EEJ model will help to understand the EEJ’s impact on orbiting satellite, Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS)-based navigation/positioning and other satellite communication links as well as electrical power grids.
About the Equatorial ElectroJet (EEJ)
- EEJ: It’s a ribbon of intense 100 kA (kiloamperes) current flowing in Earth's ionosphere (Earth’s Upper atmosphere) at 100km altitude.
- EEJ’s (North‐South) width: It’s of a few hundred kilometres (∼600 km).
- Genesis: It is formed in Earth's magnetic equator, where magnetic field lines run parallel to Earth's surface, leading to an intense current density in the ionosphere.
- Path of travelling: EEJ travels along magnetic equator(See image).
- Typically, the EEJ current flows eastward during the day, and reverses direction in the night-time & produce a characteristic magnetic signature both on ground and in space (measured by magnetometers).
Effects of EEJ
- EEJ intensifies Earth's geomagnetic field near equator.
- EEJ disruptions impact power infrastructure and electricity monitoring systems across equatorial regions.
About Magnetic equator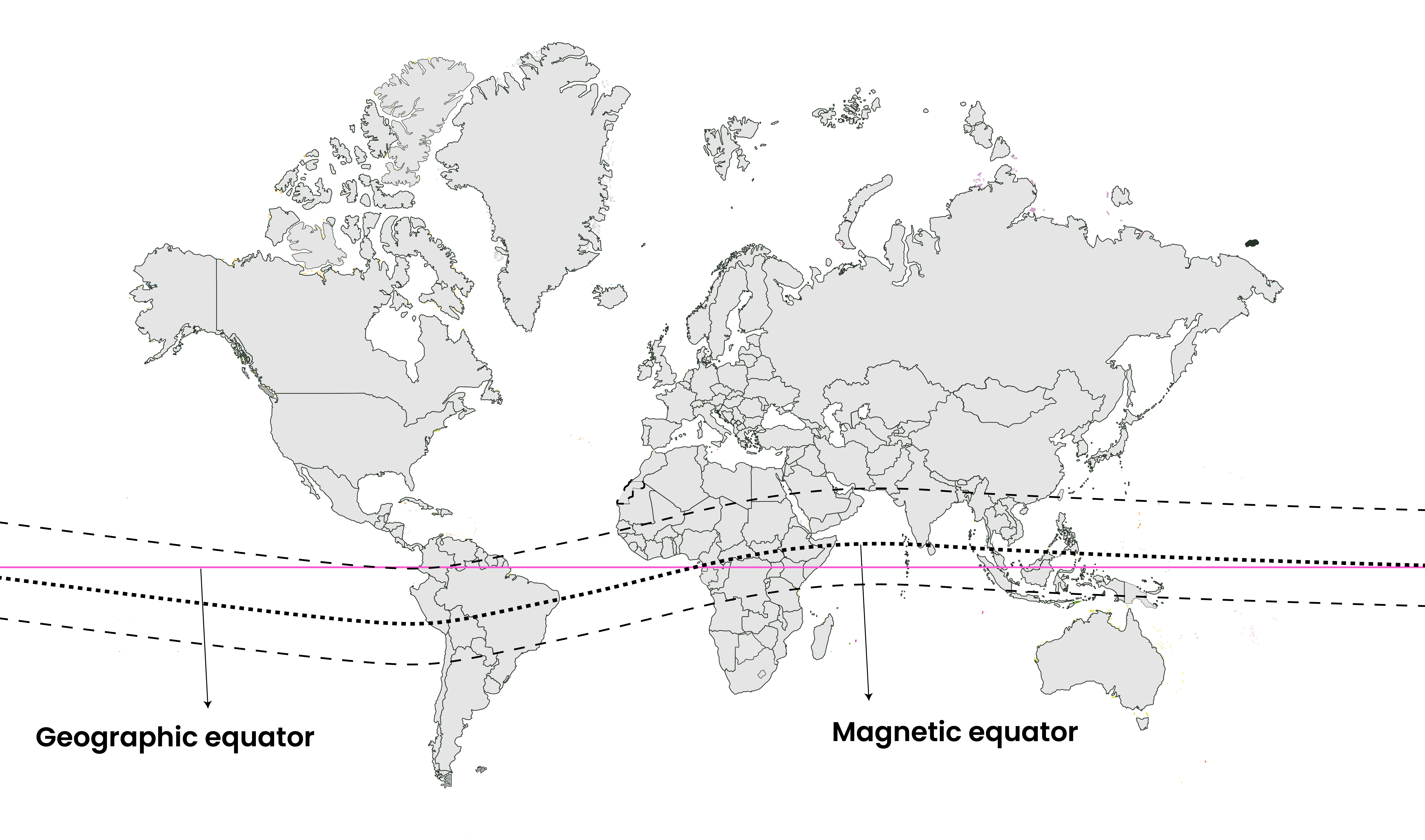
|



