Policy Brief identifies regulatory and other issues and makes policy recommendations to help develop a sustainable food system and take the country from food security to nutrition security, and help enhance quality production, exports and earnings of farmers.
What is Sustainable Food System (SFS)?
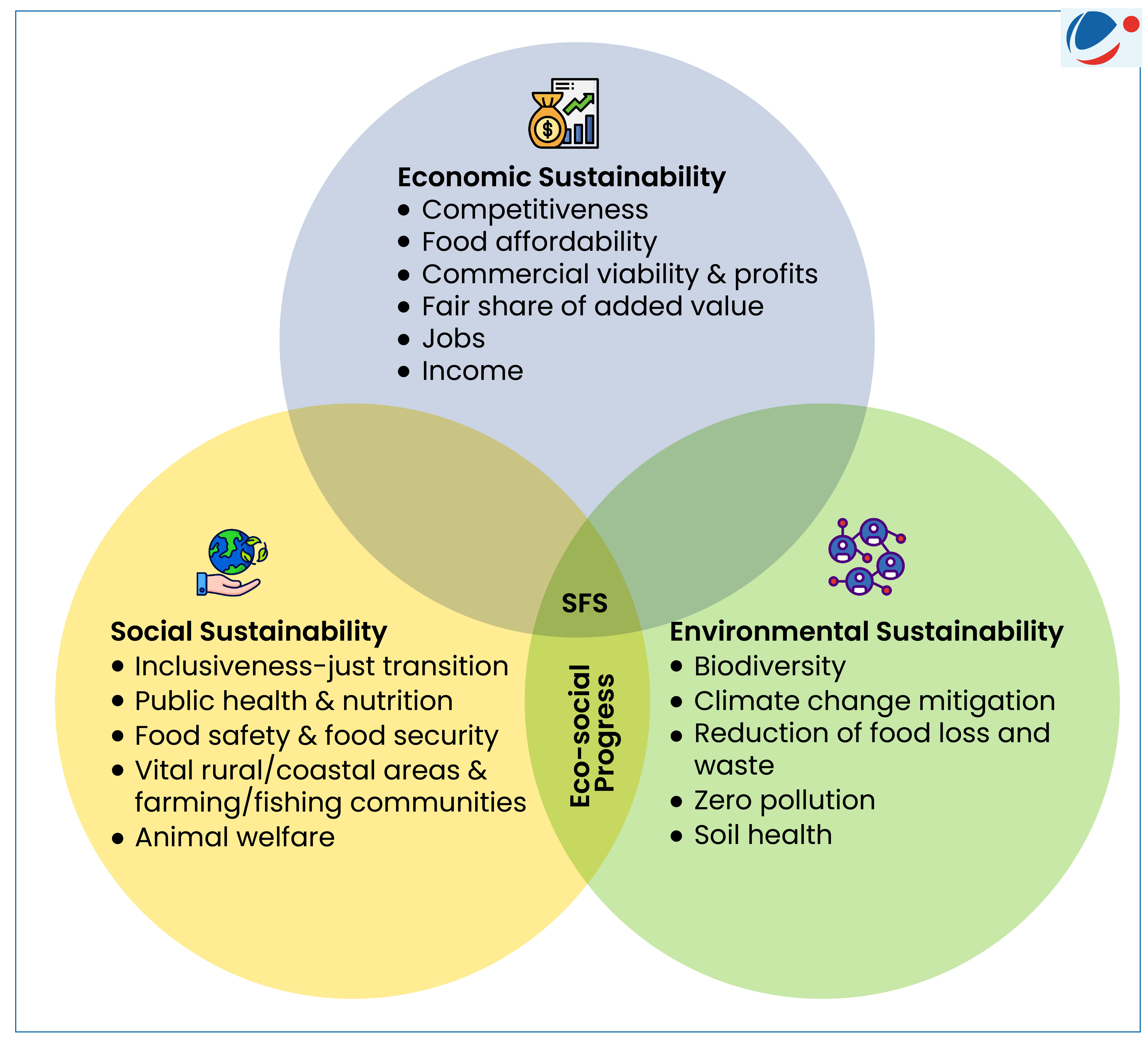
- It is a system that delivers food security, safety, and nutrition for all which is economically, socially and environmentally sustainable. (refer infographic).
Issues in India’s SFS
- Gaps in coordination across multiple government agencies: e.g., divided responsibilities among APEDA, Spices Board and the Export Inspection Council in case of spices.
- Lack of data and information on policies/schemes: e.g., Lack of impact assessment.
- Difficulties in supply chain traceability and gaps in use of technology: e.g., fragmented supply chain, lack of robust public-private partnerships on farm for technology transfer, etc.
- Trade-related issues: e.g., sporadic bans or export duties, rejection of exports due to non-adherence of SPS standards, etc.
Key Recommendations
- Comprehensive vision document with specific goals of reducing food waste, use of harmful pesticides etc.
- Streamline coordination across multiple regulators. e.g., single nodal agency for exports.
- Implement farm-to-fork product traceability. e.g., ‘GrapeNet’ monitoring fresh grapes exported from India to EU.
- Reduce trade barriers by strengthening quality testing and certification.
- Implementation of good agricultural practices. e.g., International Year of Millets 2023.





