The report is compiled on the 25th anniversary of International Mother Language Day (21 Feb), celebrating a quarter-century of dedicated efforts to preserve and promote the use of mother tongues.
Key Findings of the Report
- Nearly 40% of the global population does not have access to education in a language they speak or understand.
- In some low and middle-income countries, this figure reaches 90%.
- India ranks fourth in the list of top ten countries with the most spoken languages.
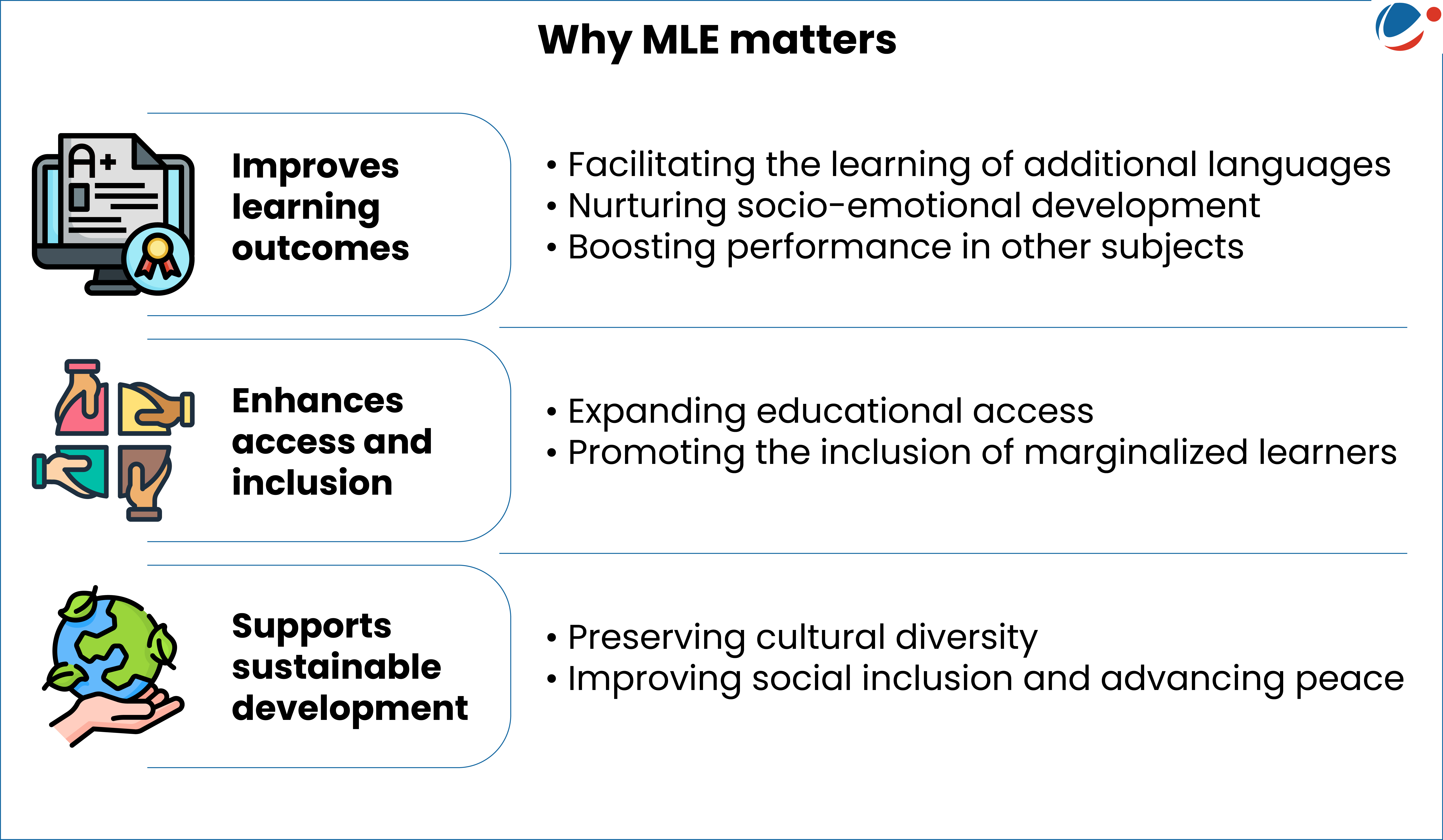
About Multilingual Education
- UNESCO defined multilingual education (MLE) as the use of at least three languages, the mother tongue, a regional or national language, and an international language in education.
- India’s New Education Policy, 2020 also promotes three language formula.
- UNESCO’s World Atlas of Languages estimates that there are 8,324 languages, spoken or signed.
Key Challenges in Multilingual Education
- Resource constrain: Insufficiently trained teachers, a shortage of multilingual learning and teaching material.
- Policy opposition: particularly from those prioritizing national or international languages over local languages.
- Other: Historical factors (often from colonialism), etc.
Key Recommendations
|






