Why in the News?
Maratha Military Landscapes of India added to the UNESCO World Heritage List as the 44th site from India.
About Maratha Military landscape
- It was placed on the Tentative List of World Heritage Sites in 2021.
- Geographical Spread: States of Maharashtra and Tamil Nadu.
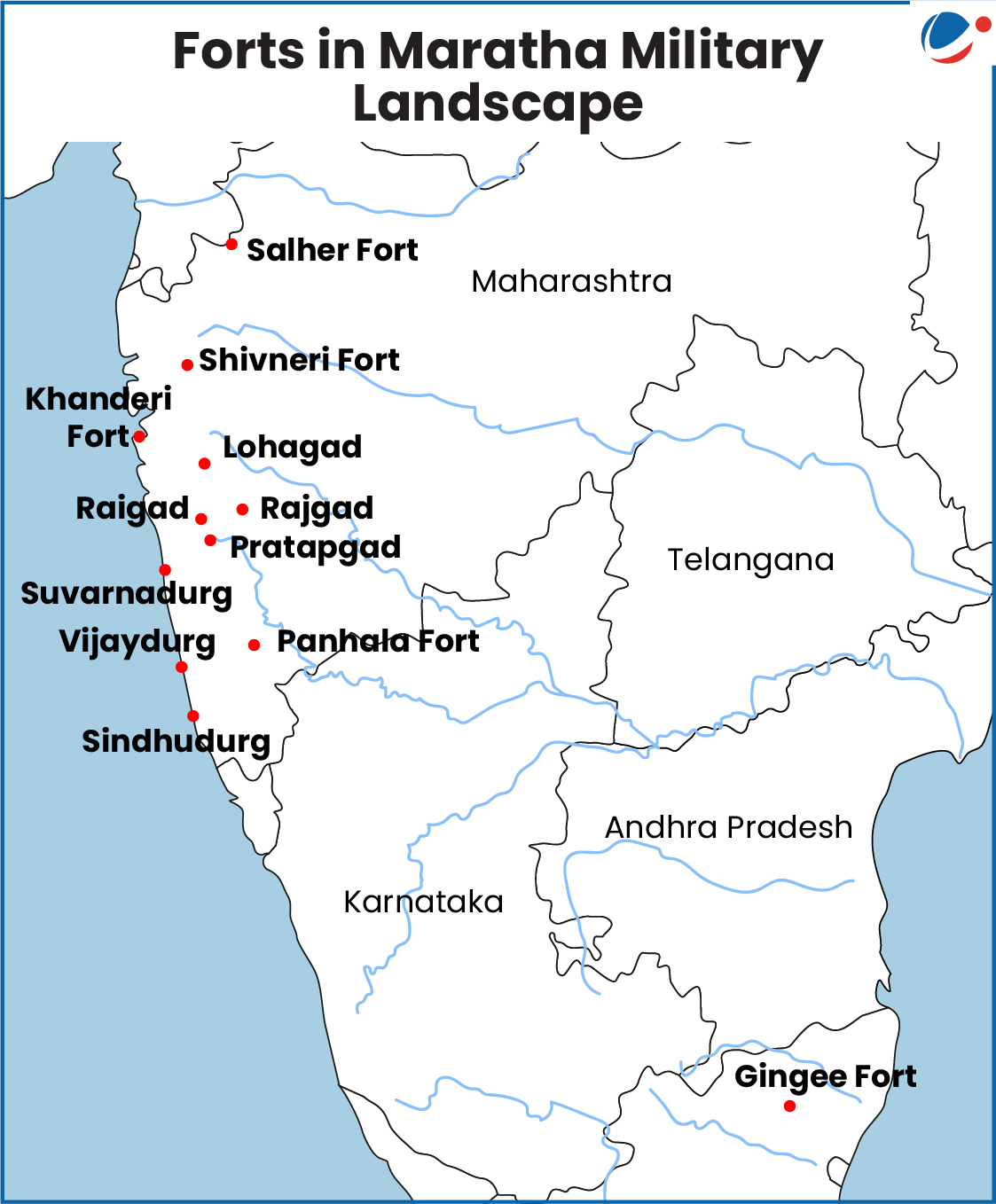
- Diverse and Strategic Locations: Situated across varied terrains, from coastal fortifications to hilltop strongholds, including the Sahyadri mountain ranges, the Konkan Coast, the Deccan Plateau, and the Eastern Ghats.
- Evolution: 17th century during the reign of the Maratha King Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj and continued through subsequent rules until Peshwas in 19th centuries as strategic military vision and architectural ingenuity of the Maratha Empire.
Forts in Maratha Military Landscapes (12) | Key Features |
Salher Hill fort | Witnessed an important battle in 1672 fought between the Marathas and the Mughals. |
Shivneri Hill fort | Birth place of Chhatrapati Shivaji. |
Lohgad Hill fort | Located near the Buddhist cavesat Bhaje. |
Raigad Hill fort |
|
Rajgad Hill fort |
|
Gingee Hill Fort (Tamil Nadu) | It has three distinct hilltop citadels and a massiveboundary of thickwalls and cliffs. |
Pratapgad Hill Forest Fort | Major fight withAfzal Khan tookplace near this fort. |
Panhala Plateau Hill Fort | Became Maratha statecapital under Tarabai. |
Sindhudurg Island forts | Occupies an islet in the Arabian Sea. |
Suvarnadurg Island forts | Presumably built by the rulers of Bijapur in the 16th century CE. |
Khanderi Island forts | Built during the reign of the Maratha king Shivaji in 1679 CE to keep a check on the Siddhis at Murud-Janjira fort. |
Vijay durg Coastal Fort |
|
About Maratha Empire
- Foundation: With the rise of Chhatrapati Shivaji in 1674.
- Carved out an independent Maratha kingdom from various Deccan states in the 17th century. It dominated a large portion of India during the 17th and 18th century.
- Capitals: Raigad Fort, Gingee, Satara, and Pune.
- Reigned: At its peak, the Maratha Empire extended from Peshawar in the north to Thanjavur in the south.
- Administration: Known as 'Ashtapradhan' was formed by Shivaji. It consisted of a council of eight ministers.
- The eight ministers were Peshwa (Prime Minister), Amatya (Finance Minister), Sachiv (Secretary),Mantri (Interior Minister), Senapati (Commander-in-Chief), Sumant (Foreign Minister), Nyayadhyaksh (Chief Justice), and Panditrao (High Priest).
- Revenue Policy
- Sardeshmukhi: 10% tax imposed upon the revenues of the entire Maratha kingdom.
- Chauth: 1/4th of the total revenue from the neighbouring chieftains whose territories did not form part of the Maratha Empire.
- Decline: With the defeat of third Battle of Panipat (with Ahmad Shāh Abdali, 1761).
Conclusion
India shows a strong commitment to preserving its rich cultural and natural heritage, with 44 UNESCO World Heritage Sites and an active Tentative List of 62 properties for future recognition.
About UNESCO World Heritage Sites (WHS)
|





