Digital Payment Intelligence Platform (DPIP)
DPIP will be developed as a Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI) under the supervision and guidance of the RBI.
- DPI refers to foundational digital systems that are accessible, secure, and interoperable, supporting essential public services e.g., Aadhaar, Unified Payment Interface (UPI) etc.
About DPIP
- It seeks to bolster fraud risk management by facilitating real intelligence sharing and gathering by harnessing advanced technologies.
- It will also strengthen existing fraud detection systems by enabling coordination among banks.
- A committee under Chairman Shri A.P. Hota constituted to examine various aspects of setting up of DPIP.
- The Reserve Bank Innovation Hub (RBIH) has been assigned to build a prototype of DPIP in consultation with 5-10 banks.
- Both Private and Public banks will be consulted.
- Need of DPIP
- As per RBI’s annual report, fraud cases in the banking sector saw a significant increase.
- The total value of frauds jumped to ₹36,014 crore in FY25, compared to ₹12,230 crore in FY24.
- Tags :
- Digital Payment Intelligence Platform
- DPIP
Priority Sector Lending (PSL) Norms For Small Finance Banks (SFBs)
The New Rule were issued by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) under Section 22(1) of the Banking Regulation Act, 1949.
Key Change in PSL Requirements for SFBs
Earlier Rule | New Rule (Effective FY 2025-26): |
|
|
About Priority Sector Lending (PSL)
- Established: In the 1970s.
- Concept: PSL framework, initiated by RBI, mandates banks to allocate a specific percentage of their Adjusted Net Bank Credit (“ANBC”) to priority sectors.
- ANBC Comprises: Net Bank Credit (NBC), Bank's investments in non-statutory liquidity ratio (non-SLR) bonds, etc.
- Categories under Priority Sector: Agriculture; Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises; Export Credit; Education; Housing; Social Infrastructure; Renewable Energy; Others.
- Applicability: Commercial Bank [including Regional Rural Bank (RRB), Small Finance Bank (SFB), Local Area Bank (LAB)] and Primary (Urban) Co-operative Bank (UCB) other than Salary Earners’ Bank.
- Tags :
- Small Finance Banks
- Priority Sector Lending
Sagarmala Finance Corporation Limited (SMFCL)
SMFCL is India’s first Non-Banking Financial Company (NBFC) in the maritime sector.
- Formerly known as Sagarmala Development Company Limited, SMFCL is a Mini Ratna, Category-I, Central Public Sector Enterprise (under Ministry of Ports,Shipping and Waterways).
- It is now formally registered as an NBFC with the Reserve Bank of India (RBI).
- It will offer tailored financial products to a diverse range of stakeholders, such as port authorities and shipping companies.
- It will also support strategic sectors like shipbuilding, renewable energy, cruise tourism, and maritime education.
- Tags :
- Sagarmala Finance Corporation Limited (SMFCL)
Indigenous Polar Research Vehicle (PRV)
India is aiming to build first indigenous Polar Research Vehicle (PRV).
- To achieve this, an MoU was signed between Garden Reach Shipbuilders and Engineers Limited (GRSE) and Norway’s Kongsberg Oslo marking an important milestone for India’s shipbuilding sector.
- GRSE (Kolkata), is a premier Warship building Mini Ratna Category I company under Ministry of Defence.
Polar Research Vehicle (PRV)
- About: It is a ship that serves as a platform for research in the polar regions (around the North and South Poles).
- Purpose: Equipped with the latest scientific equipment, enabling exploration of the oceans’ depths and study of marine ecosystems.
Significance of the Indigenous PRV for India
- Indigenous Needs: PRV would serve the requirements of National Centre for Polar and Ocean Research (NCOPR), Goa, who will use it for research activities.
- Support Existing Scientific Missions: In Antarctica (Maitri [1989] and Bharati [2011] and in the Arctic (Himadri, 2008).
- Cater to Geo-political and Geo-economic dynamics of the region: Significant for India to assert its presence and interests in the region.
- Complements Existing Maritime Visons:
- SAGAR (Security and Growth for All in the Region) that leverages India’s vast coastline, strategic location, and maritime heritage and MAHASAGAR (Mutual and Holistic Advancement for Security Across the Regions) for holistic maritime engagement.
- Sagarmala 2.0, Under Ministry of Ports, Shipping and Waterways, which is a key pillar of the Maritime Amrit Kaal Vision 2047 (MAKV),
- MAKV seeks to place India among the top five shipbuilding nations by 2047.
- Others: Climate research, oceanography, and polar logistics.
- Tags :
- indigenous Polar Research Vehicle (PRV)
Articles Sources
Report On Value of Output from Agriculture and Allied Sectors (2011-12 to 2023-24)
The National Statistics Office (NSO) released a report offering a comprehensive overview of India's agricultural performance over the past decade.
Key Highlights
- Gross Value Added (GVA) in agriculture and allied sectors rose by ~225% (current prices), while Gross Value of Output (GVO) grew by 54.6% (constant prices) from 2011–12 to 2023–24.
- Crop sector: Largest contributor to total agriculture GVO in 2023-24 with 54.1%.
- Uttar Pradesh is the top cereal-producing state.
- Paddy & wheat constitute approximately 85% of GVO of all cereals in 2023-24.
- Floriculture: GVO nearly doubled from 2011-12 to ₹28.1 thousand crore in 2023–24.
- Condiments & Spices: Madhya Pradesh (19.2%) is the top contributor, followed by Karnataka (16.6%) & Gujarat (15.5%).
- Fishing & Aquaculture: Contribution increased from 4.2% in 2011-12 to 7.0% in 2023-24.
- The share of inland fish has decreased to 50.2%, whereas the share of marine fish has increased from 2011-12 to 2023-24.
Importance of Agriculture and Allied Sector
- Contribution to GDP: ~16% of the country's GDP for FY24 (Economic Survey 2024-25).
- Livelihood: It supports ~46.1% of the population.
- Challenges: Low Agricultural productivity per unit of land, low farmer income, Overexploitation of Water Resources, climate change, & extreme weather events, etc.
- Tags :
- Agriculture and Allied Sectors
Articles Sources
Modified Interest Subvention Scheme (MISS)

Recently, Union Cabinet approved the continuation of the Interest Subvention (IS) component under the Modified Interest Subvention Scheme (MISS) for 2025-26.
About MISS
- Type: Central Sector Scheme
- Ministry: Ministry of Agriculture & Farmers Welfare
- Aim: Ensuring the availability of short-term credit to farmers at an affordable interest rate through Kisan Credit card (KCC).
- Implementation: Reserve Bank of India (RBI) and National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development (NABARD).
- Key Features
- Variant of Interest Subvention Scheme (ISS) (2006-07): which offers KCC loans at 7% interest.
- Short-term Loans: Up to ₹3 lakh through KCC at a subsidized interest rate of 7%, with 1.5% interest subvention provided to eligible lending institutions.
- Prompt Repayment Incentive (PRI): Up to 3% effectively to farmers repaying loans promptly reducing their interest rate on KCC loans to 4%.
- Loans exclusively for animal husbandry/fisheries: Interest benefit is applicable up to Rs.2 lakh.
About KCC
|
- Tags :
- Modified Interest Subvention Scheme (MISS)
International Crops Research Institute for the Semi-Arid Tropics (ICRISAT)
ICRISAT, in collaboration with the Research and Information System for Developing Countries (RIS), launched the ICRISAT Centre of Excellence for South-South Cooperation (ISSCA).
- ICRISAT also signed an MoU with DAKSHIN (Development and Knowledge Sharing Initiative), which is India’s initiative for strengthening South-South cooperation through capacity building and development partnerships.
- RIS is a New Delhi-based autonomous policy research institute.
About ISSCA
- Premier platform dedicated to accelerating agricultural innovation, collaboration, and knowledge exchange among countries of Global South.
- It is also aligned with India’s DAKSHIN initiative (A government-backed program for development and knowledge sharing among Global South countries).

- Tags :
- International Crops Research Institute for the Semi-Arid Tropics (ICRISAT)
Articles Sources
National Turmeric Board
Headquarters of National Turmeric Board was inaugurated in Nizamabad, Telangana.
About the National Turmeric Board
- Aim: To provide leadership on turmeric related matters, augment the efforts, and facilitate greater coordination with Spices Board and other Government agencies in development and growth of the turmeric sector.
- Ministry: Ministry of Commerce & Industry
- Composition:
- Chairperson to be appointed by the Central Government
- Members from the Ministry of AYUSH, Departments of Pharmaceuticals, Agriculture & Farmers Welfare etc.
- Senior State Government representatives from three states (on rotation basis),
- Select national/state institutions involved in research & representatives of turmeric farmers & exporters
- A Secretary to be appointed by the Department of Commerce.
- Role: Promotes R&D, value addition for exports, awareness of turmeric's benefits, yield improvement, and supply chain enhancement to expand markets.
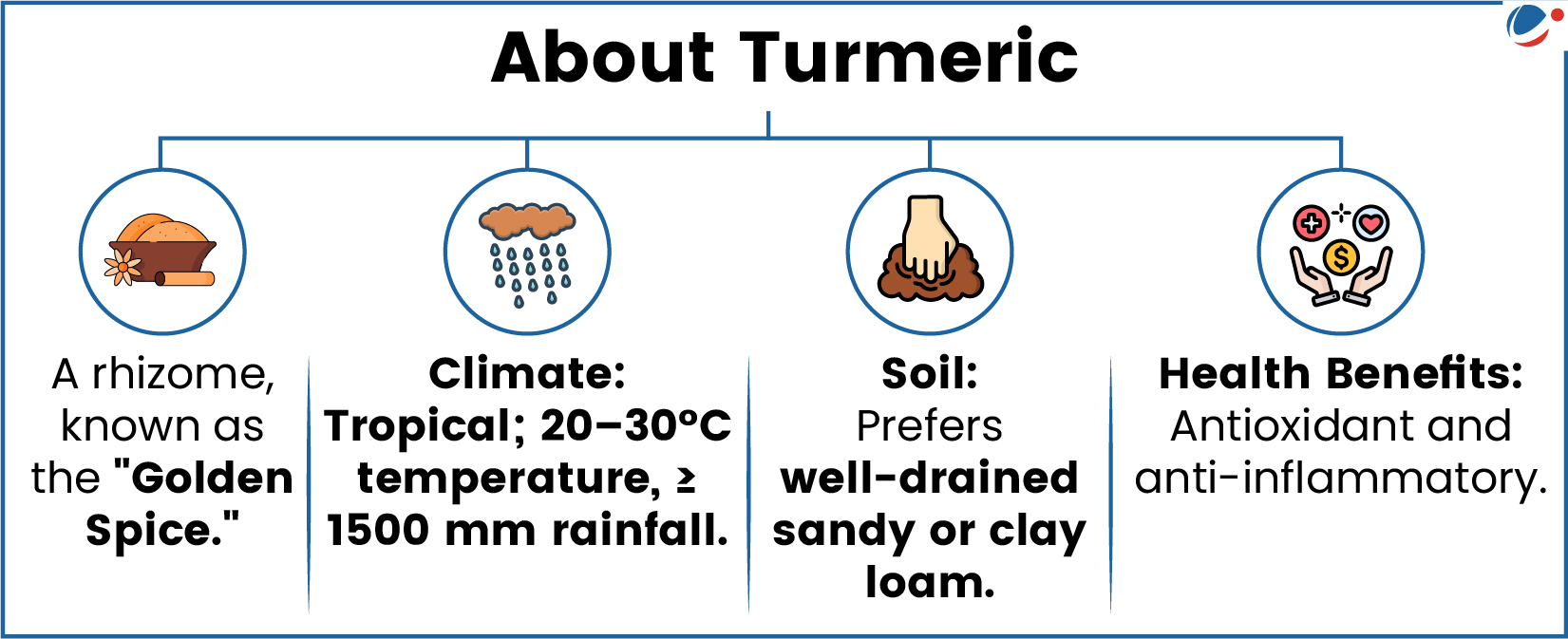
Turmeric production in India
- India is the largest producer, consumer & exporter of turmeric.
- About 30 varieties of Turmeric are grown in over 20 states in the country.
- Production: 70% of global turmeric production.
- Telangana, Maharashtra, Tamil Nadu, & Andhra Pradesh together contribute 63.4% of domestic production.
- Export: More than 62% share of world trade.
- The leading export markets for India are Bangladesh, UAE, USA & Malaysia.
- Turmeric in India with GI Tag: Sangli Turmeric & Waigaon Turmeric (Maharashtra); Erode Manjal/Turmeric (Tamil Nadu); Lakadong Turmeric (Meghalaya).
- Tags :
- National Turmeric Board
Nano Fertilizers
Indian Farmers Fertilizer Cooperative Limited (IFFCO) to set up its first overseas nano fertiliser plant in Brazil.
- IFFCO had launched world's first 'Nano Liquid Urea' fertiliser in 2021 & then Nano-DAP in 2023.
About Nano Fertilizers
- Nano fertilizers are nutrients that are encapsulated or coated within nanomaterial (measuring 100 nanometres or less).
- It enables controlled release and its subsequent slow diffusion into the soil.
Benefits
- Promotes sustainable farming: Reduces soil and water contamination.
- Cost Effectiveness: Improves nutrient absorption, reduce nutrient wastage and lower application frequency provide, etc.
- Tags :
- Nano Fertilizers



