The study depicted the potential of teal carbon as a tool to mitigate climate change, if the anthropogenic pollution in the wetlands can be controlled.
- Study also reveals elevated methane emissions can be reduced by use of a specialized type of biochar, which is a form of charcoal.
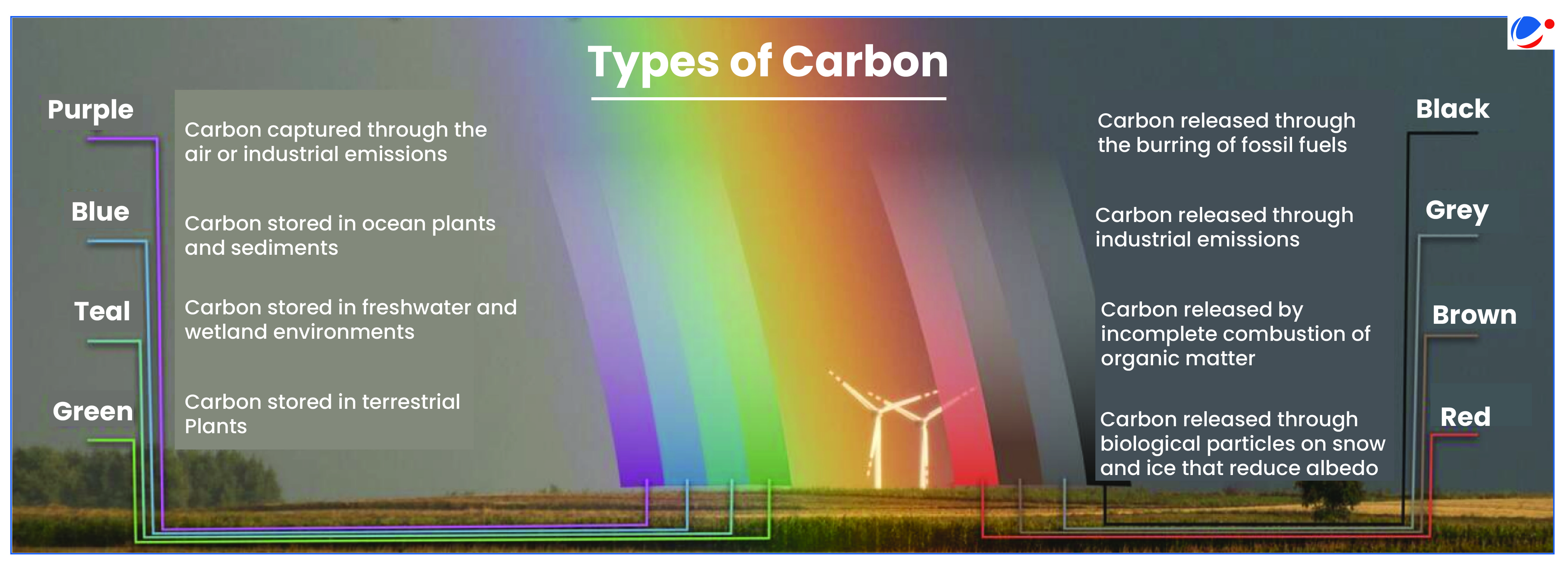
About Teal Carbon
- Teal carbon refers to carbon stored in non-tidal freshwater wetlands, encompassing carbon sequestered in vegetation, microbial biomass, and dissolved and particulate organic matter.
- Teal carbon, being a color-based terminology (refer infographics), reflects the classification of the organic carbon based on its functions and location rather than its physical properties.
- In contrast, black and brown carbon are produced by incomplete combustion of organic matter and contribute to global warming.
- Significance: It contributes to an increase in the ground water level, flood mitigation and heat island reduction, supporting a sustainable urban adaptation.
About Keoladeo National Park (Bharatpur, Rajasthan)
- Declared a national park in 1982 and a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1985.
- Home to over 370 species of birds and animals like pythons, Siberian cranes etc.
- Placed on the Montreux Record (Ramsar Convention) in 1990 due to "water shortage and an unbalanced grazing regime”.







