Why in the News?
Recently, Lok Sabha held a special discussion on Critical Role of the Space Programme for Viksit Bharat by 2047.
More on the News
- The discussion highlighted that Space experiments conducted by Subhanshu Shukla personify India as Vishwabandhu Bharat (global friend).
- Subhanshu Shukla travelled to the International Space Station (ISS) aboard the Axiom-4 (Ax-4) Mission.
- He is India's first astronaut aboard the ISS and only the second Indian to travel to space after Rakesh Sharma in 1984.
Critical Role of Space Programme/Technology
Space programme/Technology will play a pivotal role in addressing India's critical challenges while simultaneously unlocking new opportunities for growth and development
Sector/Sphere | Current Challenges | Space-based Solutions |
Agriculture & Food Security | Erratic monsoons due to climate change; low farm productivity; poor crop forecasting | INSAT-3D/3DR provide weather forecasting; Resourcesat supports crop monitoring and yield estimation |
Infrastructure | Lack of integrated planning; delays in project implementation | PM Gati Shakti uses ISRO imagery & spatial tools to integrate projects like Bharatmala, Sagarmala, railways, etc. |
Disaster Management | High vulnerability to floods, cyclones, landslides, earthquakes, forest fires | ISRO's Disaster Management Support (DMS) Programme enables real-time monitoring, early warning, and post-disaster assessment |
Security & Defence | Border surveillance gaps; communication vulnerabilities; emerging space threats | GSAT-7 & RISAT strengthen secure communication & surveillance; Mission Shakti (2019) demonstrated anti-satellite capability |
Strategic Autonomy | Dependence on US GPS for navigation | NavIC (Navigation with Indian Constellation) provides indigenous navigation services |
Climate Change & Environment | Deforestation, glacier retreat, land degradation, ocean warming | NISAR (NASA-ISRO mission) will study land & ice deformation, ecosystems, and oceans |
Healthcare Delivery | Limited access to healthcare in remote areas | ISRO's Telemedicine Project |
Education | Rural-urban education divide; limited digital learning infrastructure | EDUSAT provides distance learning & educational broadcasting |
Transparency & Accountability | Leakages & poor monitoring in welfare schemes | Geo-tagging of MGNREGA assets ensures accountability and transparency |
Water Management | Depletion of groundwater; poor watershed planning | Bhuvan–SRISHTI Geoportal enables monitoring of Integrated Watershed Management Programme (IWMP) projects |
How progress in Space Sector makes India Vishwabandhu?
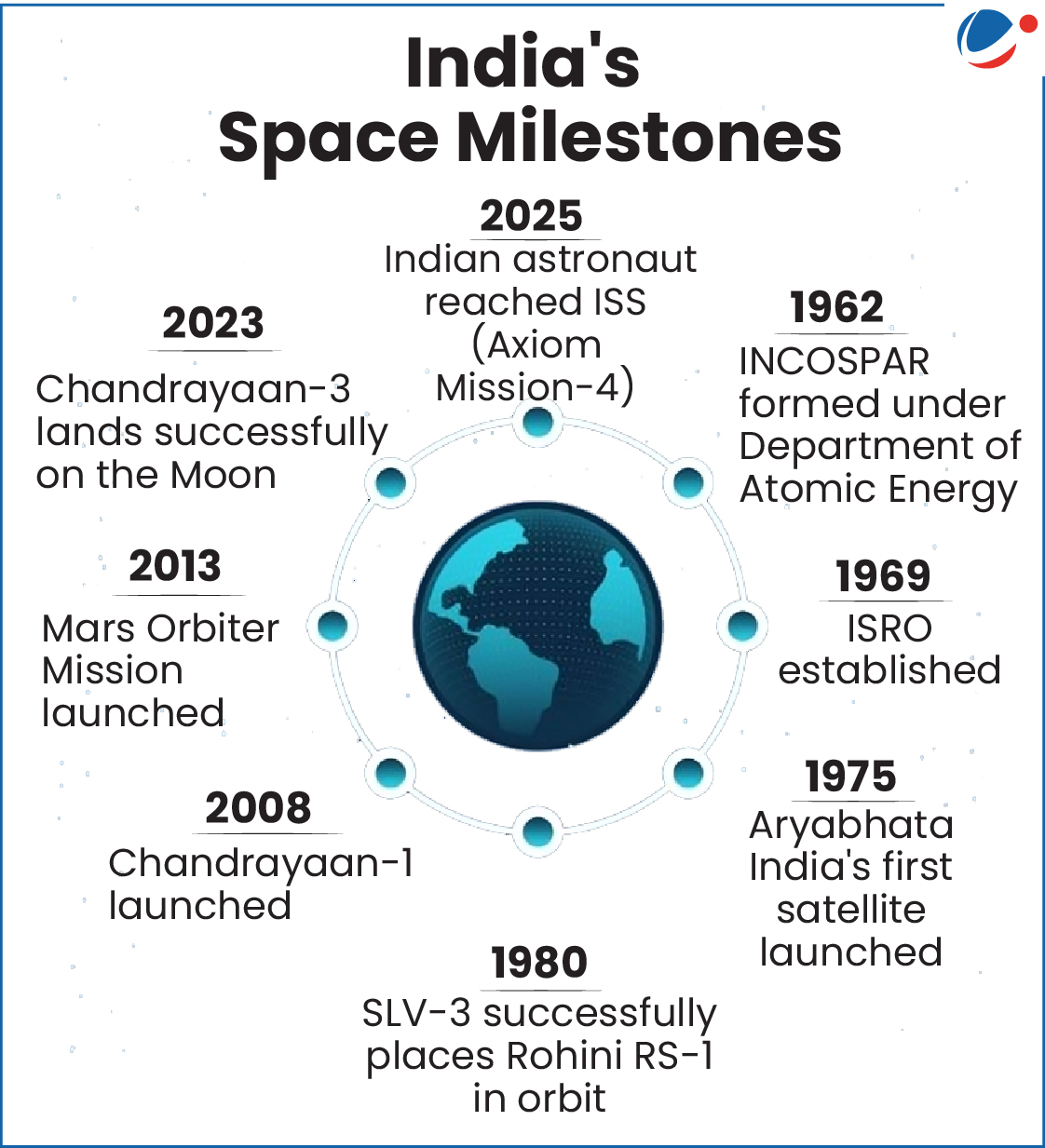
- Global Collaboration: NISAR is termed "India's scientific handshake with the world", symbolizing international collaboration by adhering to global standards for docking and interoperability.
- Regional Leadership and Support: In 2017 launched South Asia Satellite (GSAT-9) for the South Asian region (except Pakistan).
- Neighbouring countries which fall within the NavIC service area can use NavIC services.
- Sharing Technology, Expertise, & Data for Universal Benefit: E.g., Chandrayaan-3 datasets are available on PRADAN (Policy based data Retrieval, Analytics, Dissemination and Notification system) for the scientific community.
- Capacity Building Initiatives: Programs like UNNATI (UNispace Nanosatellite Assembly & Training by ISRO) offer international training on nanosatellite development.
- Cost-Effectiveness & Reliability: E.g., Mars Orbiter Mission (MOM) was most economical interplanetary mission in the world and paved way for cost-effective access to deep space.
- Over 400 satellites for 34 nations have been launched on India's launch vehicles.
- Responsible Space Player: India's Debris-Free Space Missions (DFSM) initiative, aiming for all Indian space missions to be debris-free by 2030, demonstrates a commitment to ensuring a safe, secure, and sustainable outer space for future generations.
- Humanitarian Aid: ISRO is member of the COSPAS–SARSAT, an international satellite-based search and rescue (SAR) system.
Recent policy intervention for the rapid development in space sector
- India Space Policy 2023: Policy was launched to pursue a holistic approach by encouraging and promoting greater private sector participation in the entire value chain of the Space Economy.
- FDI and Startup Ecosystem: The amended Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) policy allows up to 100% FDI in manufacturing components for space systems under the automatic route.
- This progressive environment has fueled the growth of over 300 space startups in recent years, significantly boosting innovation
- New Institutional Framework: NewSpace India Limited (NSIL) acts as ISRO's commercial arm, promoting and commercializing its products and services and enabling industries to undertake high-tech space activities.
- The Indian National Space Promotion & Authorisation Centre (IN-SPACe) serves as a single-window facilitator for private sector participation in all space activities, from launches to orbital slot filings and data dissemination.
Conclusion
India's space programme is a driver of national growth, global cooperation, and sustainable development. With clear milestones such as establishing the Bharatiya Antariksh Station (BAS) by 2035 and launching a crewed lunar mission by 2040, India is steadily positioning itself as a leader in space exploration. By combining innovation, inclusivity, and international collaboration, India's space journey embodies the vision of Viksit Bharat@2047.



