: From 2000-19, mining volumes from tropical moist forest ecosystems doubled.

Article Sources
1 sourceThe European Commission has proposed to extend the implementation of the EUDR, by one year.
About EUDR
- It aims to ensure that a set of key goods placed on the EU market will no longer contribute to deforestation and forest degradation in the EU and elsewhere in the world.
- Applies to a wide range of products including palm oil, soy, beef, cocoa, and timber.
- This requires companies to verify the origin of the products and ensure that they are produced in a sustainable manner.
- It will act as a barrier for countries who export to the EU.
A coalition of civil society organizations has raised concerns over promotion of biodiversity credits.
Biodiversity Credits
- Definition: An economic instrument that allows private companies to finance activities, such as forest conservation or restoration.
- Purpose: To have a net-positive impact on nature and biodiversity.
- Unlike biodiversity offset, biodiversity credits are not limited to compensating for companies’ negative and unavoidable impacts on nature.
- Functioning:
- Stakeholders that have a goal to conserve or restore land generate a supply of credits, or “certificates.
- Private companies then purchase these credits to meet their biodiversity- or nature-based commitments.
Plant cover across Antarctic Peninsula is increasing due to climate crisis.
About Greening of Antarctica:
- It is growth of vegetation e.g. moss on a continent dominated by ice and bare rock due to extreme heat waves.
- Warming in the region is happening much faster than global average, accelerating between 2016 and 2021.
- Vegetation has expanded over tenfold between 1986 and 2021.
Impact
- Invasive species: Greening may introduce invasive species, and harm local wildlife.
- Worsen Climate effect: It will reduce the continent’s ability to reflect sunlight (albedo), worsening climate effects.
Union Government has set up the Coordination Committee for Air Quality Management in the Indo-Gangetic Plain (IGP) region.
- The ten-member panel will work on comprehensive mitigation measures to check air pollution across Bihar, Chandigarh, Delhi, Haryana, Jharkhand, Punjab, Uttar Pradesh, and West Bengal.
- On account of typical geography and meteorology, these states have high baseline levels of air pollution which requires regional airshed management to abate air pollution.
- Coordination Panel has been tasked with integrating state action plans to develop IGP Regional Airshed Management Plan and monitor its implementation.
Centre notifies guidelines for ‘Innovative Projects’ component under PM-Surya Ghar: Muft Bijli Yojana.
- Ministry of New and Renewable Energy has notified operational guidelines to encourage advancements in rooftop solar technologies, business models, and integration techniques.
- Earlier guidelines had been issued for other sub-components such as Model solar village etc.
About ‘Innovative Projects’ Component
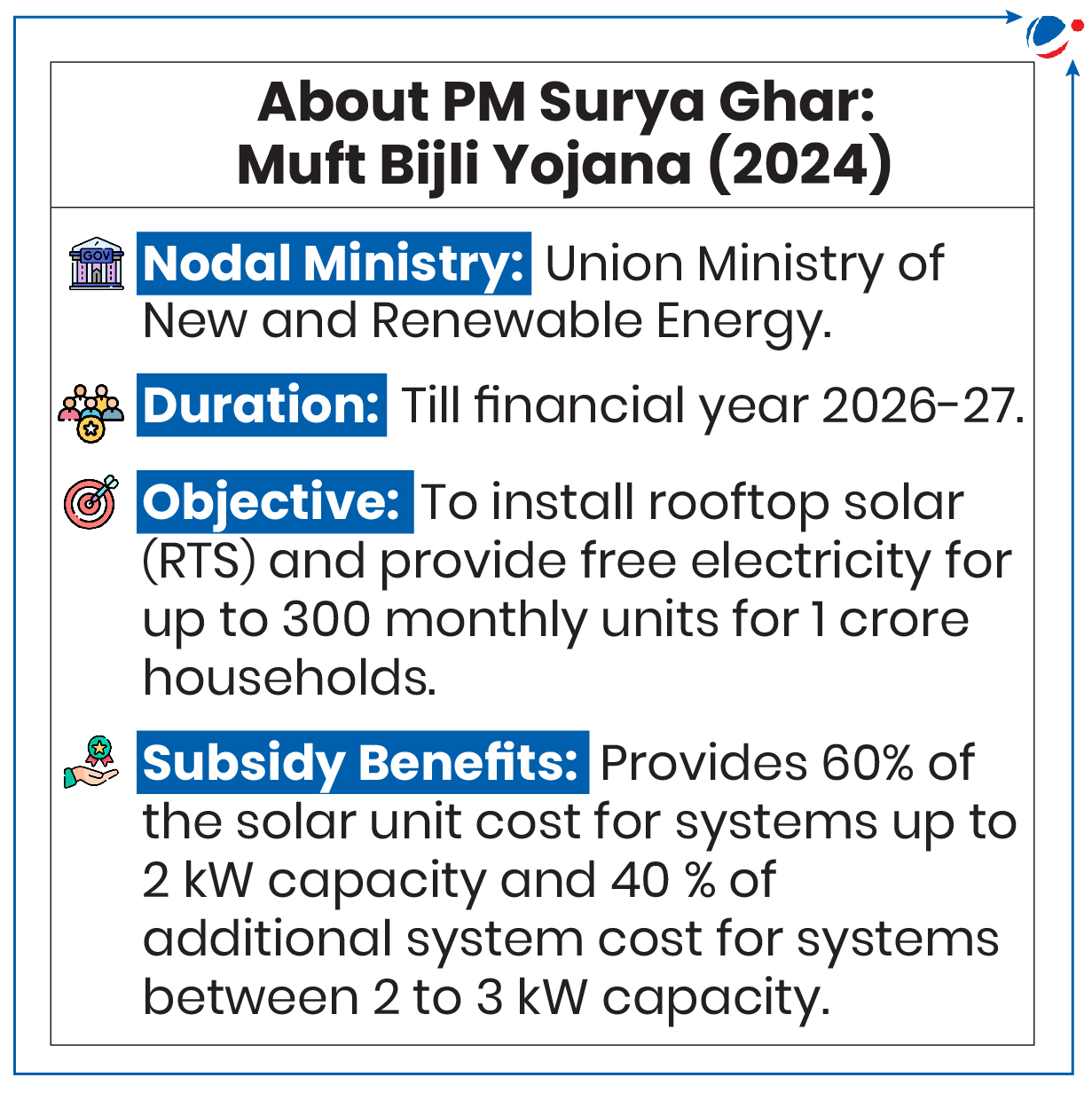
- Objective: To support startups, institutions, and industries in piloting new concepts, with a focus on emerging solutions like blockchain-based peer-to-peer solar trading, etc.
- Eligibility/Target Group: Any entity or individual and International Cooperation (Taking up joint research and design.)
- Tenure: Project will have a maximum duration of 18 months.
- Funds: ₹500 crore to encourage advancements in rooftop solar technologies,
- Funding for Projects: Financial assistance of up to 60% of project cost or ₹30 crore, whichever is lower.
- Scheme Implementation Agency: National Institute of Solar Energy (NISE)
Article Sources
1 sourceInternational Energy Agency released its flagship World Energy Outlook 2024.
Key Observations
- Geopolitical tensions and fragmentation are major risks for energy security.
- Around 20% of today’s global oil and LNG supplies flow through the Strait of Hormuz, a maritime chokepoint in the Middle East.
- Clean energy is entering the energy system at an unprecedented rate, with more than 560 gigawatts (GW) of new renewables capacity added in 2023.
- More than half of the world's electricity will be generated by low-emission sources before 2030.
Article Sources
1 sourceUnion Cabinet has approved the signing of a letter of intent enabling India to join the IEEH.
- Bureau of Energy Efficiency (BEE) has been designated as the implementing agency for the Hub on behalf of India.
About International Energy Efficiency Hub
- Genesis: Established in 2020 as the successor to the International Partnership for Energy Efficiency (IPEEC) in which India was a member.
- Mandate: It is a global platform dedicated to fostering collaboration and promoting energy efficiency worldwide.
Article Sources
1 sourceGFC Fund has launched its first project call for targeting safe and sustainable management of chemicals and waste.
About GFC Fund
- Setup during fifth International Conference on Chemicals Management (ICCM5) in 2023 in Bonn, Germany.
- Executive Board takes operational decisions and oversees its functioning. It is composed of
- 2 National representatives of each United Nations region; and Representatives of all donors and contributors.
- It complements existing financial mechanisms, like Global Environment Facility etc. and funds that support biodiversity and climate action.
Objectives:

- Support low-and middle-income countries, including small island developing states, in addressing chemicals, including products and waste in line with international standards.
- Target medium-scale projects that strengthen national and regional abilities managing chemicals and waste.
- Financial Support: Selected projects will receive 300,000 to 800,000 USD for up to three years to minimize harm from chemicals and waste and protect environment and human health.
- Funding is provided through voluntary contributions.
About GFC (Bonn Declaration adopted at ICCM5)
- Multi-sectoral agreement that outlines set of 28 targets to address chemicals and waste management including prevention of illegal trade, elimination of highly hazardous pesticides in agriculture by 2035 etc.
Recently, Union Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change notified Ecomark Rules, 2024.
- Ecomark labeling system will promote eco-friendly products in categories like food, cosmetics, soaps, and electronics, etc.
- It aligns with the principle of LIFE (Lifestyle for Environment), focusing on sustainability and resource efficiency.
Rules notifies
- Granting Criteria: To a product that has a licence or a certificate of conformity with Indian Standards granted under the Bureau of Indian Standards Act and/or a mandate of the Quality Control Orders and that fulfills the criteria as prescribed in the rules.
- According to rules, the Ecomark may be granted to products that meet specified environmental criteria with respect to resource consumption and environmental impacts.
- Application Process- Manufacturers must apply for Ecomark through the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB).
- Duration- mark will be valid for three years.
- Oversight and Implementation- By Steering Committee, headed by the Environment Secretary.
Significance
- It enables consumers to make informed purchase decisions as well as encourage manufacturers to transition to production of environment-friendly products.
- It will lead to circular economy and prevent misleading information on environmental aspects of products.
- It will promote lower energy consumption, resource efficiency and conservation.
Other Environmental Certification in India
|
International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) released a flagship report titled “Agriculture and Conservation” which comprehensively explores the complex relationship between agriculture and conservation.
Impact of Agriculture on Biodiversity
- Negative Impacts
- Agriculture directly threatens 34% of species assessed on the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.
- Direct threats from agriculture include conversion of natural habitats to croplands, pasturelands, plantations and irrigation.
- Indirect impacts through introduction of invasive alien species, nutrient loading, soil erosion, agrochemicals, and climate change.
- Positive Impact: About 17% of species on IUCN Red List have agriculture documented as a habitat.
Impact of Biodiversity on Agriculture
- Positive Impact: Ecosystems support agriculture through two main categories:
- Provisioning services i.e. production of biomass and genetic materials, and
- Regulating and maintenance services i.e. climate regulation, sediment retention, nutrient cycling, water flow regulation, pollination etc.
- Negative Impact: Ecosystem disservices such as crop predation, pests and pathogens.

World Wildlife Fund (WWF) released the latest edition of its biennial ‘Living Planet’ report.
Key finding:
- Biodiversity loss: Wildlife population declined by 73% over the past 50 years (1970–2020).
- Freshwater populations have suffered heaviest declines followed by terrestrial and marine populations.
- Reasons for decline: Habitat loss, degradation, climate change, invasive species.
- Findings on India
- Adopting India's consumption patterns worldwide would need less than one Earth by 2050.
- Andhra Pradesh Community-Managed Natural Farming (APCNF) is a good example of the positive socio-economic impacts of nature-positive food production.
- Praised India’s millet mission.
National Tiger Conservation Authority's (NTCA) has given approval to develop Kaimur Wildlife Sanctuary (KWS) as Bihar’s second tiger reserve after Valmiki Tiger Reserve.
- NTCA is a statutory body established under Wildlife (Protection) Act of 1972.
About NTCA
- Location: Located on a Kaimur Hills plateau between the Son River (south) and Karmanasa River (west).
- It is spread over Central highlands (include Satpura-Maikal hills and Vindhya-Bagelkhand hills) and Chota Nagpur Plateau.
- It is linked to Bandhavgarh-Sanjay-Guru Ghasidas-Palamau tiger landscape.
- Fauna: leopards, wild boars, sloth bears, etc.
- Forest Type: Northern Tropical Mixed Dry Deciduous Forests
10th Wild Ass Population Survey conducted by Gujarat Forest Department has found a 26.14% (6,082 in 2020 to 7,672 in 2024) increase in the population of Indian Wild Ass.
Indian Wild Ass (Equus hemionus khur)
- About: One of the five subspecies of the Asiatic wild ass, referred to as ‘Ghudkhur’.
- Habitat: Arid zone of northwestern Indian subcontinent; presently only restricted to the Little Rann of Kutch (LRK) in Gujarat.
- Behavioral Characteristics: Solitary, Shy, present in low densities across its distribution range.
- Horns found only in adult males, for browsing preferred nutrient rich forage.
Conservation Status:
- IUCN Red List of Threatened: Near Threatened
- Wildlife Protection Act, 1972: Schedule I
- CITES: Appendix I
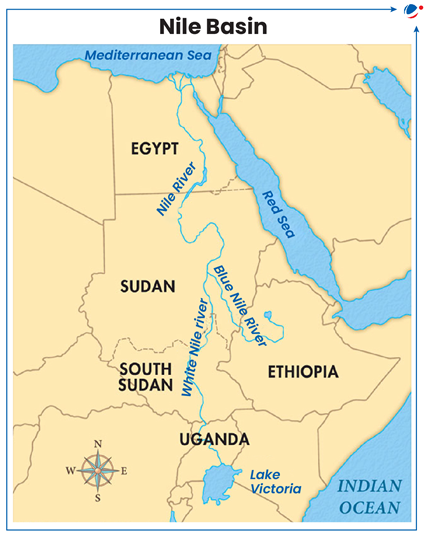
Recently, agreement on the equitable use of water resources from the Nile River basin has come into force despite the notable opposition of Egypt.
About Nile Basin
- The Nile is the world’s longest river and has a drainage area of nearly 10% of the landmass of the African continent.
- Runs through 11 countries from south to north.
- 2 main tributaries: White Nile (Originate from Burundi and Rwanda) and Blue Nile (originating in Ethiopia).
- Other tributaries: Sobat River, Atbara River, Bahr el Ghazal, etc.
A recent study by Indian Institute of Geomagnetism establishes the role of volcanism in shaping space weather.
Key findings of the study
- Ionospheric Disturbance: Volcanic eruptions produce strong atmospheric gravity waves triggering formation of Equatorial Plasma Bubbles (EPBs).
- EPBs, normally observed in the equatorial ionosphere, are depletions in ionospheric plasma density formed during post-sunset hours.
- Impacts Satellite Communication and Navigation Systems: Generated EPBs can impact satellite communication and satellite-based technologies.
Volcanism and its Impacts
- A volcano is an opening in Earth's crust through which lava, ash, and gases erupt. Recent incidents include Mount Ruang (Indonesia, 2024), Whakaari/White Island (New Zealand, 2024), etc.
Positive Impacts of Volcanic activities
- Short periods of cooling Earth’s atmosphere: Particles from volcanoes can cause temporary cooling by shading incoming solar radiation
- Source of geothermal energy: can provide free electricity for locals
- Improvement in soil fertility by ejected volcanic ash
- Provides Mining opportunities as magma brings valuable minerals to the surface.
- Others: Tourism potential; ash acts as soil fertilizer, etc.
Negative Consequences of Volcanic activity
- Impact on Climate: With the release of dust, ash, and other gases into the atmosphere.
- Lead to disasters such as Tsunami (E.g. Tonga eruptions (2022)
- Others: Leads to damage of lives, property, habitat, and landscapes
Article Sources
1 source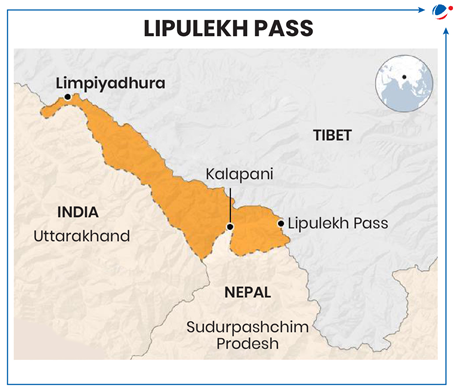
First batch of pilgrims viewed Mount Kailash (abode of Lord Shiva) from Old Lipulekh pass.
- Previously, pilgrims had to travel to Tibet Autonomous Region (TAR) to view the peak.
About Lipulekh Pass
- Location: International Mountain pass, above Kalapani valley, forming tri-junction between India, Nepal, and TAR (China).
- Situated in Vyas valley, Pithoragarh district, Uttarakhand inhabited by Bhutiya people.
- Significance: Ancient trade and pilgrimage route.
- Closed in 1962 by India fearing Chinese incursions and was reopened in 2020.






