Why in the News?
RBI removes prior approval requirements for banks to open Special Rupee Vostro Accounts (SRVAs), speeding up rupee-based trade settlements and supporting the internationalization of the Indian Rupee.
More on the News
- Special Rupee Vostro Account (SRVA) mechanism was introduced in July 2022 to enable exporters and importers to invoice and settle trade in Indian Rupees (i.e. Internationalization of Indian Rupee).
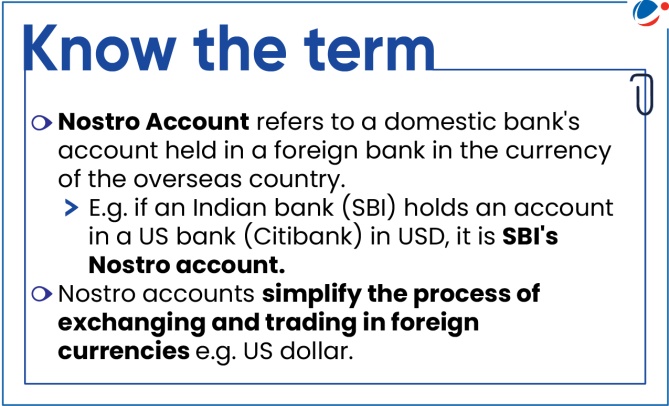
- Vostro Account: Refers to a foreign bank's account held in a domestic bank in the local currency.
- E.g. if a US bank holds an account in an Indian bank in rupees, it is SBI's Vostro account.
- How it Works?
- For Importers: When an Indian importer pays a foreign trader in rupees, the amount is credited to the Vostro account.
- For Exporters: When an Indian exporter receives payment, money is deducted from the Vostro account and credited to the exporter's regular account.
What is Internationalization of Rupee?
- Internationalization of Rupee refers to a process that involves increasing use of the rupee in cross-border transactions.
- It involves promoting the rupee for import and export trade and then other current account transactions, followed by its use in capital account transactions.
What is an International currency?
- An international currency is a currency, like the US dollar or the Euro, used for transactions between countries and beyond the borders of the issuing nation.
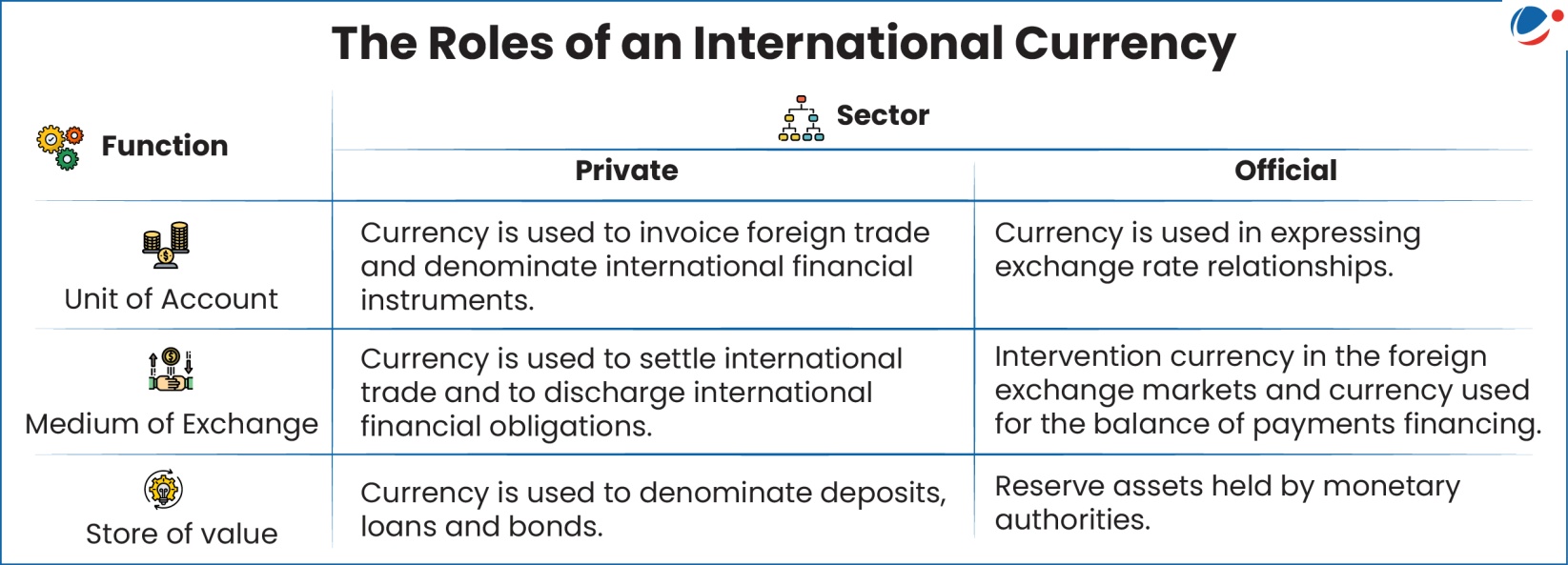
- Just like domestic currency, it performs the three functions of money (As a medium of exchange, a unit of account, and a store of value).
- It does so at two distinct levels, for private and public transactions and resultantly plays six roles in total.
- Currently, the US dollar, the Euro, Japanese yen, Chinese renminbi/Yuan and the pound sterling are the leading reserve currencies in the world.

Benefits of Internationalization of Rupee
- Lower Currency Risk & FX Reserve Needs: Settling trade in rupees reduces forex losses, transaction costs, and dependence on large foreign reserves.
- Global Standing & Bargaining Power: Wider INR usage strengthens India's role in trade negotiations and boosts its economic influence.
- Trade & Policy Flexibility: Trading in rupees can soften the impact of sanctions, diversify partners, and ease fiscal management through potential rupee-denominated debt.
- Financial Market Development: Greater global demand for INR deepens Indian bond and equity markets, attracts investment, and ensures faster, more transparent transactions.
Challenges in Internationalization of Rupee
- Increased Exchange Rate Volatility: Greater global rupee trading increases vulnerability to international market fluctuations, raising transaction costs and complicating financial planning for businesses and investors.
- Reduced Monetary Policy Autonomy: Widespread rupee trading would limit RBI's control over currency value, making inflation and macroeconomic management more challenging.
- Triffin Dilemma, where a country struggles to balance global currency demand with domestic monetary needs.
- Higher Capital Flight Risk: Increased foreign rupee holdings raise the risk of sudden capital outflows, potentially causing financial crisis and currency depreciation.
- Greater External Shock Vulnerability: Deeper integration with global financial markets increases rupee's susceptibility to external shocks like interest rate changes and commodity price fluctuations, destabilizing the Indian economy.
- Competition: The global reserve currency landscape is dominated by US dollar, Euro, Japanese yen, and pound sterling.
- Ensuring Liquidity and Convertibility: The rupee is currently not fully convertible and cannot be freely bought or sold on international markets, lesser capital account convertibility hinders internationalization of rupee.
- In India, full current account convertibility is allowed, whereas on capital accounts only partial convertibility is allowed.
Steps taken for Internationalization of Rupee
|
Way Forward
- Recommendations of Inter‐Departmental Group of RBI
- SDR is an international reserve asset created by IMF in 1969 to supplement its member countries' official reserves.
- Value of the SDR is calculated from a weighted basket of 5 major currencies - U.S. Dollar, Euro, Japanese Yen, Chinese Renminbi, & British Pound.
- Short-Term Measures: Promoting Rupee Accounts for Non-Residents, Integration of Payment Systems, and Internationalization of Indian Payment Systems, etc.
- Medium-Term Measures: Masala bonds framework liberalization, Expanding Real Time Gross Settlement (RTGS) system for settling international transactions, etc.
- Long-term Measures: Inclusion of INR in Special Drawing Rights (SDR) basket
- Specific Reforms: India can pursue specific reforms like increasing the rupee's convertibility, developing a more robust bond market, enticing exporters and importers to conduct business in rupees etc.
- Addressing Macroeconomic Fundamentals: India needs to concentrate on strengthening its macroeconomic foundations to overcome inflation, non-performing assets etc.
- Harmonization of KYC norms: RBI and SEBI can ease access of foreign investors to INR assets.





