Introduction
Traditionally, education was focussed mainly on development of cognitive skills and intelligence is seen as the primary driver of educational achievement. However, a recent study suggests that non-cognitive skills and Emotional Intelligence (EI) is as crucial in shaping a student's academic journey as brain intelligence.
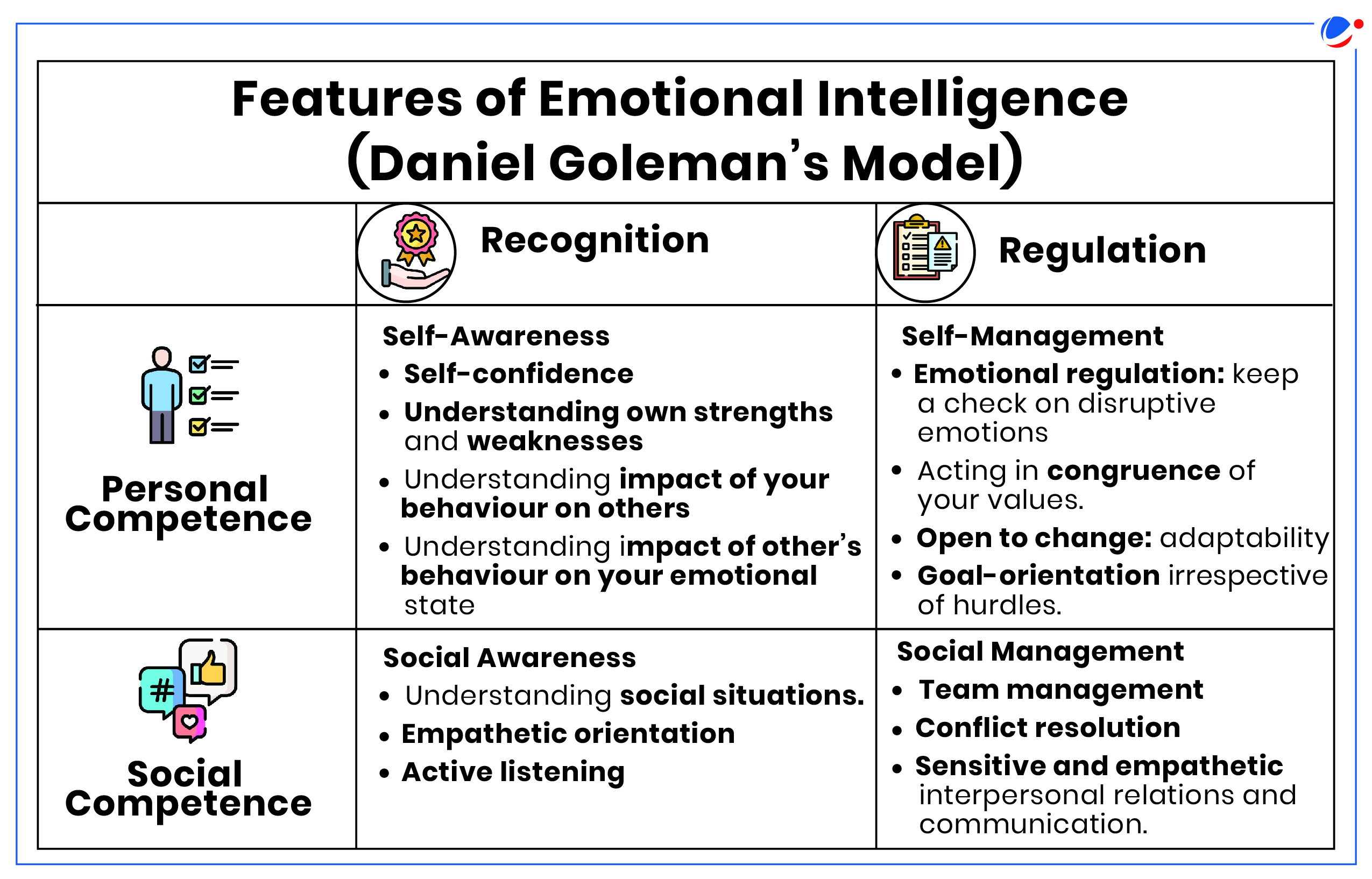
About Emotional Intelligence
- It is defined as the ability to recognize, understand, manage, and influence your own emotions and the emotions of others.
- The term was first coined in 1990 by researchers John Mayer and Peter Salovey but was later popularized by psychologist Daniel Goleman.
- A high EI aids in strengthening interpersonal skills, especially related to conflict management and communication and a holistic personality development by developing non-cognitive skills.
- E.g. non-cognitive skills such as grit, perseverance, academic interest, and the value attributed to learning etc.
Difference between EQ and IQ
Emotional Quotient (EQ) | Intelligence Quotient (IQ) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Importance of EI in education
- Enhanced Academic Performance: Emotionally intelligent students can better manage stress, setbacks, and persevere through challenges.
- They exhibit improved focus and problem-solving abilities, enabling them to engage more effectively in the learning process.
- Positive mental health: Emotionally intelligent students are more likely to exhibit higher self-esteem, lower levels of anxiety and depression, and better overall mental well-being.
- Developing Empathy and Compassion: By understanding and recognizing emotions in themselves and others, students can develop empathy and compassion towards peers.
- It helps in creation of a supportive and inclusive learning environment, where students feel valued and understood.
- E.g. students taught gender-sensitivity, sharing through experiential learning.
- Nurturing Relationships through Effective Communication: EI equips students with the skills necessary to communicate their thoughts, needs, and emotions effectively. E.g. through debate and elocution competitions
- They learn to listen actively, respond empathetically, and resolve conflicts constructively. These skills contribute to positive relationships with peers, teachers, and other members.
- E.g. learning to accept own mistakes.
- Ensure Success in the long-term: EI is highly valued by employers and organizations as it helps to manage emotions, collaborate effectively, and exhibit strong interpersonal skills which are critical in the workplace.
- E.g. coordination with colleagues, handling work pressures.
- Effective Leadership and Decision-making: Students with EI understand their strengths and weaknesses, possess self-confidence, and can motivate and inspire others.
Ways to inculcate Emotional intelligence
- Social-emotional learning (SEL) programs: Designed to teach students the skills they need to manage their emotions, set and achieve positive goals, feel and show empathy, establish and maintain positive relationships, and make responsible decisions.
- E.g. Prerana Experiential Learning School in Vadnagar, Gujarat which is a one-week residential program providing experiential and inspirational learning.
- Collaborative Learning: Group projects, peer tutoring, and team-based activities encourage students to work together, share ideas, and develop social skills aids in improving teamwork, communication, and conflict resolution skills.
- E.g. Happiness Curriculum, Delhi.
- Reflection and self-awareness practices: Meditation, journaling helps students develop self-awareness and self-regulation.
- Empowering Teachers and Staff: EI helps teachers in recognizing and responding to emotional needs, creating emotionally safe classrooms, implementing restorative practices instead of punitive measures etc.
- Involving Parents and the Community: To holistically foster EI with practices at home and society.
- Feedback system: Measuring the impact steps taken through Student Surveys, impact on academic performance, and behavioural indicators like peer relationships, discipline referrals etc.
- National Education Policy, 2020 emphasises on developing creative potential of each individual by focussing on social, ethical and emotional dispositions along with foundational and cognitive capabilities.
- E.g. multi-disciplinary education with freedom to choose subjects, professional academic and career counselling etc.
Application of Emotional Intelligence for administrative practices
|
Check your ethical aptitudeYou are the Principal of a District School. During regular inspection, you notice that there is a informal segregation of students on caste lines. Students have formed peer groups with similar caste students and tend to fight often, reinforcing caste discrimination in informal settings. On discussion with the teachers, this observation is confirmed. The students come from nearby villages where caste discrimination is prevalent in social settings.
|




