IIT Madras has unveiled India's first Hyperloop test track, measuring 410 meters. This track serves as a prototype to validate Hyperloop’s feasibility in Indian conditions.
- Mumbai-Pune route has been selected for India's first full-scale Hyperloop system.
What is Hyperloop?
- About: Hyperloop is a high-speed transportation system consist of a low pressure tube through which capsules may travel free of friction & air resistance.
- It was first proposed by Elon Musk in 2013.
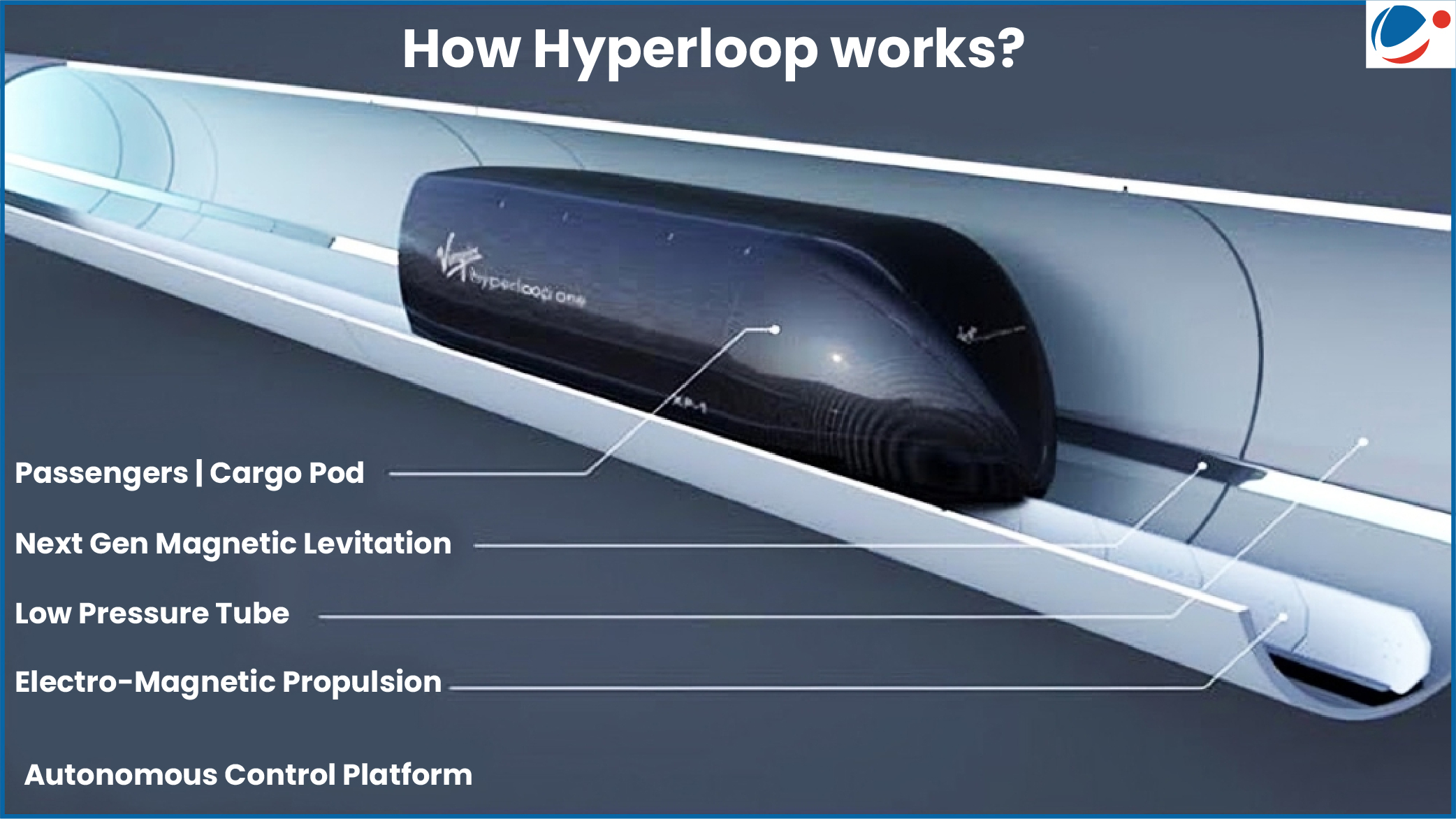
- Key Components & working Mechanism:
- Tube: Near-vacuum tubes reduce air resistance, allowing travel at high speeds.
- Capsule/pods: Carries passengers/cargo. Pods utilize magnetic levitation to hover above track, eliminating friction with ground.
- Compressor: It sucks air & allows capsule to traverse through low pressure tube.
- Suspension: Air bearing suspension provides stability & minimizes drag.
- Propulsion: Pods are propelled forward using linear induction motors.
Significance:
- High Speed: It is designed to allow pods to travel at speeds up to 1,100 km/h, with an operational speed targeted at around 360 km/h.
- Zero Emissions: The whole hyperloop system is powered by the solar panels.
Challenges in mainstreaming hyperloop
- Infrastructure Challenges: High initial cost, complex land acquisition process, difficult terrain.
- Regulatory Bottlenecks: Absence of specific regulatory framework, safety certification challenges, complex environmental laws etc.
- Technological Barriers: limited expertise, lack of comprehensive testing facilities etc.







