Why in the News?
As per Bank for International Settlements (BIS), Project mBridge reached the minimum viable product (MVP) stage in mid-2024.
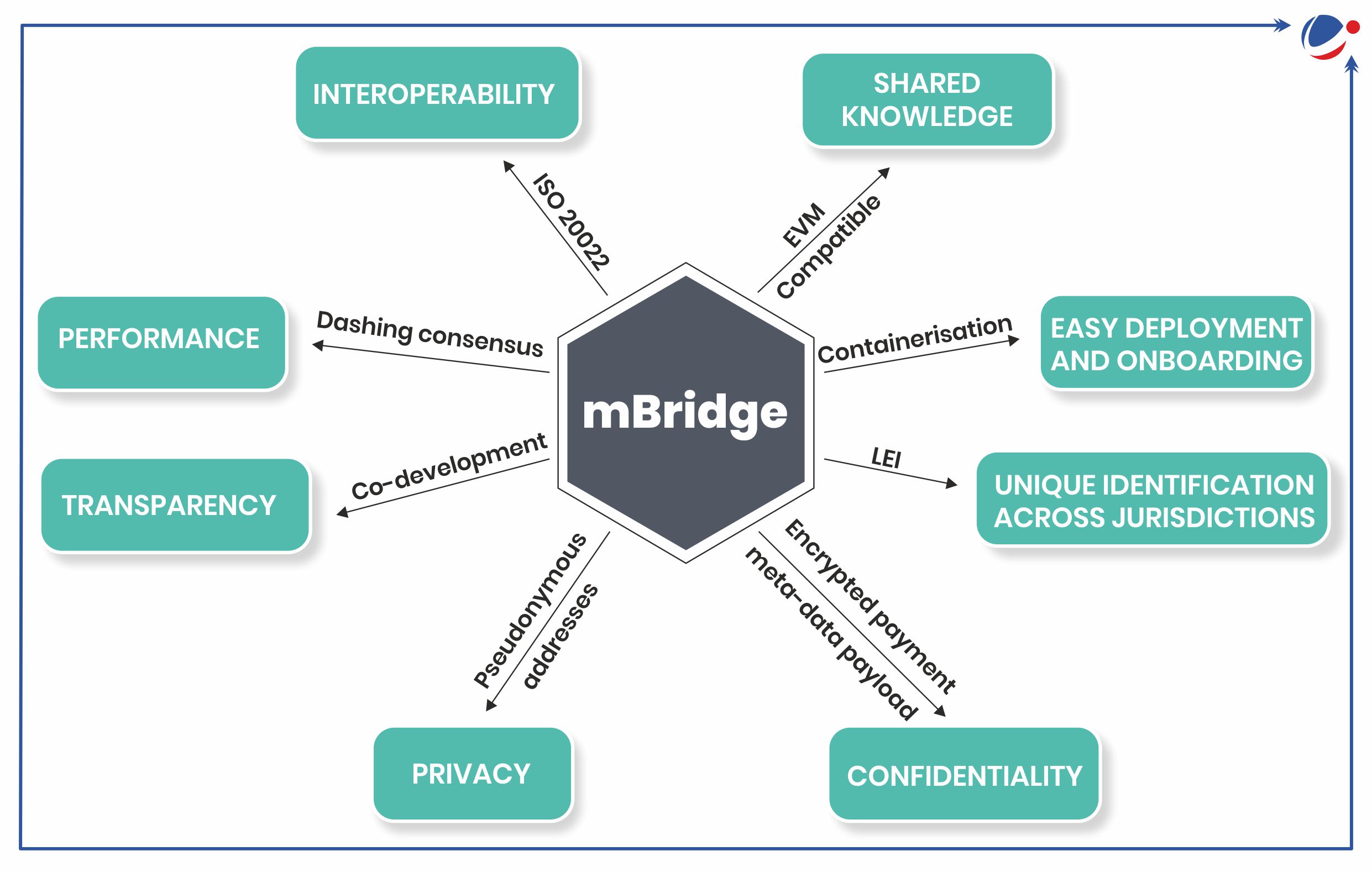
About Project mBridge
- Launched in 2021, mBridge is a cross-border, decentralised, multiple central bank digital currency (mCBDC) platform.
- A platform based on a new blockchain 'the mBridge Ledger' was also built to support real-time, peer-to-peer, cross-border payments and foreign exchange transactions.
- It is built on distributed ledger technology (DLT)- a decentralized ledger network that uses the resources of many nodes to ensure data security and transparency.
- Participants: Initially led by the BIS Innovation Hub, in collaboration with the other four central banks of China, Thailand, the United Arab Emirates (UAE) and Hong Kong.
- Saudi Central Bank joined in 2024.
- There are more than 31 observing members including Reserve Bank of India.
Significance of mCBDC
- Lower Transaction Cost, Increased Efficiency and Transaction Speed.
- Enhanced Security and Transparency through the use of Blockchain technology, AI.
- Monetary Sovereignty, credibility, and trust among countries.
- Preventing Monopoly and Digital Dollarization (replacement of other currencies by more influent one) etc.

Challenges associated with mCBDC
- Global Acceptance and credibility as BIS has announced backing out from project after involvement for about four years.
- Regulatory Uncertainty due to lack of a coherent regulatory framework across jurisdictions.
- Volatility and Macroeconomic Stability associated with digital currencies.
- Security Concerns regarding data breaches, Illegal uses such as money laundering, tax evasion or financing illegal activities, etc.
- Risks of creating Parallel and unregulated structures of transactions.
Similar Global Initiatives
|
Conclusion
mBridge represents a potential shift toward a more multipolar global financial system, where digital currencies backed by local economies can play a much larger role in international trade. mBridge promises to enhance economic sovereignty by giving countries more control over their financial transactions, mitigating the risk of sanctions or other forms of economic pressure but comes challenges.






