Smuggling of Gum Arabic from war-torn Sudan is impacting global supply chains.
- Sudan produces ~80% of the world’s gum arabic.

About Gum Arabic (Acacia Gum)
- It is a dried water-soluble exudate obtained from the Acacia trees.
- Acacia trees grow across Africa's Sahel region – known as the ‘gum belt’ and are well-known landmarks in the veld and savanna.
- Composition: Polysaccharides and its calcium, magnesium, and potassium salts, which on hydrolysis yield arabinose, galactose, rhamnose, and glucuronic acid.
- Uses: Emulsifier, stabilizer, and thickener in food industry, cosmetics; painting, soft drinks, pharmaceuticals etc.
- It is an ideal functional dietary fiber ingredient in food.
Article Sources
1 sourceWHO recommended trivalent Influenza vaccines for use in 2025–2026 northern hemisphere influenza season.
- It contains Egg-based vaccines and Cell culture-, recombinant protein- or nucleic acid-based vaccines for Influenza.
About Egg-based vaccines
- Made by growing viruses in fertilized chicken eggs.
- Fluid containing virus is extracted from eggs, then virus is either inactivated (for killed-virus vaccines) or weakened (for live attenuated vaccines).
- Challenges: ‘Egg adaptation’ (vaccine seed viruses to adapt to avian receptors) leading to genetic mutations impacting effectiveness.
- Other Vaccines:
- Cell culture based vaccines: Utilize mammalian cells as substrate for virus growth.
- Recombinant Protein-Based Vaccines: specific protein (antigen) from a virus is produced using genetic engineering.
- Nucleic Acid-Based Vaccines: Deliver genetic instructions (DNA or mRNA) to cells, so they produce viral protein themselves.
The ‘Wallace Line’ explains the species differences across continents.
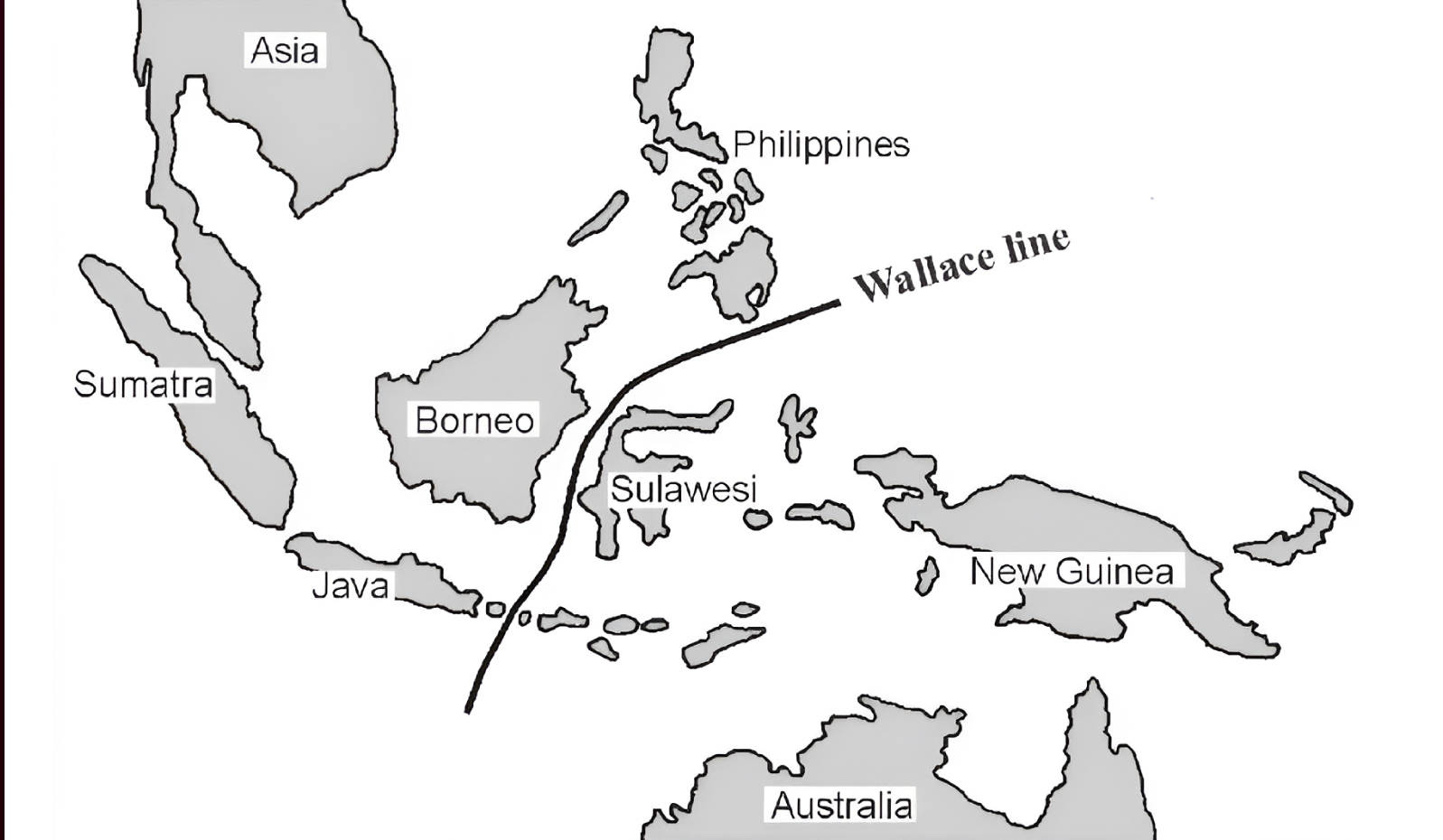
What is Wallace Line?
- Definition: An invisible biogeographical boundary proposed by Alfred Wallace (in 19th century), separating Asian and Australian fauna.
- Marks a dramatic shift in species characteristics over a narrow distance.
- Geography (Southeast Asia): Runs between Bali and Lombok, extends north between Borneo and Sulawesi, and curves south of Mindanao (Philippines).
- Reason behind distinct species development: The collision and interaction between the Australian and Asian tectonic plates formed volcanic islands (e.g., Bali, Lombok, Sulawesi).
- These islands acted as isolated habitats, separating species and allowing independent evolution.
Recent increase in number of solar missions has been attributed to approaching solar maximum in solar cycle.
- Recent solar missions include Aditya L1 by ISRO, Proba-3 by European Space Agency and PUNCH by NASA.
What is the solar cycle?
- Definition: Every ~11 years, the Sun’s magnetic field flips, switching magnetic poles, in a process called the solar cycle.
- Phases of the Solar Cycle
- Solar Maximum: Considered the best period to study the Sun, it marks the peak of solar activity with most sunspots.
- Characterized by eruption of solar flares and coronal mass ejections (CMEs).
- Solar Minimum: Follows the solar maximum and marks the lowest solar activity with the fewest sunspots.
- Solar Maximum: Considered the best period to study the Sun, it marks the peak of solar activity with most sunspots.
Article Sources
1 sourceRBI has directed large NBFCs to stop new lines of credit and renewals.
About Line of Credit (LoC)
- A line of credit is a flexible, working capital-like debt facility often extended to self-employed individuals and small businesses.
- Features:
- Funds can be withdrawn multiple times up to an approved limit.
- Surplus funds can be deposited back into the loan account.
- Interest-only payments are allowed initially, with the principal deferred.
An Australian blood donor who saved 2.4 million babies recently passed away
- His rare blood, rich in anti-D antibodies, helped develop 2.4 million doses of anti-D medication.
- Anti D injection prevents an Rh-negative mother's immune system from producing antibodies that attack fetal red blood cells causing HDFN.
About HDFN
- It is a blood disorder that causes red blood cells to break down quickly in a fetus (hemolysis).
- Causes:
- When a mother and her unborn baby have different blood types.
- Or if mother is Rh-negative and baby in womb has Rh-positive cells, her antibodies to Rh antigen can cross placenta and cause very severe anemia in baby.
- Rhesus (Rh) factor is an inherited protein that can be found on surface of red blood cells.
- Complications: Can lead to miscarriage, stillbirth, severe anemia, jaundice, and life-threatening complications in newborns.
A recent study revealed new insights into how anemonefish contribute to their host’s well-being by providing food.
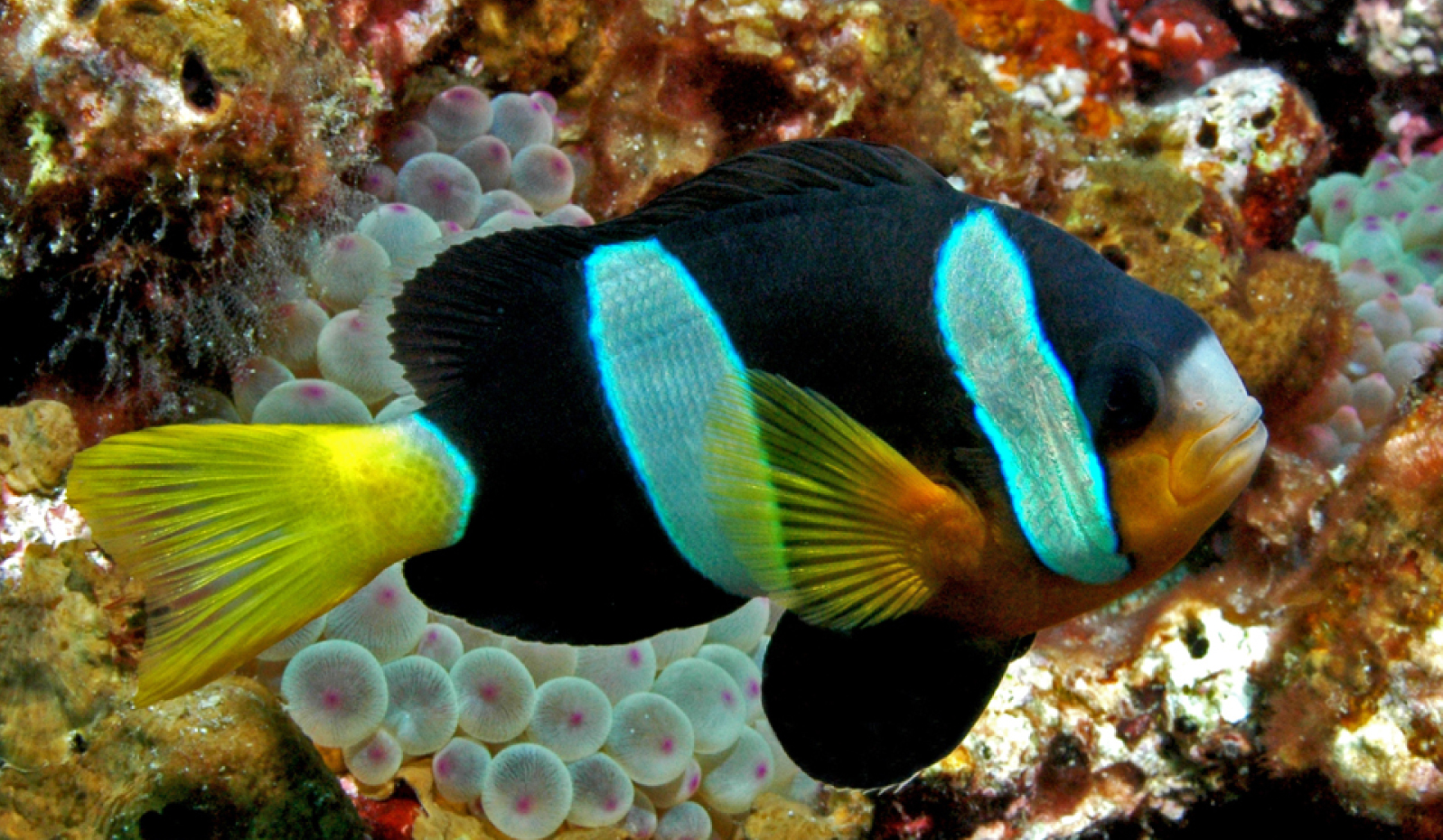

About Anemonefish
- Anemonefish are poor swimmers;forms symbiotic relationship with anemone species.
- Anemones are stinging polyps closely related to corals and jellyfish.
- Anemonefish seek refuge in sea anemones, which protect them from predators with their stinging tentacles.
- In return, anemonefish play a crucial role in maintaining their hosts by driving away organisms that could harm or compete with the anemones.
Article Sources
1 sourceResearchers Find Strong Evidence of Bose Metal in Niobium Diselenide (NbSe2).
About Bose Metal
- It is a kind of anomalous metallic state (AMS). In this Cooper pairs are formed but don’t condense into a superconductor.
- Exist in a state where conductivity is neither infinite (like a superconductor) nor zero (like an insulator).
- Cooper pairs are coupled electrons in a superconductor that behave like bosons and condense into a collective quantum state.
- Applications: It helps in probing Quantum Processes.



