India’s External Debt
As per Finance Ministry’s Quarterly External Debt Report (December 2024), External Debt has risen by 10.7% (from December 2023) mainly due to Valuation Effect.
- Valuation effect occurs due to the appreciation of US dollar vis-à-vis the Indian Rupee.
Other Key Highlights of the Report
- External Debt to GDP ratio: Stood at 19.1% (December, 2024) from 19.0% (September, 2024).
- Composition: US dollar Denominated Debt and Loans constituted the largest component.
- Debt service (Principal repayments plus interest payments): Declined by 0.1% (September – December, 2024).
- Long Term Vs Short Term Debt: Former recorded a marginal increase while the latter observed a marginal decline.

About External Debt
- Meaning: Refers to the money borrowed from sources outside the country, by both the Central Government and Corporations (External Commercial Borrowings).
- Predominantly denominated in other currencies viz., US Dollar, SDR, etc.,
- Sources: Could be foreign commercial banks, international financial institutions like IMF, World Bank, etc., or foreign governments.
Challenges with rising External Debt
- Repayment Burden: Since, it is usually denominated in other currencies, changes in exchange rate affects its repayment burden.
- Rising Inflation: Prolonged inflation further increases the interest rates, slowing down growth, resulting in a higher external debt to GDP ratio.
- Global Scenario: Global threat of stagflation may lower the demand for India’s exports affecting the debt service ratio.
- Tags :
- India’s External Debt
Liquidity coverage ratio (LCR)
The Reserve Bank of India has come up with new guidelines regarding LCR.
- RBI also said that banks need to assign a lower run-off factor on retail deposits.
- Run-off factor refers to the percentage of deposits that could be withdrawn by depositors in a stress scenario.
About Liquidity coverage ratio (LCR)
- It is the amount of High-Quality Liquid Assets (HQLAs) that financial institutions must have on hand to ensure they can meet their short-term obligations in the event of market turmoil.
- The LCR is a result of updates to the Basel Accords, regulations created by the Basel Committee on Banking Supervision.
- High LCR decreases money supply by requiring banks to hold a larger proportion of highly liquid assets.
- Tags :
- Liquidity coverage ratio (LCR)
IMF’s Global Financial Stability Report
The report, which is released semiannually, assessed the impact of geopolitical risks on global financial stability.
- According to the Report, Global geopolitical risks remain elevated, raising concerns about their potential impact on macro financial stability.
Geopolitical Risks
- Multiple threats to supply chains: Geopolitical rivalries, conflict, competition for resources, cyberattacks, etc.
- Tectonic shifts in power, economic centers and trade: New trade alliances and investment hubs are redefining global power dynamics.
- A fragmented tax environment. E.g., Minimum global tax is becoming adopted by many countries, while others are withdrawing from multilateral tax policy.
- Demographic, technological and cultural pressures on workforces: E.g., Aging populations, mass retirement, falling birth rates (in developed markets), culture wars, AI integration, etc.
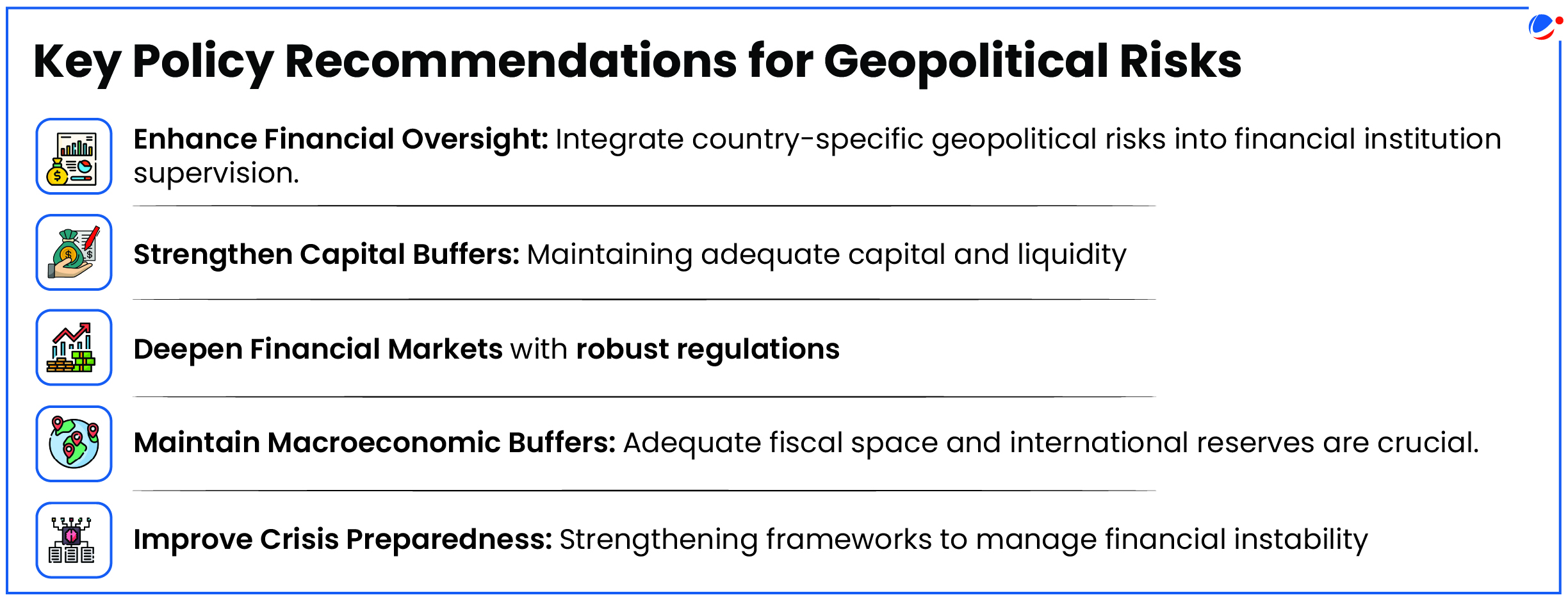
Implications of geopolitical risks
- Sovereign Risk: Increased military spending and economic downturns raise public-debt-to-GDP ratios, escalating fiscal sustainability concerns and sovereign risk.
- Financial Contagion: Geopolitical risks can spill over to other economies through trade & financial linkages, raising the risk of contagion.
- Macroeconomic Impact: Increased geopolitical risk can lead to economic disruptions, such as supply chain disruptions and capital flow reversals.
- Investor Confidence: Geopolitical risks generally lower investor confidence, leading to market uncertainty and increased volatility.
- E.g., The U.S.-China trade war significantly impacted stock prices in both economies.
- Tags :
- Global Financial Stability Report
Global Trade Outlook and Statistics 2025
It is released by the World Trade Organisation (WTO).
Major findings
- Under current conditions, the volume of world merchandise trade is likely to fall by 0.2% in 2025.
- The decline is expected to be particularly steep in North America, where exports are forecasted to drop by 12.6%.
- Severe downside risks exist, including the application of “reciprocal” tariffs and broader spillover of policy uncertainty.
- The report contains for the first time a forecast for services trade to complement its projections for merchandise trade.
- The volume of services trade is forecasted to grow by 4.0% in 2025.
- Tags :
- Global Trade Outlook and Statistics 2025
Articles Sources
UNCTAD Releases Technology and Innovation Report 2025
Report provides a roadmap for ensuring AI (Artificial Intelligence) drives inclusive growth rather than deepening divides.
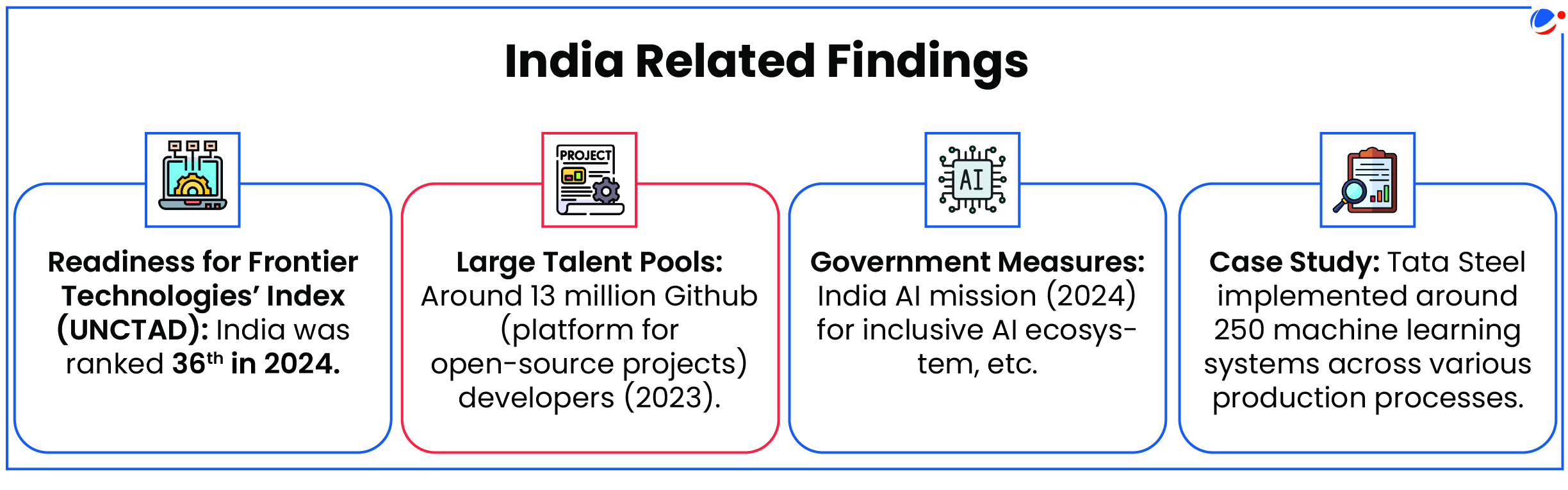
Key Findings of the Report
- Potential of AI: Globally, AI is expected to reach $4.8 trillion in market value by 2033.
- Impact on jobs: AI could impact 40% jobs worldwide, offering productivity gains along with concerns regarding automation and job displacement.
- Market dominance at National and Corporate Levels:
- 40% of global corporate R&D spending stems from 100 firms mainly in US and China.
- US accounts for 70% of global AI private investment.
Way Forward on Inclusive AI
- Promoting AI Adoption in Developing countries: By redesigning AI solutions around locally available digital infrastructure, lowering the skill barriers; building international partnerships, etc.
- Adopting Worker Centric Approach: Job workflows and tasks should be rearranged to integrate AI effectively.
- Role of the Government: Assessment of the national AI capacities across the three leverage points of infrastructure, data and skills.
- Tags :
- Technology and Innovation Report 2025
Articles Sources
International Standards of Accounting and Reporting
India secured an uncontested position in the United Nations Intergovernmental Working Group of Experts ISAR for 2025–2027 term.
About ISAR
- About: ISAR is a UN global forum of policy-makers, regulators, standard-setters and lead experts in the area of enterprise accounting and reporting.
- Mandate: To assist member States to improving the quality and international comparability of financial reporting and non-financial disclosure, such as environmental issues, corporate governance and corporate social responsibility.
- Mission: To facilitate investment, development and economic stability by promoting good practices in corporate transparency and accounting through policy frameworks and guiding tools.
- Sessions: It holds its annual sessions in Geneva to address emerging issues in enterprise accounting and reporting.
- Membership: ISAR allows for 34 formal members to serve three-year terms.
- These members include nine African, seven Asian, six Latin American, three Eastern European, and nine Western European and Other States.
- Tags :
- International Standards of Accounting and Reporting
- Financial reporting
Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE)
The year 2025 marks the 150 years of the Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE).
About BSE
- Established as ‘The Native Share & Stock Brokers’ Association’ in 1875, it is Asia’s first & world’s fastest Stock Exchange.
- In 2017, BSE became 1st listed stock exchange of India.
- Role: BSE provides an efficient and transparent market for trading in equity, currencies, debt instruments, derivatives, mutual funds.
- Regulated by: Securities Exchange Board of India (SEBI).
- SEBI is a statutory body under SEBI Act, 1992.
- Tags :
- Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE)
- Securities Exchange Board of India
Cape Town Convention and Protocol
Rajya Sabha passed ‘The Protection of Interests in Aircraft Objects Bill, 2025’ aiming to align it as per Cape Town Convention (Convention on International Interests in Mobile Equipment) and Protocol on Matters Specific to Aircraft Equipment.
About Cape Town Convention and Protocol
- Aim: Standardize transactions involving movable property, particularly high-value assets like aircraft, engines, and helicopters, to ensure creditors can enforce their rights in case of default.
- Adoption: Jointly by International Civil Aviation Organisation (ICAO) and UNIDROIT (International Institute for the Unification of Private Law) in 2001.
- Parties: 65 Parties (2016) [India signed in 2008].
- Tags :
- Cape Town Convention and Protocol
- Protection of Interests in Aircraft Objects Bill, 2025
Articles Sources
Nano Sulphur
TERI scientists have developed nano sulphur which reportedly increased mustard yield by 30-40%.
- DMH-11 is the genetically-modified mustard.
About TERI’s Nano-sulphur
- It is a completely green product that uses biological agents like plant promoting bacteria that secrete enzymes and metabolites.
- This makes it different from other nono-fertilizers such as nano urea and nano diammonium phosphate.
- Nano-sulfur has antibacterial and insecticidal properties.
- Benefits: Acts as a plant growth promoter, enhancing plant stress resistance, and improving the nutritional quality of plants, etc.
- Tags :
- Nano Sulphur
- Genetically modified mustard
Saline Aquaculture Hubs
Union Government is pushing for saline aquaculture hubs in Haryana, Punjab, Rajasthan, and Uttar Pradesh.
About Saline Aquaculture
- Meaning: It refers to the use of saline-affected lands (often unsuitable for traditional agriculture) for inland saline aquaculture.
- Aquaculture is the farming of aquatic organisms, including fish, molluscs, crustaceans and aquatic plants for enhancing production.
- Significance: Generate employment and livelihood opportunities by tapping the potential of saline land resources for aquaculture, Increase Aquaculture productivity, etc.
- Potential in India:
- Only 2, 608 hectares of the 58,000 hectares identified saline area from the above 4 states is being currently utilized.
- India stands as the second-largest producer of cultured shrimp globally, earning 65% of its seafood export value from shrimp alone, which can be better realized through Saline Aquaculture.
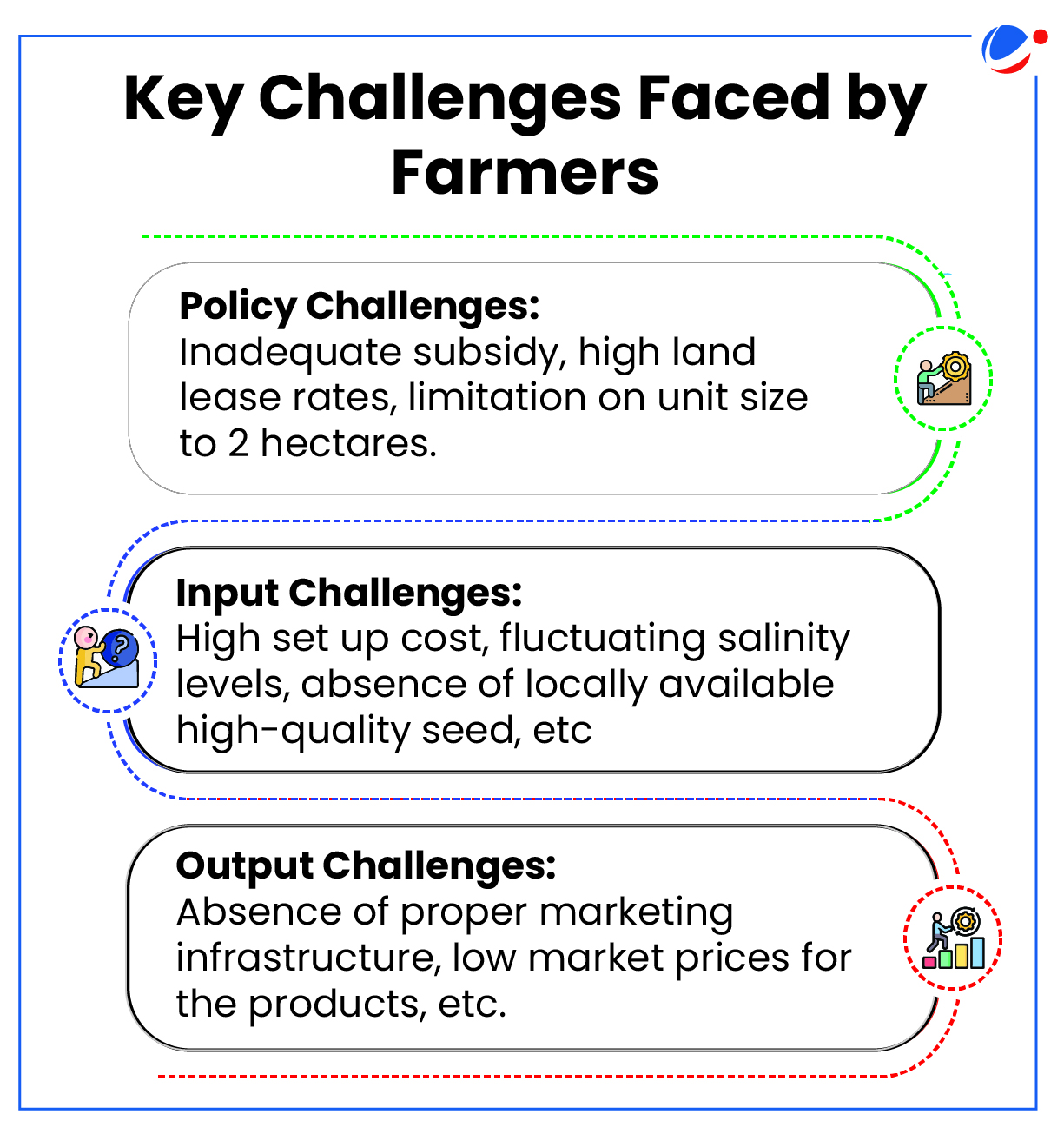
Measures to tap the potential of Saline Aquaculture
- Policy Reforms: Increasing the area limit from 2 hectares to 5 hectares, a National Level Committee to prepare a roadmap for the sustainable development of saline aquaculture in North Indian states.
- Improved marketing channels: Recommendations for establishment of an Integrated Aqua Park in Sirsa to improved marketing channels to be considered.
- Dissemination of Technical Knowledge: States to leverage Krishi Vigyan Kendras (KVKs) to identify new areas for saline aquaculture, and conduct outreach-based research.
- Tags :
- Aquaculture
- Saline Aquaculture Hubs



