Why in the News?
Recently, Supreme Court highlighted that in international jurisprudence, India was the first country to shift from an anthropocentric approach to an eco-centric one.
More on the News
- Supreme Court of India directed the Telangana Wildlife Warden to take immediate steps to protect the wildlife affected by the destruction of 100 acres of the Kancha Gachibowli "forest" area.
- This came in the backdrop of the Telangana Government's plan to auction some 400 acres of forested land adjacent to the University of Hyderabad to build IT parks, which led to massive student protests.
About Eco-centric Approach
- It prioritizes the well-being of the entire ecosystem and its components, viewing nature as valuable for its own sake, not just for human use.
- However, Anthropocentric approach, on the other hand, is based on the belief that human beings are the most important entity on earth, and other beings and things are valued primarily for their utility to humans.
- For example, in M.C. Mehta vs. Union of India (1986), the SC held that the right to live in a pollution-free environment is a fundamental right to life under Article 21 of the Constitution.
- However, Anthropocentric approach, on the other hand, is based on the belief that human beings are the most important entity on earth, and other beings and things are valued primarily for their utility to humans.
- This approach also found recognition in the deep ecology movement (by Arne Naess, a Norwegian philosopher).
- This movement fostered the idea that humans must radically change their relationship to nature from one that values nature solely for its usefulness to human beings to one that recognizes that nature has an inherent value.
- This approach is also backed by Interest theory which states that an individual can hold rights if his or her well-being is of intrinsic or ultimate value.
Difference between anthropocentric and an eco-centric Approach | ||
| Anthropocentric | Eco-centric |
Legal Rights | Legal rights are extended only to humans or human interests. | Nature (E.g. Rivers) can have legal rights. |
Ethical Basis | Considered a human being as an End.
| Egalitarian Approach |
Policy Approach | Environmental protection is reactive and human-interest driven. | Pro-active ecological preservation. |
Conservation Strategy | Utilitarian conservation (conserve what is useful). | Holistic conservation (conserve all biodiversity equally). |
Examples | Promoting Ecotourism (Linking conservation with economic activity). | Granting legal personhood to rivers or forests. Uttarakhand HC declared Ganga and Yamuna as legal persons with rights. |
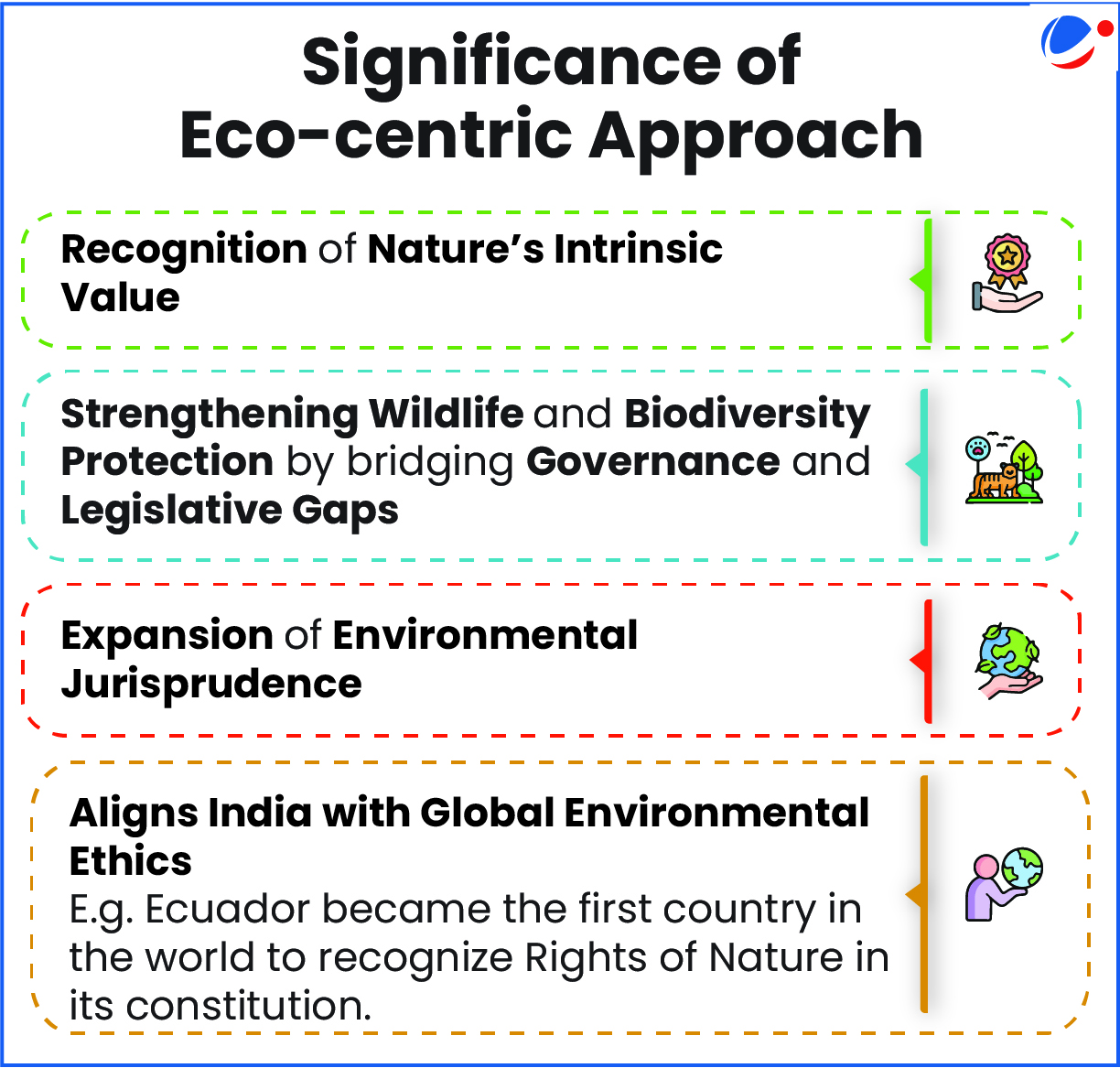
Key Driver/Facilitator to the Eco-Centric Approach
- Constitutional Mandate:
- Article 21 (Right to life and personal liberty)
- Article 48A (Directs the State to protect and improve the environment and wildlife) and Article 51A(g) (Fundamental Duty of citizens to protect natural resources)
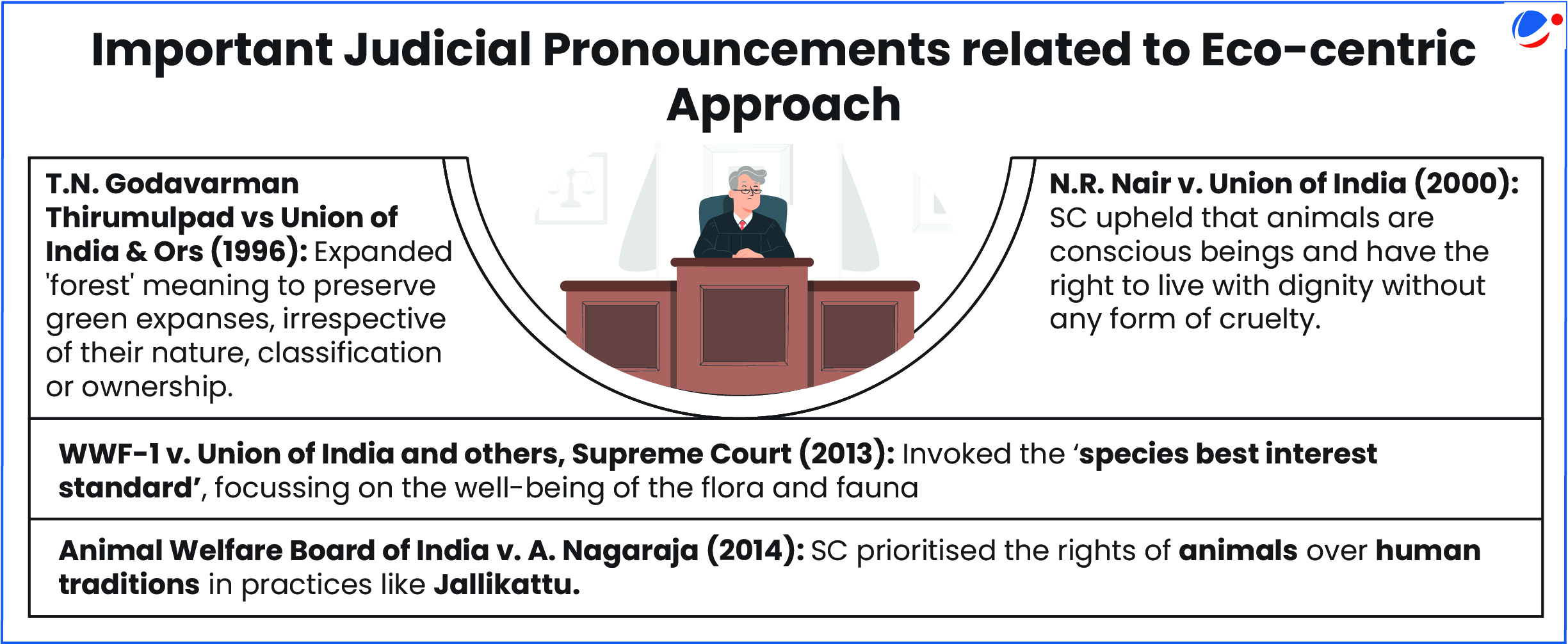
- Judicial Activism: Using this mechanism Judiciary gave voice to the voiceless, such as Animals, forests, etc.
- Public Interest Litigations (PILs) by activists, NGOs, and citizens played an instrumental role in it.
- Evolution of Environmental Jurisprudence: E.g. Public Trust Doctrine (nature belongs to all, held in trust by the state) and Precautionary Principle (act before harm occurs).
- Environmental Degradation and Ecological Crises: E.g. Deforestation, river pollution, etc.
- Cultural Ethos: Traditional Indian wisdom never believed humans to be superior to the environment and instead viewed ecology as a living being, of which humans were a part.
- Legislative Measures: E.g., Prevention of Cruelty to Animals Act (1960), Wildlife (Protection) Act (1972), etc.
Conclusion
India Judiciary's shift to an eco-centric approach marks a transformative step in Indian environmental jurisprudence, recognizing the intrinsic value of nature. It reaffirms the constitutional vision of harmonious coexistence between humans and the environment, ensuring long-term ecological justice.






