It has been awarded jointly to Victor Ambros and Gary Ruvkun for the discovery of microRNA and its role in post-transcriptional gene regulation.
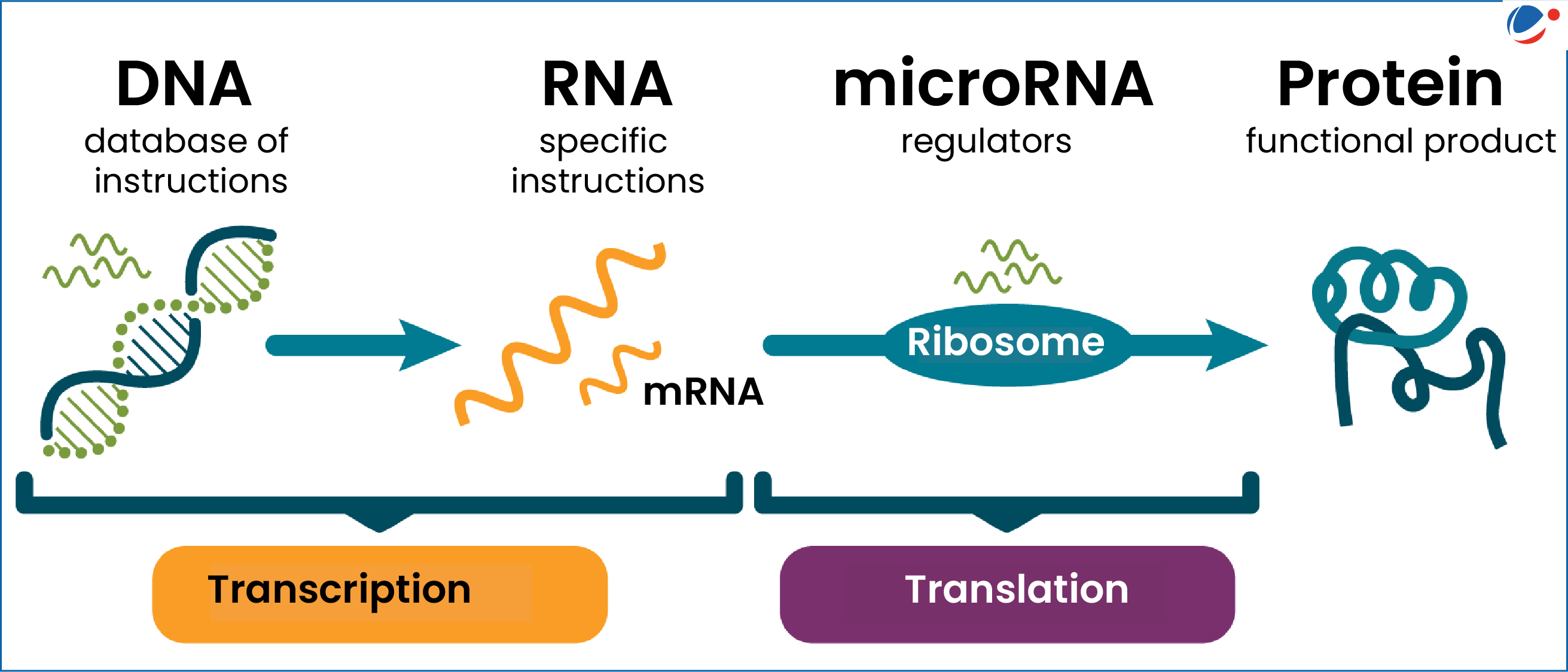
- Gene regulation is how a cell controls which genes, out of many genes in its genome, are expressed, allowing for production of a specific protein.
- Genetic information flows from DNA to messenger RNA (mRNA), via a process called transcription, and then on to the cellular machinery for protein production.
- Human organs and tissues consist of different cell types, all with identical genetic information stored in their DNA.
- However, due to gene regulation, these different cells (like muscle cells, nerve cells etc.) express unique sets of proteins, enabling them to perform their specialized functions.
About microRNA
- microRNAs are small non-coding RNA (single-stranded molecules playing key role in turning DNA instructions into proteins) that helps cells regulate gene expression.
- microRNA controls gene expression by binding with mRNA and preventing them from being translated into proteins or by degrading mRNA altogether.
- There are more than a thousand genes for different microRNAs in humans, and gene regulation by microRNA is universal among multicellular organisms.
Other Roles of microRNA
|




