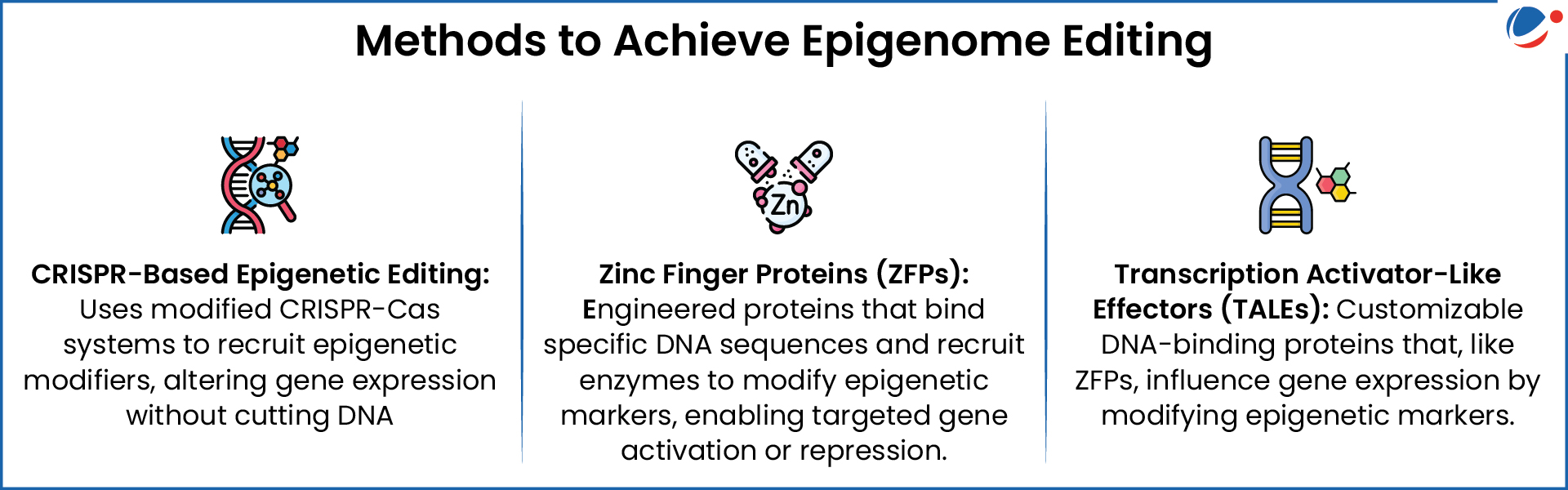
Epigenome editing is genetic engineering technology that adjusts gene transcription through modifying epigenome, directly targeting root of dysregulation while leaving primary DNA sequence intact.
- Epigenome refers to all chemical compounds and modifications (like methyl groups or histone modifications) that regulate gene expression without changing DNA sequence.
- Unlike traditional gene editing methods that involve cutting DNA, epigenome editing allows for precise control over gene expression (With Reversible Changes), making it a safer alternative.
- Epigenetic processes predominantly regulate gene expression at level of transcription.
- Transcription is the process of copying a gene's DNA sequence into an RNA molecule.
Epigenetic processes/markers to Regulate Gene Expression
- DNA Methylation: Addition of a methyl group to DNA, which can silence genes by preventing transcription factors from binding.
- Histone Modification: Alters histone proteins (basic proteins that DNA wraps around) with chemical changes affecting gene expression.
- RNA-Mediated Processes: Uses non-coding RNAs to regulate genes.
Key Application of Epigenome Editing
- Treatment of Complex Diseases: Effective for conditions like cancer, neurological disorders, and metabolic syndromes caused by multiple genetic factors.
- Regenerative Medicine: Enhances stem cell therapies by controlling differentiation and promoting tissue repair.
- Immune System Engineering: Optimizes immune cell functions for advanced cancer immunotherapies.
- Safe and Reversible Gene Therapies: Reduces risks of permanent genetic modifications, offering precise and controlled treatments.