Himalayan Outpost for Planetary Exploration (HOPE) is a specially designed Habitat Module for crew living and a Utility Module for operations and support systems which are interconnected for seamless workflow.
The HOPE station set up by ISRO aims to simulate space-like conditions on Earth to aid research for future interplanetary missions.
About HOPE Mission
- Led by: ISRO’s Human Space Flight Centre (HSFC), with industry partners and top Indian institutions.
- Objectives
- Simulates extraterrestrial environments like the Moon and Mars.
- Enables testing of human survival, health protocols, and equipment in space-like environments.
- Studies to be conducted:
- Epigenetics, genomics, physiology, psychology.
- Sample collection and microbial analysis techniques.
- Validation of health monitoring and planetary surface operation protocols.
- Why Tso Kar Valley was chosen?
- For Mars-like conditions: High UV radiation, Low atmospheric pressure, Extreme cold and Saline permafrost
- Supports both technological tests and astrobiology research.
- Part of broader analog missions trend globally, aimed at preparing for long-term extra-terrestrial human missions.
- Other similar research stations across the World: Mars Desert Research Station of the US, Flashline Mars Arctic Station of Canada, and BIOS-3 of Russia.

Article Sources
1 sourceKey Features of LMLV
- Design: Improved version of the NGLV (Next Generation Launch Vehicle).
- As tall as a 40-storey building.
- Purpose: Lunar missions, including India's first human mission to the Moon planned by 2040.
- Payload: It can carry 80 tonnes to low Earth orbit (LEO) or approximately 27 tonnes to the Moon.
- 3 Stages: Liquid propellent for its first two stages and a cryogenic propellant for its third stage.
ISRO's Key Launch Vehicles and Capabilities
- PSLV (Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle): ISRO's workhorse, a third-generation vehicle with liquid stages, capable of launching satellites into Sun-synchronous Polar Orbit, LEO, Geosynchronous Transfer Orbit (GTO) (e.g., Chandrayaan-1, Mars Orbiter Mission).
- GSLV (Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle): A fourth-generation, three-stage vehicle designed to launch 2.0-ton class satellites into GTO for communication satellites.
- LVM 3: A heavy-lift, three-stage vehicle capable of carrying 4-ton class satellites to GTO or about 10 tons to LEO (Chandrayaan-2 and 3).
- It is proposed to be used for Bharatiya Antariksh Station.
- SSLV (Small Satellite Launch Vehicle): Three-stage, all-solid propulsion vehicle designed for launching Mini, Micro, or Nano satellites (10 to 500 kg mass).
26 major tech companies, including Amazon, Google, Microsoft, and IBM, have voluntarily signed the EU Commission’s AI Code of Practice on GPAI.
- Code is voluntary, signatories may benefit from enhanced legal certainty and a smoother transition into the binding requirements of the EU AI Act slated to take effect within the next two years.
- The code has three chapters i.e. transparency, copyright and Safety & Security
- About EU AI Act
- EU AI Act is the world’s first comprehensive AI law.
- The act takes a risk-based approach to regulation, applying different rules to AI according to the risk they pose.
- It ensures clearer accountability for AI providers, with a direct impact on businesses using generative AI through their value chains and third-party risk management.
- Much like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), the EU AI Act is anticipated to become a global standard, aiming to ensure AI's positive rather than negative effects on lives worldwide.
- Compliance: Penalties for non-compliance are significant—up to 7% of global turnover.
- Key concerns raised by companies
- Code introduces legal uncertainties for model developers and extends beyond the scope of the forthcoming AI Act.
- Regulatory complexity and administrative burdens may impact Europe’s AI competitiveness
Stanford scientists have created password-protected mind reading Brain-Computer Interface (BCI).
The innovation ensures brain-computer interfaces respect user privacy by requiring mental passwords before decoding thoughts into text or audio.
What is a Brain-Computer Interface?
- A BCI enables direct brain-to-device communication, translating neural signals into commands.
- This bypasses muscular control, allowing users to operate applications with thought alone.
- BCIs acquire brain activity (via invasive implants or non-invasive wearables), process signals, and send commands, with feedback crucial for user adaptation.
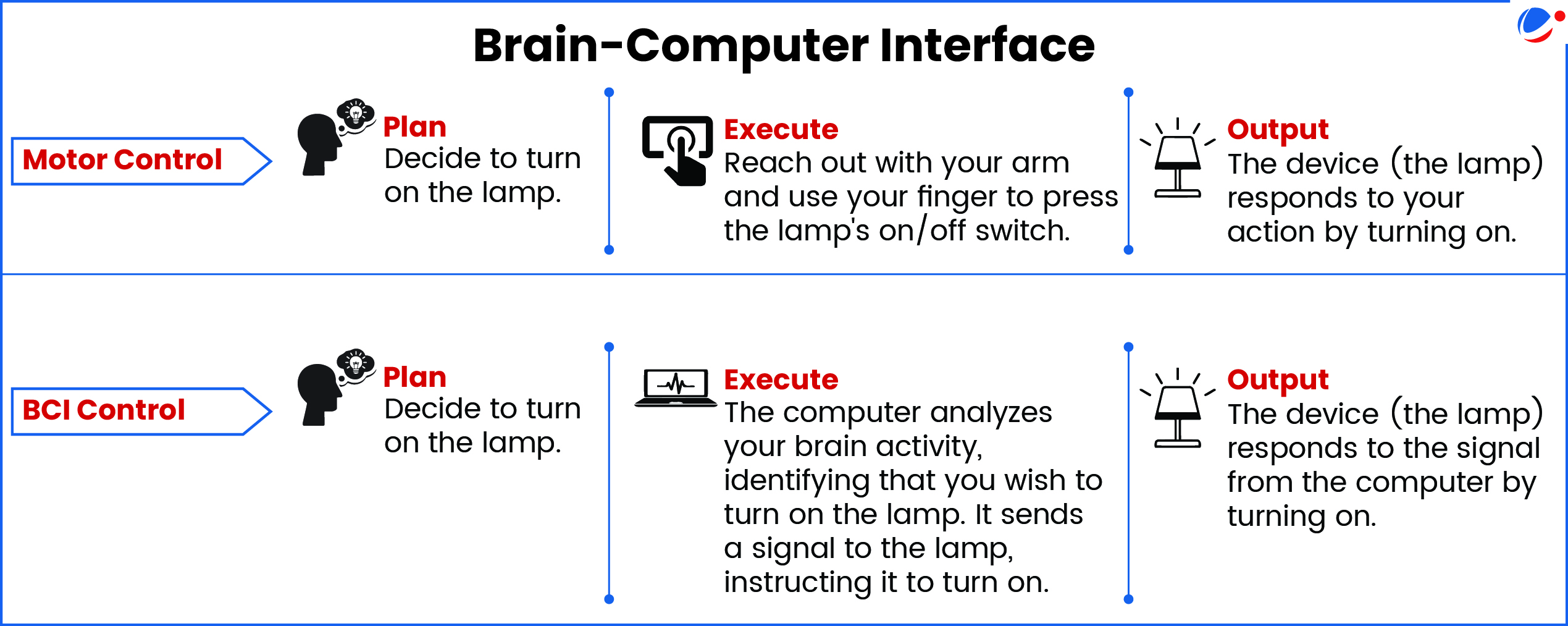
Key Applications of BCIs:
- Medical: Restoring mobility and speech for patients with paralysis, ALS, or stroke.
- Mental Wellness: Providing feedback for mental health management.
- Gaming/Industry: Enabling immersive gaming and decision support systems.
- Cognitive Enhancement: Potential for enhancing memory, attention, and decision making.
Key Concerns Related to BCIs:
- Cybersecurity: Risks like brain tapping (intercepting private thoughts/beliefs), misleading stimuli attacks (mind control), and adversarial attacks on AI components.
- Privacy: Protecting sensitive neural data from unauthorized access.
- Cognitive Liberty: Threat to an individual's mental self-determination.
- Health Impacts: Unclear long-term consequences of BCI use.
- Regulatory & Cost: Lack of standardized regulations and high costs limit accessibility.
Way Forward
- Robust Regulations: Implementing tailored data privacy laws, ensuring transparency and informed consent.
- Enhanced Security: Developing BCI-specific access controls and defense strategies.
- Establishing neurorights: To safeguard mental privacy, cognitive autonomy, and freedom of thought of individuals from exploitation and unauthorized interference.
Ministry of Road Transport and Highways launched FASTag Annual Pass facility.
- Annual Pass eliminates the need to frequently recharge FASTag through one-time fee of Rs. 3,000 for one year or 200 toll plaza crossings.
About FASTAG
- It is a device that employs Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technology for making toll payments directly from account while the vehicle is in motion.
- RFID consists of tags and readers and employs radio waves to communicate information of objects or people to nearby readers.
- It is a short-range technology.
- It is managed by National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI) and the National Highways Authority of India (NHAI).
Proposed Linear Induction Motor (LIM)-based hyperloop mobility system will connect Jawaharlal Nehru Port Trust in Navi Mumbai to the upcoming Vadhavan Port in Palghar district.
About Hyperloop Mobility System
- In 2013, the CEO of SpaceX, Elon Musk, proposed a concept of ultra-high-speed rail (UHSR) called hyperloop and open-sourced it.
- It is basically a magnetic levitation (maglev) system where pods travel at ultra-high speeds through low-pressure tubes.
- Its Functioning and Key Components
- Hyperloop functions in a sealed tube with minimal air resistance, utilizing vacuums and magnetic levitation for hovering.
- Linear Induction Motors (LIM) propels pods silently enabling the theoretical speed of 1,200 km/h.
- Key components include steel tubes (100Pa pressure), pressurized capsules, a compressor for airflow, and air bearing suspension.
- Advantages: Ultra-high speeds (e.g., Mumbai-Pune in 25 mins), energy efficiency (potentially carbon-free), noise reduction, and logistics redefinition (moving cargo quickly and efficiently).
- Issues with technology: Conceptual status, high costs ($25-$27 million/mile for technology), safety concerns (fire in pods, difficult evacuation), vacuum maintenance challenges, demanding straight-line infrastructure requiring new regulations etc.
Substantial financial backing, continuous research and development complemented by new regulatory frameworks are crucial for overcoming technical and safety challenges of hyperloop technology.
Union Health Ministry launched State Health Regulatory Excellence Index (SHRESTH), a national initiative to benchmark and strengthens state drug regulatory systems.
About SHRESTH
- Proposed by the Central Drugs Standard Control Organization (CDSCO).
- Aim: To drive improvements in the performance of state drug regulatory authorities across India, ensuring drug safety and quality standards are consistently met.
- It will have Indices based on five key themes: Human Resources, Infrastructure, Licensing Activities, Surveillance Activities and Responsiveness.







