NPT represents the only binding commitment in a multilateral treaty with the goal of disarmament by the Nuclear-Weapon States (NWS) and promotion of peaceful uses of nuclear energy.
About NPT
- Background: Enforced in 1970.
- Membership: 191 States.
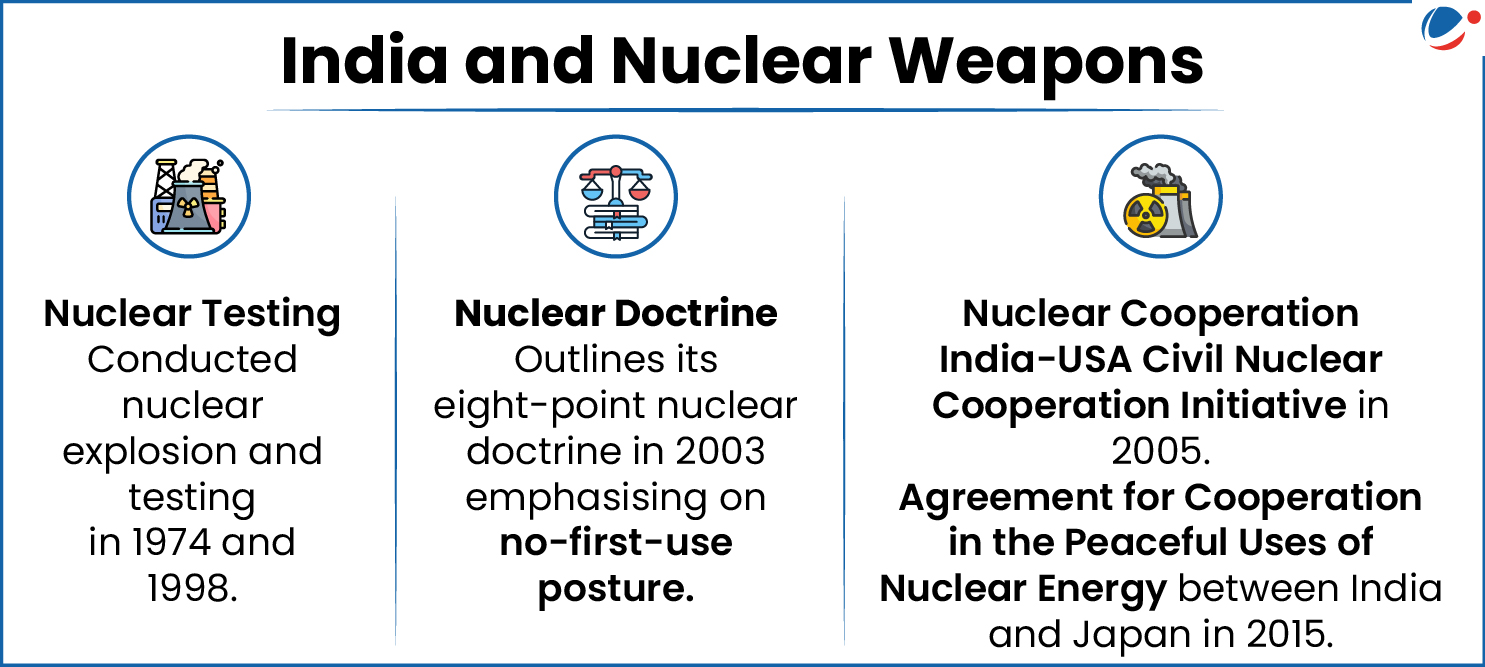
- India has not signed owing to discrimination of states into “nuclear haves” and “nuclear have-nots.”
Major Provisions of the Treaty
- Key Principles: Non-Proliferation (Parties to the Treaty should refrain from acquiring or transferring nuclear-weapons); Disarmament;Access to Peaceful Nuclear Technology.
- Role of International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA): Compliance with the Treaty is verified through inspections conducted by IAEA.
- IAEA was created in 1957 under the United Nations to promote safe, secure and peaceful use of nuclear technologies.
- Review of the operation of the Treaty: Every five years.
Significance of NPT in the present times
- Rising Nuclear Threats: In the form of small arms, evolving technologies like artificial intelligence, etc.
- Strengthening of Nuclear arsenals: As per Stockholm International Peace Research Institute (SIPRI), most nations have expanded their nuclear arsenals.
- Weakening Nuclear Diplomacy: E.g., Russia withdrew its ratification of the Comprehensive Nuclear-Test-Ban Treaty (CTBT).
Other Major Treaties on Nuclear Disarmaments
|








