Why in the news?
Cabinet approved scheme for Sustainable development of Horticulture with a total outlay of Rs 1129.30 crore.
More on the News
- The scheme aimed at increasing farmers' income from horticulture plants comprises the following -
- Tropical, sub-tropical and temperate horticulture crops
- Root, tuber, bulbous and arid crops
- Vegetable, floriculture, and mushroom crops
- Plantation, spices, medicinal, and aromatic plants
- Recently the government also approved a Rs 1,766-crore 'Clean Plant Programme' under the Mission for Integrated Development of Horticulture (MIDH) to boost horticulture sector.
About Clean Plant Programme (CPP)
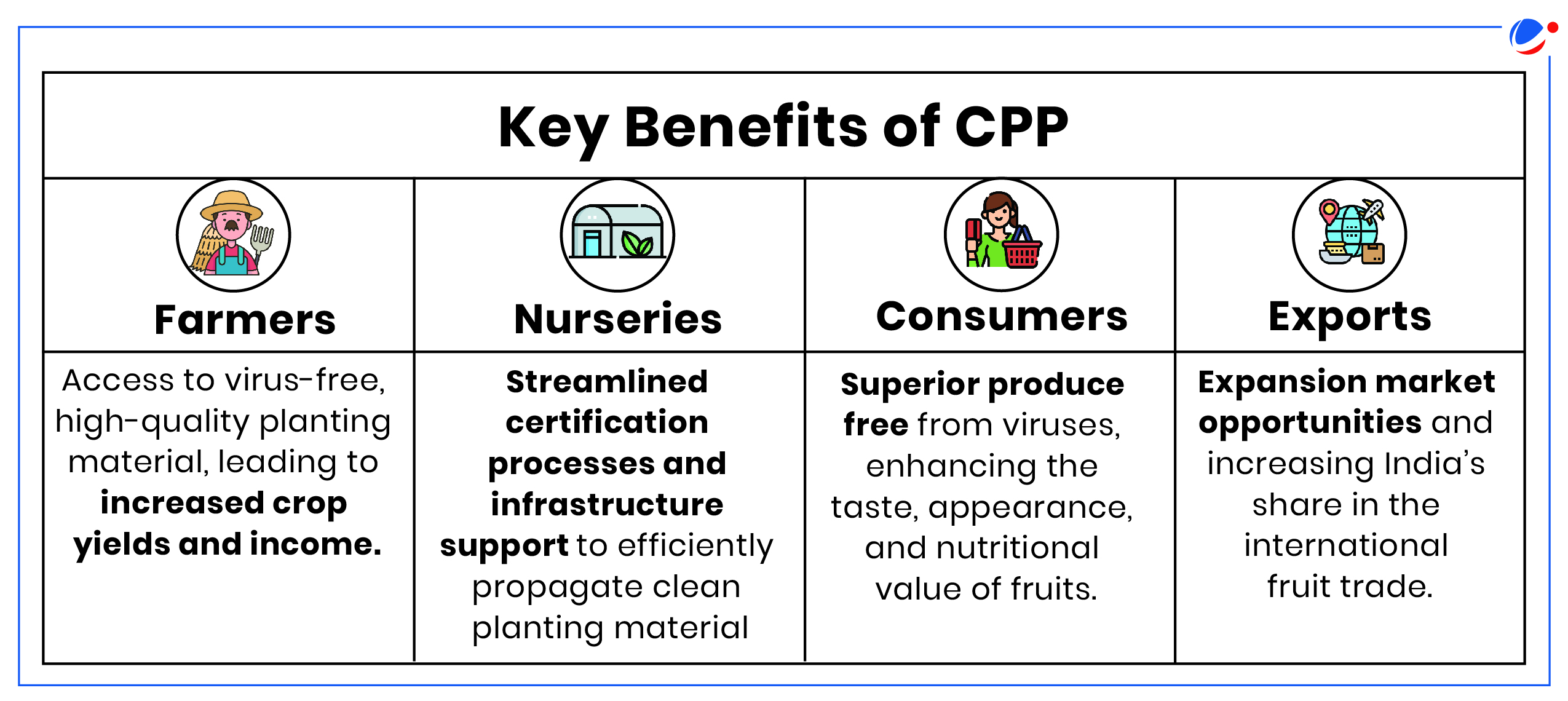 |
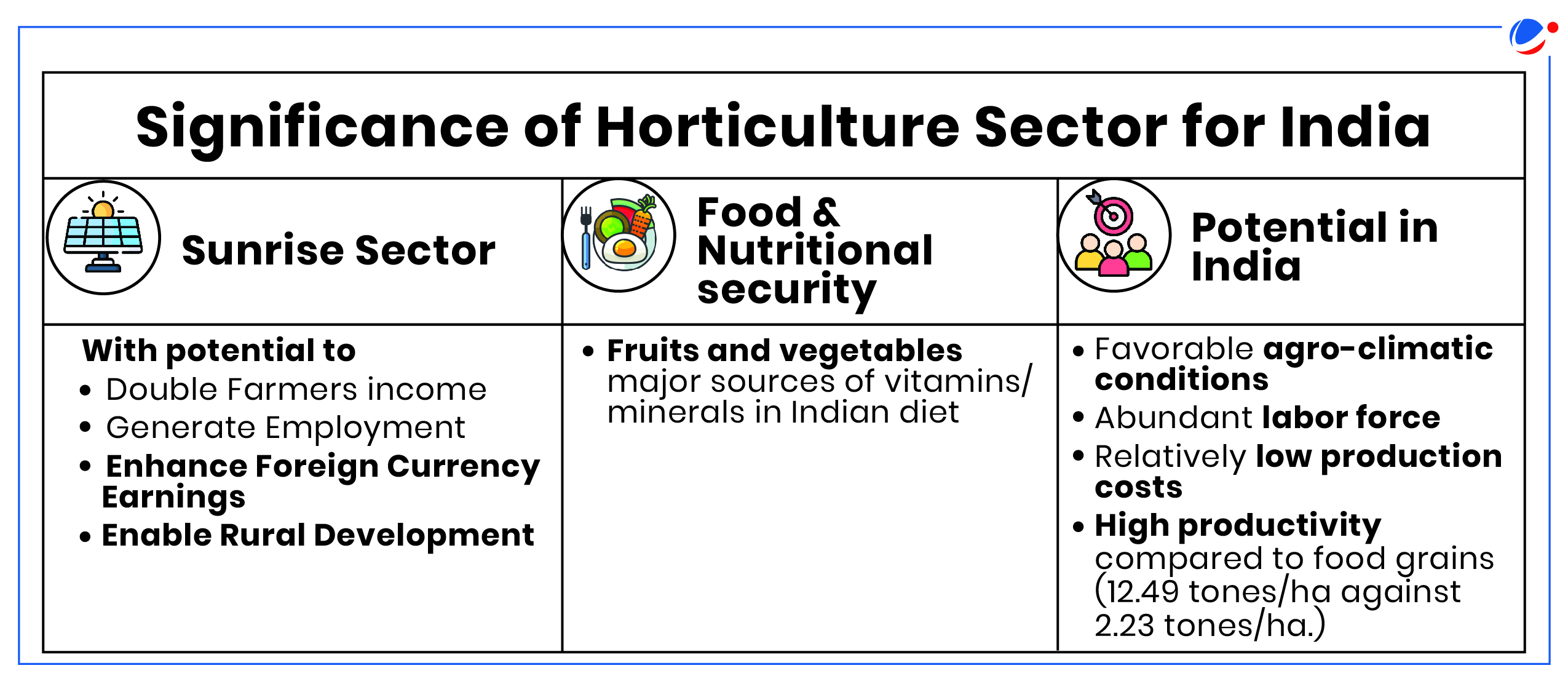
About Horticulture Sector
- It is a vast and diverse field that encompasses the cultivation, production, processing, and marketing of fruits, vegetables, flowers, and ornamental plants.
- Major types of horticulture: Pomology [Fruit cultivation and includes Viticulture (grape cultivation)]; Olericulture (cultivation of vegetables); Floriculture (cultivation of flowers and ornamental plant); Arboriculture (cultivation of trees and shrubs).
Status of India's Horticulture Sector
- Production: 355.48 Million Tonnes in 2022-23, 13.1% of the gross cropped area.
- Fruits and vegetables account for almost 90% of India's total horticulture production.
- Contribution to Agriculture Gross Value Added (GVA): 33%
- Global Status: India ranks 2nd in fruits and vegetable production in the world after China.
- According to FAO (2022), India is the largest producer of Onions, ginger and okra among vegetables and ranks 2nd in production of Potatoes, Cauliflowers, Brinjal, Cabbages, etc.
- Amongst fruits, the country ranks 1st in the production of Bananas, Mangoes and Papayas.
- Exports: India is ranked 14th in vegetables and 23rd in fruits.
Other Initiatives Undertaken for the sector
- Mission for Integrated Development of Horticulture (2014): Centrally Sponsored Scheme, for the holistic growth of the horticulture sector with 2 sub-schemes -
- National Horticulture Mission (2005-06): aims at holistic development of horticulture sector by ensuring forward & backward linkage through a cluster approach under Horticulture Cluster Development Programme.
- Horticulture Mission for North East and Himalayan States.
- Agriculture Ministry announced Rs 18,000 cr for 100 export oriented horticulture clusters.
- Coordinated programme on Horticulture Assessment and Management using geoinformatics (CHAMAN): To develop and firm up scientific methodology for estimation of area and production under horticulture crops.
- Capital Investment Subsidy Scheme: for construction/ expansion/ modernization of Cold Storages/Storages of Horticulture Products.
- Commercial cultivation: During 2022-23, 347 varieties/hybrids of 44 crops were released, and 99 varieties of horticultural crops were notified for commercial cultivation.
Challenges
- Low Export share: India's share in the global horticultural market is a mere 1 %.
- Indian exports face food safety and standards related issues due to non-tariff trade barriers like Sanitary and phytosanitary measures.
- E.g., pesticide residue has led to rejection of exports in key markets like the EU.
- Infrastructure Deficit: Poor logistics and lack of equitable cold storage and warehousing facilities contribute to delays and wastages as Horticulture crops are highly perishable.
- Cold storage distribution among the states is inequitable, with around 59% of the storage capacity (i.e., 21 MMT) present in 4 states Uttar Pradesh, West Bengal, Gujarat, and Punjab.
- Small operational landholdings: They limit the amount of land available for cultivation, for crop rotation and sustainable soil management resulting in reduced yields and decreased soil fertility.
- Other challenges: Limited value addition; Lack of irrigation; Pests & diseases; limited outreach of farm insurance & farm mechanization; lack of access to institutional credit especially to small & marginal farmers; climate change-induced extreme weather events and changes in weather patterns etc.
Way Forward
- Capacity-building initiatives at the level of the farmer, the processor and the exporter for meeting all mandatory requirements as per international standards, such as global Good Agricultural Practices (GAP).
- Improving Value Chain Efficiency by expanding cold storage capacity; investing in better roads, railways, and transportation infrastructure to reduce post-harvest losses.
- Encourage the development of value-added horticultural products, such as processed foods, juices, and jams, to increase market demand and farmer income.
- Encourage entrepreneurship in the horticulture sector to create new businesses and job opportunities.
- Promote agricultural technologies, such as precision agriculture, hydroponics, and tissue culture, to improve productivity and efficiency.
- Develop and promote climate-smart agricultural practices that are resilient to changing weather patterns.
- Other: Promoting integrated pest & disease management, water-saving technologies and practices, farm mechanization, expanding access to institutional credit etc.






