Why in the news?
NITI Aayog & KPMG published a report on Impact Assessment of Pradhan Mantri Mudra Yojana (PMMY).
About PM Mudra Yojana (PMMY)
- The PMMY is a flagship scheme of the Government of India announced in 2015 during Union Budget FY-2016 to extend affordable credit to micro and small enterprises (MSMEs).
- Objective: To fund the unfunded by bringing MSMEs to the formal financial system and extending affordable credit to them.
Key Features of the scheme
- Type: Central Sector Scheme.
- Loans through Member Lending Institution (MLIs): Public Sector Banks, Private Sector Bank, State operated cooperative banks, Regional Rural banks, Micro Finance Institution (MFI), Non-Banking Finance Company (NBFC), Small Finance Banks (SFBs) etc.
- MUDRA (Micro Units Development & Refinance Agency Ltd.) is responsible for refinancing MLIs.
- MUDRA does not lend directly to the micro entrepreneurs/individuals.
- Loans are provided to meet both term loan and working capital components of financing.
- Eligible borrowers: Non–Corporate Small Business Segment (NCSB) consisting of Individuals, Proprietary concern, Partnership Firm, Private Ltd. Company, Public Company and Any other legal forms.
- Credit Guarantee: To eligible micro units through Credit Guarantee Fund for Micro Units (CGFMU).
- CGFMU was established in 2015 for guaranteeing loans sanctioned under PMMY.
- Other benefits:
- No need to pay processing charges or offer collateral, improved access to affordable credit, and flexible repayment options.
- MUDRA Card: Debit card issued against the MUDRA loan account, for working capital portion of the loan.
Key Achievements highlighted in the report
- Credit Support to MSMEs: Since 2015, the scheme has reached out to ~35 crore Micro and Small Entrepreneur Accounts and provided credit support amounting to ~ ₹18.39 lakh crore.
- Average loan size has gradually increased for almost all the banks over the years.
- Financial Inclusion:
- Women entrepreneurs have the major share of PMMY loans, with around 71.4 % of the total number of accounts (FY 2022).
- The sanctioned amount for New entrepreneurs has increased from INR 61,650 Crore to INR 72,685 Crore.
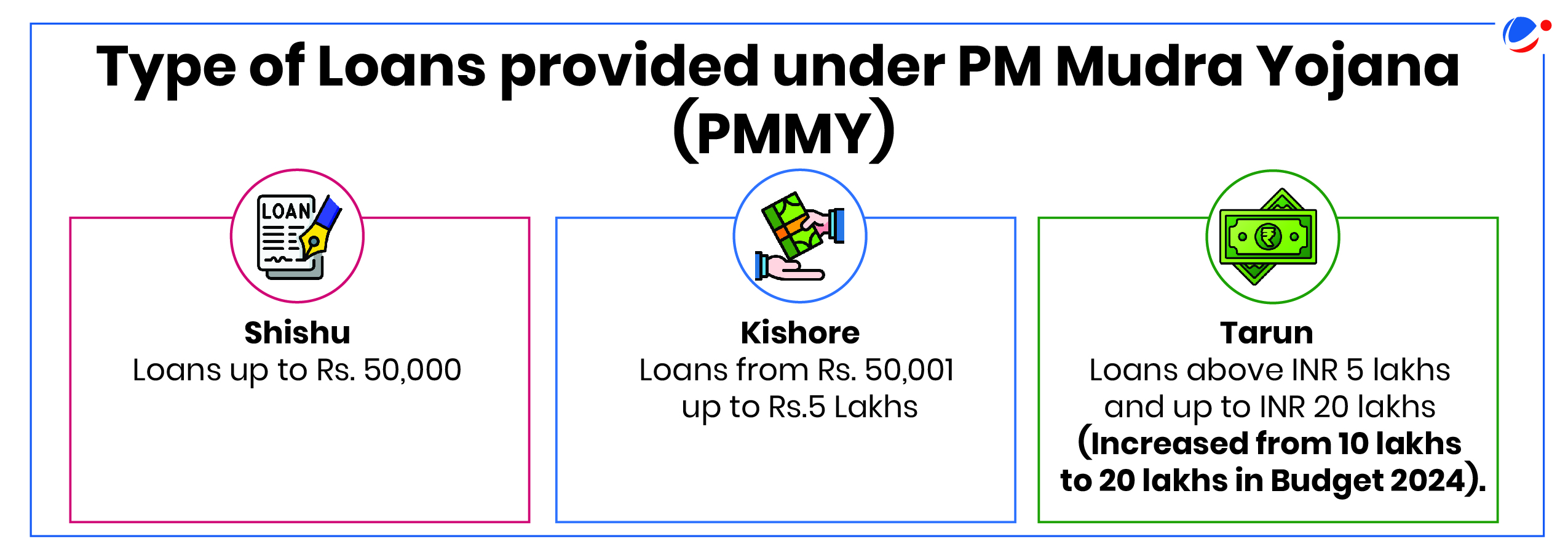
- Encourages small businesses: Majority loan accounts (~80%) are in the Shishu category (FY 2021), followed by Kishore at 18.70 %.
- People belonging to SC, ST, OBCs have more number of Shishu accounts (83.92 %, 83.53 %, 78.68% respectively for FY 2022).
- Performance of Aspirational Districts: Increase in the number of loan accounts and amount sanctioned to these districts Under PMMY with a YoY change of 12 % and 14.7 % respectively.
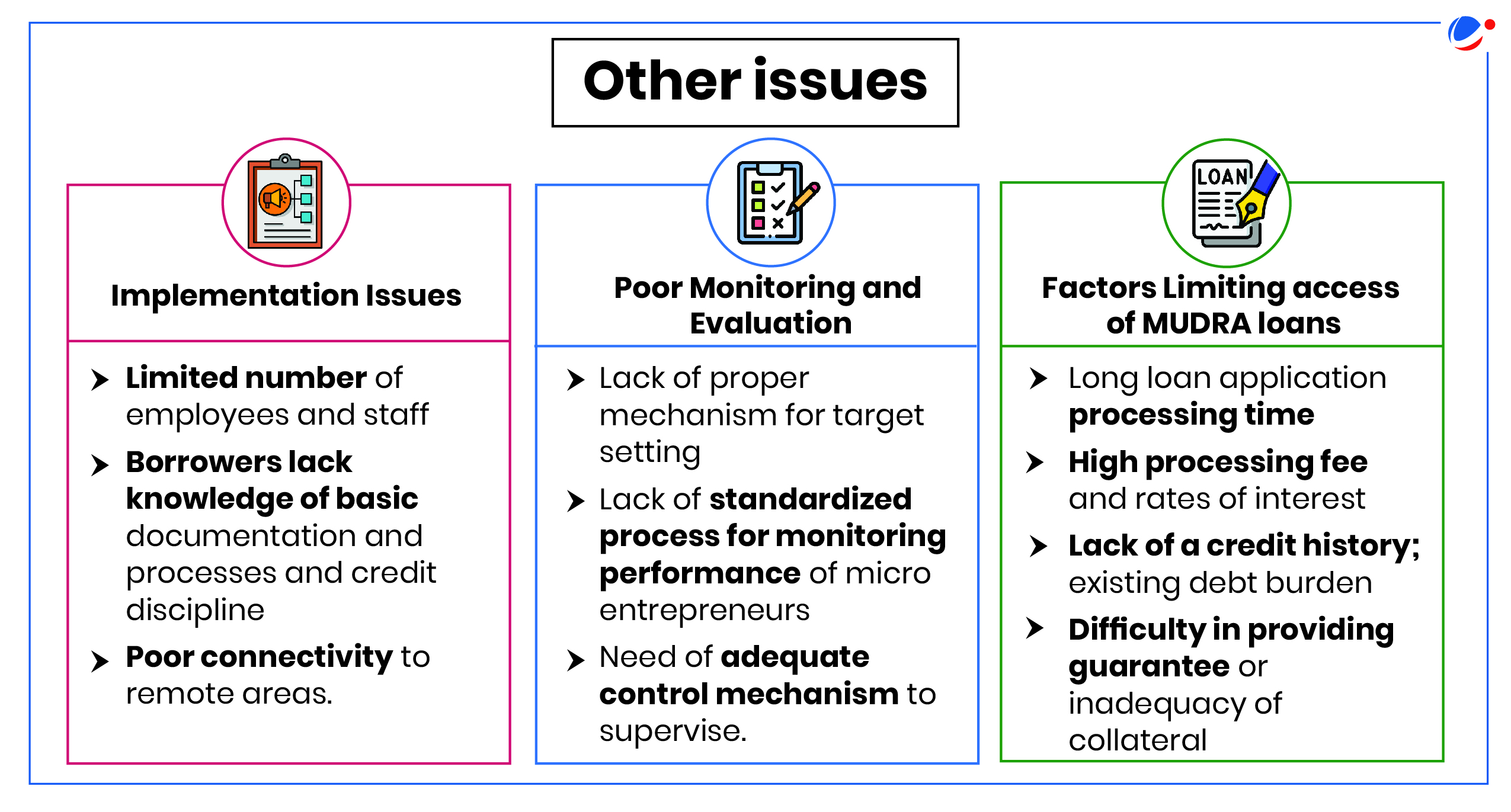
Issues & Challenges highlighted by the report
- Regional Variation: The Cumulative number of accounts and the amount sanctioned for the Northeast region (2015 – 2022) is not only the lowest at ~4% but is also decreasing year after year post FY-2018.
- Rising NPAs: NPA accounts & amount have been increasing year after year with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 22.51 % & 36.61 % respectively from FY17 to FY22.
- Public sector banks have the highest NPA of 22.6 % and NBFCs have the lowest NPA of 1.3 %.
- Kishore accounts have the highest NPA while Shishu accounts have the lowest NPA amount.
- Issues in Scheme Design:
- Ceiling of 15% on pay out under CGFMU (maximum amount the CGFMU is willing to cover for a defaulted loan) restricts the benefits of the banks.
- Complex (XML format, errors not easily rectifiable, high upload time to upload), and lengthy claim settlement process under CGFMU.
- Other issues: High Guarantee fee; high refinancing rates; security risk due to Lack of collateral etc.
- Issues in Institutional Mechanism:
- Lack of centralized database for collecting information.
- Poor credit penetration to weaker sections and deficient areas.
- Lack of digitized platform for quick addressal of queries on issues pertaining to guarantee covers or other operational/ technical guidelines.
Way Forward (Recommendations)
- Using Traditional Advertising (Mass promotion using television/newspapers/radio, displaying posters and banners in regional languages) and Online Advertising (through social media platforms, Facebook ads, google ads etc.) to inform, persuade and reinforce the benefits of the scheme.
- Digitization of the Lending Process to make it more transparent and hassle free for the potential beneficiaries.
- Digital Portal enabling real-time upload of beneficiary data to enhance the overall efficiency and transparency of the scheme with better data management.
- Feedback/Query Redressal Portal and Chatbots for query redressal to benefit the MLIs as well as the beneficiaries or borrowers of the scheme.
- Recognition Mechanism to incentivize well performing MLIs to perform better.
Success Stories, Best Practices and Case Studies
|







