Research team working under Department of Science and Technology has developed a super-fast charging sodium-ion battery (SIB) that can charge up to 80% in just six minutes and last over 3000 charge cycles.
About Sodium-Ion Battery (SIB)
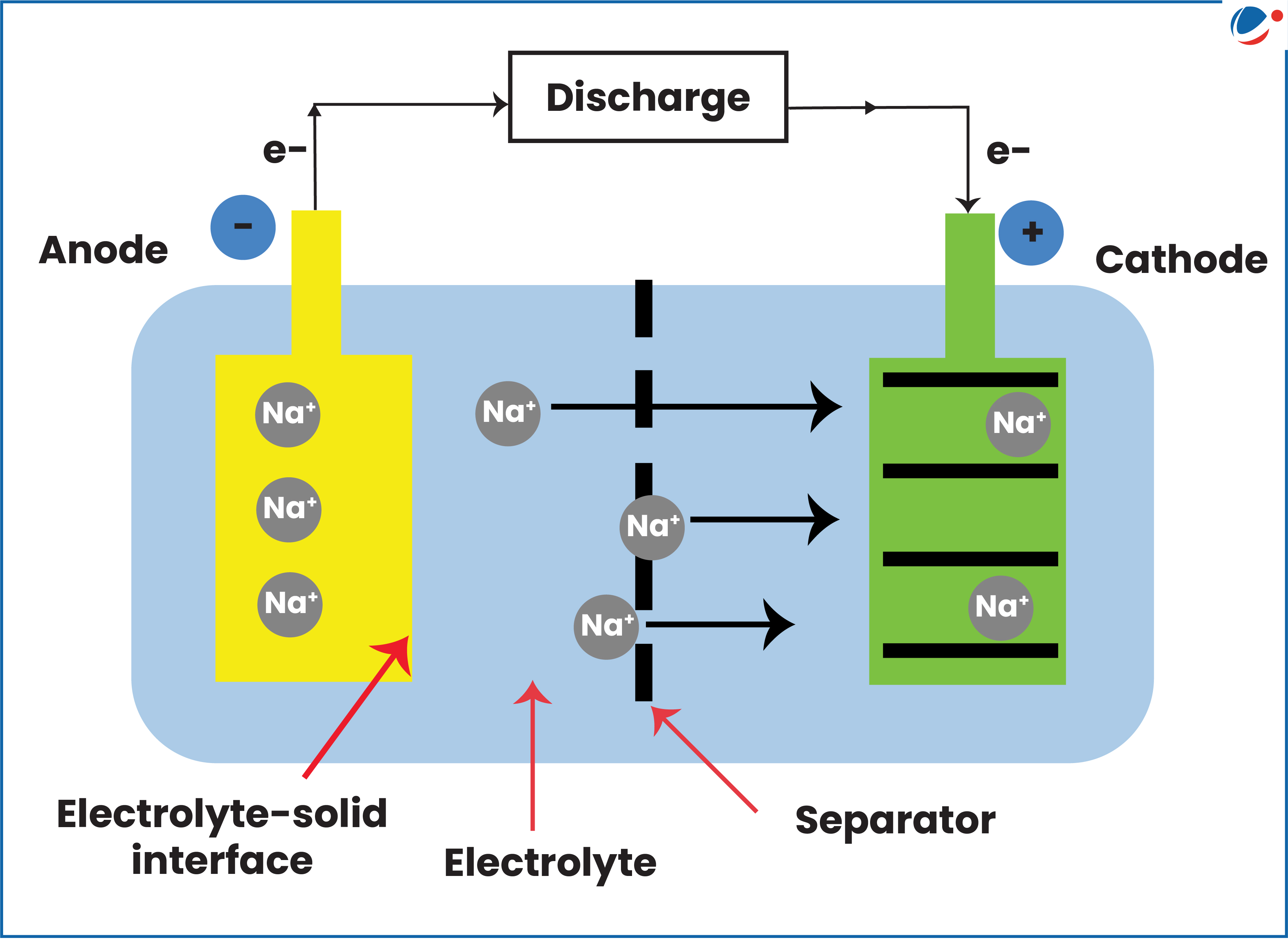
- Definition: SIBs are a type of rechargeable battery similar to lithium batteries, but carry the charge using sodium ions (Na+) instead of lithium ions (Li+).
- How Sodium-Ion Batteries (SIBs) Work?
- During discharge: Sodium ions move from anode (negative electrode) to cathode (positive electrode), which hosts ions and undergoes reduction.
- These ions travel through an electrolyte (an electrical conductor) that enables the flow of current by creating a potential difference.
- During Recharge: Sodium ions return to the anode.
Advantages of Sodium-Ion Batteries (SIBs) Compared to Lithium-Ion Batteries (LIBs):
- Cost: SIBs are cost-competitive (overall costs could be 15%-20% lower) than LIBs since sodium compounds are cheaper than lithium equivalents.
- Supply chain decentralisation: Sodium’s abundance enables diverse global manufacturing, reducing geopolitical risks.
- E.g., As of 2023, China accounted for nearly 60% of global lithium processing, highlighting the current concentration in lithium supply chains that SIBs can help diversify.
- Technology: SIBs have a better range of operational temperatures than LIBs, allowing them to be safely deployed in areas with greater temperature variation.
- Safety: SIBs can be transported at zero voltage (fully discharged), reducing fire risks and costly safety measures compared to LIBs



