Recently, NSCSTI 2.0 framework was launched by the Minister of State for Personnel, Public Grievances and Pensions.
About National Standards for Civil Service Training Institutes
- Developed by: Capacity Building Commission (CBC) under Mission Karmayogi.
- Mission Karmayogi aims to create a competent and future-ready civil service working towards effective public service delivery and an Atmanirbhar Bharat.

- The primary objectives of NSCSTI are to establish a baseline of capacities within Central Training Institutes, provide a structured tool to enhance the management of these institutes, and standardise capacity building by setting clear procedures for civil service training institutes.
- The NSCSTI 2.0 framework introduces
- hybrid and AI-driven learning models,
- incorporates an inclusive design suitable for all levels of government training institutes, and
- fosters the adoption of best practices by removing barriers between the public and private sectors.

Article Sources
1 source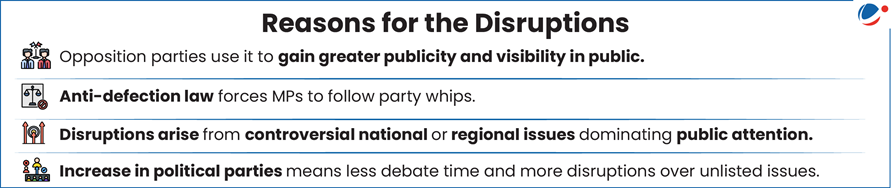
In the 17th Lok Sabha session, Lok Sabha functioned for 88% of its scheduled time, while Rajya Sabha worked for 73%.
- In the 1950s, the Indian Parliament met for 120-140 days every year, now the number ranges between 60 to 70 days.
Issues with Parliamentary Disruptions
- Weakening Democratic Accountability: Parliamentary debates let elected leaders question the government, but disruptions hinder this key part of democracy.
- Monetary cost: The cost of running Parliament is around Rs 2.5 lakh per minute.
- Eroding Public Trust in Parliament: Frequent disruptions shift MPs’ focus from solving important issues to stalling proceedings.
Measures that can be adopted to address parliament disruption
- Ensuring dedicated time for Opposition: For e.g., the British Parliament sets aside 20 days each year for the opposition to decide the agenda.
- Strengthen ethics committees: To monitor and report disruptions, ensuring accountability.
- Annual Parliamentary Calendar: Calendar of sittings should be announced at the beginning of each year for limited flexibility.
Member of Parliaments across party lines submit motion in Parliament to remove Justice Yashwant Varma.
- A total of 145 Lok Sabha members have signed a motion against Justice Verma under Articles 124, 217, and 218 of the Constitution.
- Also, the Rajya Sabha Chairman received a motion for the removal signed by more than 50 members of Rajya Sabha.
Constitutional provisions regarding removal of judges
- Article 124(4): It deals with removal of judges of the Supreme Court.
- Grounds for Removal : Proven misbehavior and incapacity.
- Article 124(5): It deals with the power of parliament to regulate the procedure for the presentation of an address and for the investigation and proof of the misbehavior or incapacity of a Judge under clause (4)
- Procedure is regulated by Judges Enquiry Act (1968). (enacted under article 124(5)).
- Article 217(1)(b): It deals with removal of a Judge of a High Court.
- It states that a High Court Judge may be removed from his office by the President in the manner provided in clause (4) of article 124 for the removal of a Judge of the Supreme Court.
- Article 218: It extends the Applicability of clause (4) and clause (5) of article 124 to High courts.
Steps in removal process
Initiation |
|
Committee formation and Investigation |
|
Parliamentary Approval |
|
Presidential order |
|
Note: There is no mention of word impeachment for removal of judges in the constitution. | |
Recently, NSCSTI 2.0 framework was launched by the Minister of State for Personnel, Public Grievances and Pensions.
About National Standards for Civil Service Training Institutes
- Developed by: Capacity Building Commission (CBC) under Mission Karmayogi.
- Mission Karmayogi aims to create a competent and future-ready civil service working towards effective public service delivery and an Atmanirbhar Bharat.

- The primary objectives of NSCSTI are to establish a baseline of capacities within Central Training Institutes, provide a structured tool to enhance the management of these institutes, and standardise capacity building by setting clear procedures for civil service training institutes.
- The NSCSTI 2.0 framework introduces
- hybrid and AI-driven learning models,
- incorporates an inclusive design suitable for all levels of government training institutes, and
- fosters the adoption of best practices by removing barriers between the public and private sectors.

Article Sources
1 sourceParliament has passed the Bills of Lading Bill 2025.
About Bills of Lading Bill 2025
- It aims to update and simplify the legal framework for shipping documents.
- It will replace the Indian Bills of Lading Act, 1856.
- A bill of lading refers to a document issued by a freight carrier to a shipper.
- It contains details including the type, quantity, condition, and destination of goods being carried.




