The Indian government has announced that Pakistan nationals will not be permitted to travel to India under the SAARC Visa Exemption Scheme (SVES).
About SAARC Visa Exemption Scheme
- Launched: In 1992, following the decision at the 4th SAARC Summit held in Islamabad in 1988.
- Aim: Promote people-to-people contact and enhance regional cooperation among SAARC members.
- Currently, the list included 24 categories of entitled persons, which include Dignitaries, Judges of higher courts, etc.
Article Sources
1 sourceThe declaration addresses two pivotal themes: “Artificial Intelligence (AI) and the Future of Work” and “The Impacts of Climate Change on the World of Work and a Just Transition”.
- The meeting, held under Brazil’s Presidency in Brasília, was convened under the theme “Strengthening the Cooperation of the Global South for More Inclusive and Sustainable Governance”.
Key Highlights of the Declaration
- Supported by: ILO for advancing labour rights.
- The declaration commits BRICS nations to:
- Promote inclusive AI policies that balance innovation with worker protection.
- Advance social dialogue to ensure fair climate transitions.
- Strengthen South-South cooperation on labour governance, digital inclusion, and green job creation.
Significance of declaration for workers
- Harnessing AI for Decent Work: Equitable access to AI means ensuring that workers have a voice, through meaningful social dialogue.
- BRICS countries are uniquely placed to shape the transformations needed regarding the rights-based use of AI at work through South-South cooperation.” (ILO)
- Just Transition – Green Jobs, Inclusive Policies: 1.2 billion livelihoods are under threat from ecosystem collapse; 2.4 billion workers endure dangerous heat levels.
- Universal Social Protection: Protection gap is increasingly widening, including for platform workers with no safety net and the 83 per cent of people even lack basic coverage.
- Impetus to Social Justice: ILO commits to support BRICS through Global Coalition for Social Justice, offering normative guidance, research, and technical cooperation.
Article Sources
1 sourceIndia hosts 8th Meeting of Joint Committee on ASEAN-India Trade in Goods Agreement (AITIGA).
- The Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN), established in August 1967 in Bangkok, Thailand, is a group of 10 countries.
About AITIGA
- Genesis: Signed in 2009 and entered into force in 2010.
- Mandates: Each party shall accord National Treatment to goods of other parties in line with GATT, 1994.
- Trade: Bilateral trade between India and ASEAN reached USD 121 billion (2023-24).
- ASEAN constitutes for about 11% share in India’s global trade.
26/11 Mumbai Terror Attack Accused Extradited to India From the US
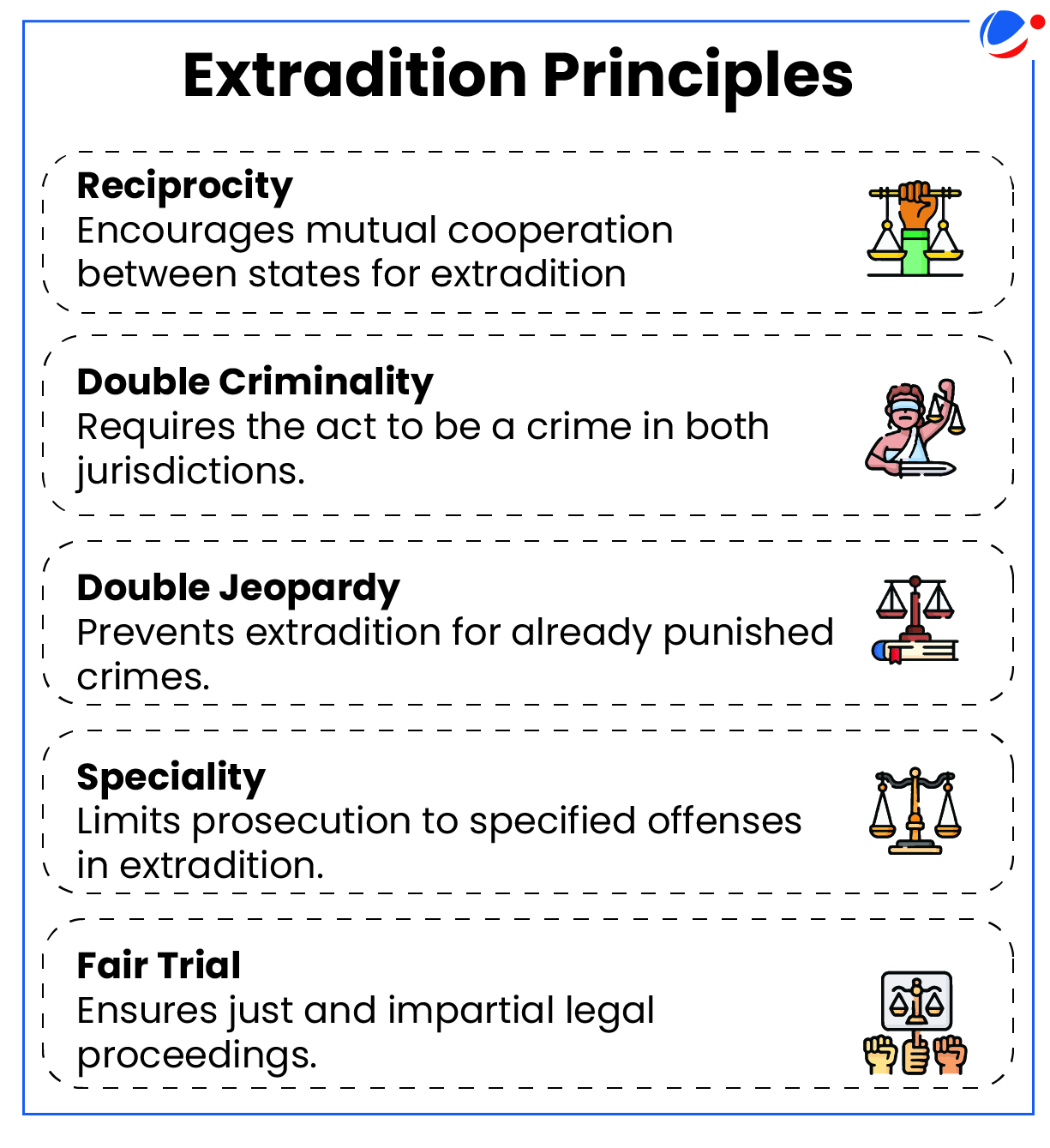
- According to the UN Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC), extradition means the surrender of any person who is sought by the requesting State for criminal prosecution for an extraditable offence.
- Extraditable offence refers to an offence provided for in extradition treaty with that State or the offence is punishable with at least 1 year of imprisonment either in India or in foreign State (in case of no treaty).
What is the framework for Extradition?
- In India:
- The Extradition Act 1962 (substantially modified in 1993) consolidated the law relating to the extradition of criminal fugitives from India to foreign states.
- The Ministry of External Affairs is the nodal authority for Extradition in India.
- India has extradition treaties with 48 nations, including Bangladesh and the USA.
- The Government of India finally decides on Extradition and this decision can be appealed in a higher court.
- The Extradition Act 1962 (substantially modified in 1993) consolidated the law relating to the extradition of criminal fugitives from India to foreign states.
- Globally: United Nations Model Treaty on Extradition (1990), UN Model Law on Extradition (2004), United Nations Convention against Transnational Organized Crime (2000), etc. are some of the international frameworks which deal with various principles of extradition.
Challenges in Extradition Law
|
India-Thailand inked joint declaration towards establishing strategic partnership.
- Strategic partnership, though less formal, is based on cooperation between the states on shared common objectives, primarily security but also extends to trade, economy, technology, etc.
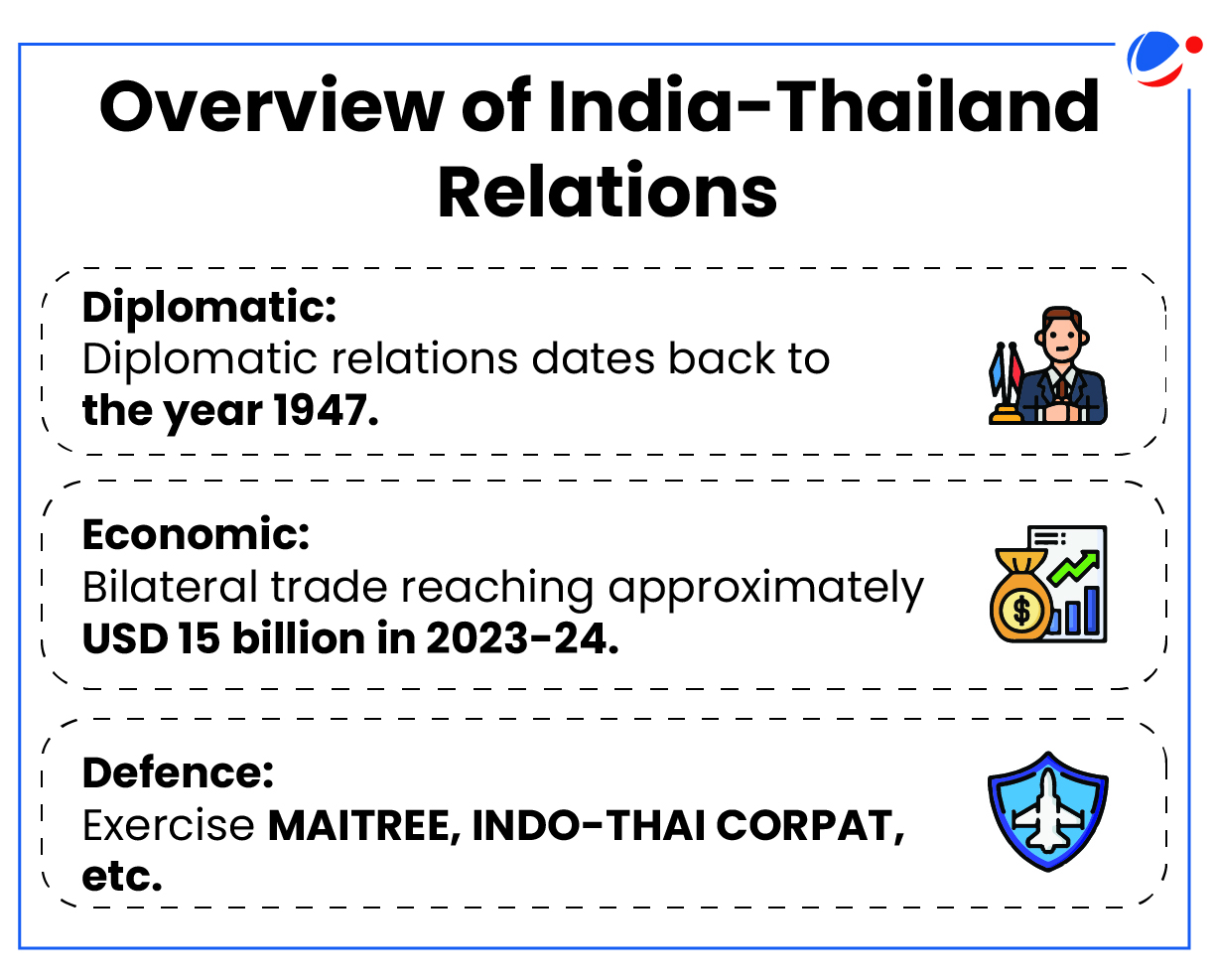
Significance of India-Thailand Strategic Partnership
- Mutually-Beneficial Goals: Both have shared interests in a free, open, transparent, rules-based, inclusive, and resilient Indo-Pacific and support for ASEAN (Association of Southeast Asian Nations) Centrality.
- ‘ASEAN centrality’ emphasizes the role of ASEAN as the driving force behind the geopolitics or geo-economics of the region.
- Strategic Location: Thailand is India’s Maritime Neighbour with key interest in regional peace.
- Complementing Policies: India’s “Act East” and Thailand’s “Act West” policies complement each other.
- Role in its Regional and Sub-regional Groupings: Thailand is an important partner of India in the ASEAN; Bay of Bengal Initiative for Multi-Sectoral Technical and Economic Cooperation (BIMSTEC), etc.
Other Key Agreements Inked
- MoUs on cooperation in various sectors: Development of National Maritime Heritage Complex (NMHC) at Lothal, Development of North Eastern Region (MDoNER), etc.
- Facilitate People-to People Contact: Establishment of an India-Thailand Consular Dialogue.
- Trade facilitation: Exploring the establishment of local currency-based settlement mechanism.

Recently, India has increased its claim in the Central Arabian Sea, as part of its ‘extended continental shelf’ by nearly 10,000 square km but also modified an earlier claim to avoid a long-standing dispute with Pakistan.
Dispute over the maritime boundary
- Exclusive Economic Zone: Coastal countries have an “exclusive economic zone,” (EEZ) which gives exclusive mining and fishing rights, upto 200 nautical miles from their coastlines.
- This area extends unbroken from their landmass all the way till the sea bed.
- All of this oceanic area is considered part of a country’s extended continental shelf.
- India made its first claim in 2009 in vast stretches of sea to a UN body, called the Commission on the Limits of the Continental Shelf (CLCS).
- Pakistan in 2021 objected claiming that the area was under ‘dispute’, specifically, Sir Creek.
- In March 2023, CLCS rejected the entirety of India’s claim in the Arabian Sea region. However, the Commission allowed countries to submit ‘modified claims.’
About Sir Creek
- It is a 96-km-long disputed tidal estuary.
- It extends into the Arabian Sea and roughly divides the Sindh province of Pakistan from the Kutch region of Gujarat.
- In 1947, India wanted it to be settled according to international principles of maritime law, called the Thalweg Principle (boundary can be fixed only in the middle of the navigable channel) in 1947.
- Pakistan, however, claimed that Sir Creek was not navigable, so the dispute could not be settled according to the Thalweg principle.
India formally revoked transshipment facility for Bangladesh exports from India.
- The 2020 agreement facilitated export of Bangladeshi goods through Indian Land Customs Stations (LCSs) to ports for destinations in third countries in Europe, West Asia, and beyond.
- India cited logistical challenges such as significant congestion at Indian ports and airports hindering India’s own export processes, as primary reason for revoking the agreement.
- However, decision also follows strained bilateral relations and recent remarks by Bangladesh government’s Chief Advisor that Bangladesh is the only guardian for all in the Indian Ocean Region (IOR), denouncing India’s role as Net Security Provider.
India’s role as Net Security Provider in IOR
- Geo-Strategic: India’s central position in the IOR, with a 7,500-km coastline and proximity to key chokepoints (e.g., Strait of Malacca, Bab al-Mandab).
- India’s MAHASAGAR (Mutual and Holistic Advancement for Security and Growth Across Regions) Vision, 2025 as an extension of the 2015 SAGAR doctrine.
- Maritime Security: India undertakes anti-piracy and counter-trafficking operations in the IOR, ensuring security of Sea Lines of Communication.
- Development and Humanitarian Assistance: India’s rapid response to the 2004 Indian Ocean tsunami, water crisis in Maldives (2004), economic crisis in Sri Lanka (2022), etc. establish its credentials as the first responder to the crisis in the IOR.
US President announced reciprocal 10% tariffs for several US trade partners, including Heard and McDonald Island
- The President called April 2 “Liberation Day” and declaring it “one of the most important days in American history.
About Islands
- Heard Island and McDonald Islands are uninhabited subantarctic islands in the Southern Ocean, with no permanent human population.
- They are administered by Australia.
- As the only volcanically active subantarctic islands they ‘open a window into the earth’, thus providing the opportunity to observe ongoing geomorphic processes and glacial dynamics.
- They are listed as UNESCO World Heritage Sites.
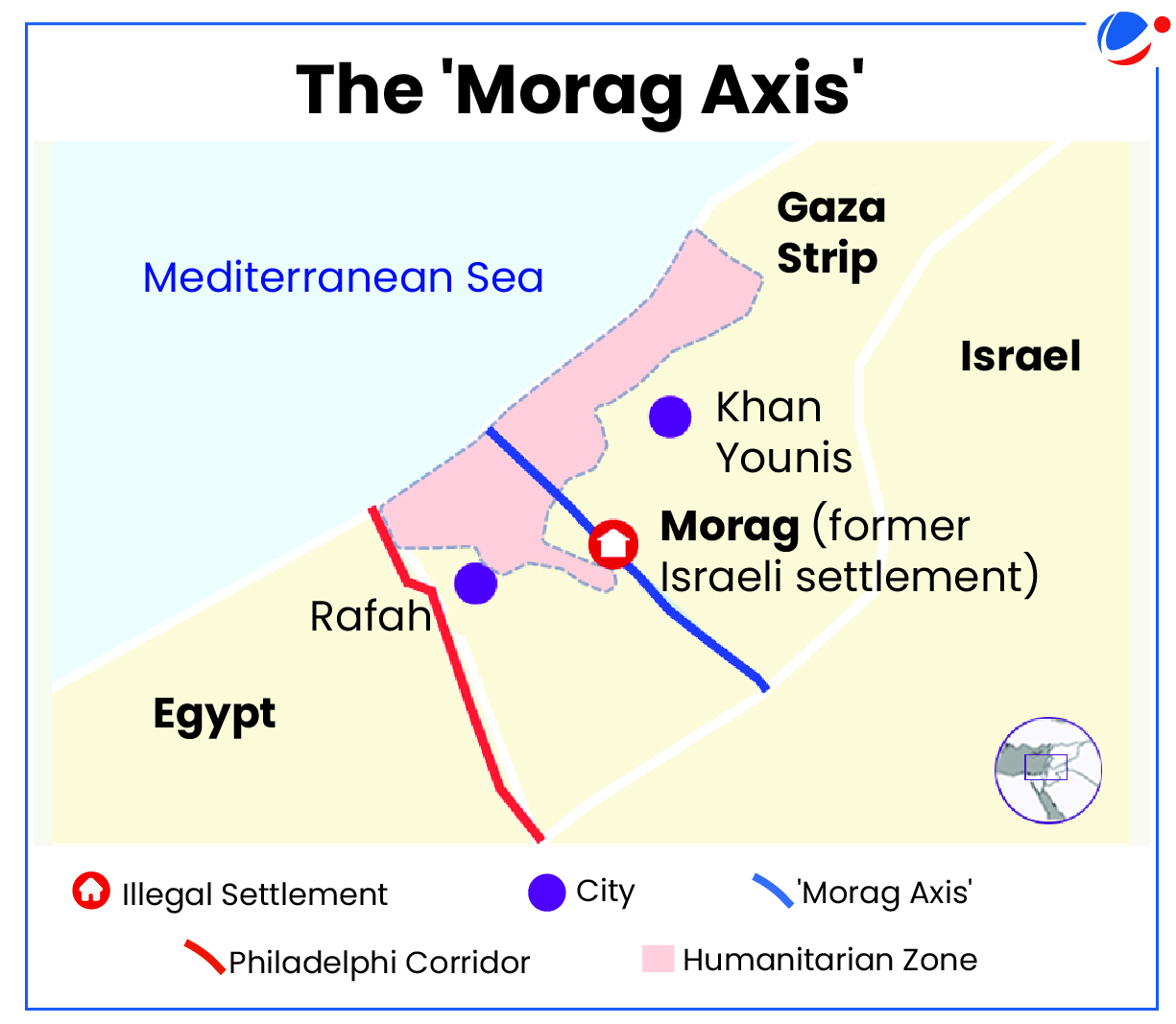
Israel has completed the takeover of a new security corridor known as the Morag axis.
Morag axis
- This area consists mainly of agricultural land located between Khan Younis and Rafah, stretching from east to west across the Gaza Strip.
- The name “Morag” refers to an illegal Israeli settlement that was established in the region between 1972 and 2005.





